JPA Queries
Topics to be covered¶
- JPA Queries:
- Implementation of selfProductService using Your Own Database:
JPA Queries¶
Overview of JPA and ORM¶
-
JPA (Java Persistence API) is a specification that allows developers to manage relational data in Java applications without writing SQL queries. Instead, it relies on Object-Relational Mapping (ORM), a technique that converts data between incompatible type systems in object-oriented programming and relational databases.
-
ORM allows your application code, which is written in an object-oriented manner, to seamlessly interact with the database. This is achieved by mapping your Java objects (entities) to database tables.
-
Key Benefits of Using ORM:
- Object-Oriented Codebase: Your application remains in an object-oriented paradigm, promoting maintainability and readability.
- Model-Table Alignment: The structure of database tables closely mirrors the Java entities, simplifying data management and retrieval.
- Automatic Query Generation: Instead of writing complex SQL queries, developers can write descriptive methods. The ORM framework, such as Hibernate, interprets these method names and generates the corresponding SQL queries automatically.
-
Example: Consider a method like
Products findById(long id). This method name is interpreted by the ORM to generate a query equivalent toSELECT * FROM Products WHERE id = .... The entire process is abstracted away, allowing the developer to focus on business logic rather than database intricacies.
-
Understanding Query Methods in JPA¶
-
Structure of English Sentences:
- An English sentence typically consists of two main parts:
- Subject: The "who" or "what" that the sentence is about (e.g., "Naman").
- Predicate: The "what" or action that the subject performs (e.g., "is teaching the class").
- An English sentence typically consists of two main parts:
-
JPA Query Methods:
-
JPA methods are similarly structured, with the method name divided into two distinct parts:
- What: The action to be performed (e.g.,
find,count,delete). - How: The condition or criteria that specifies how the action is performed (e.g.,
ById,ByName).
- What: The action to be performed (e.g.,
-
Examples:
findById(long Id): This method retrieves a product based on its ID. The ORM framework translates this into the SQL query:SELECT * FROM product WHERE id = Id.findByName(String name): Retrieves products based on their name.findByIdAndName(long Id, String name): Combines two conditions to retrieve a product that matches both the ID and name.countById(long Id): Counts the number of records that match the given ID, equivalent toSELECT COUNT(*) FROM product WHERE id = Id.
-
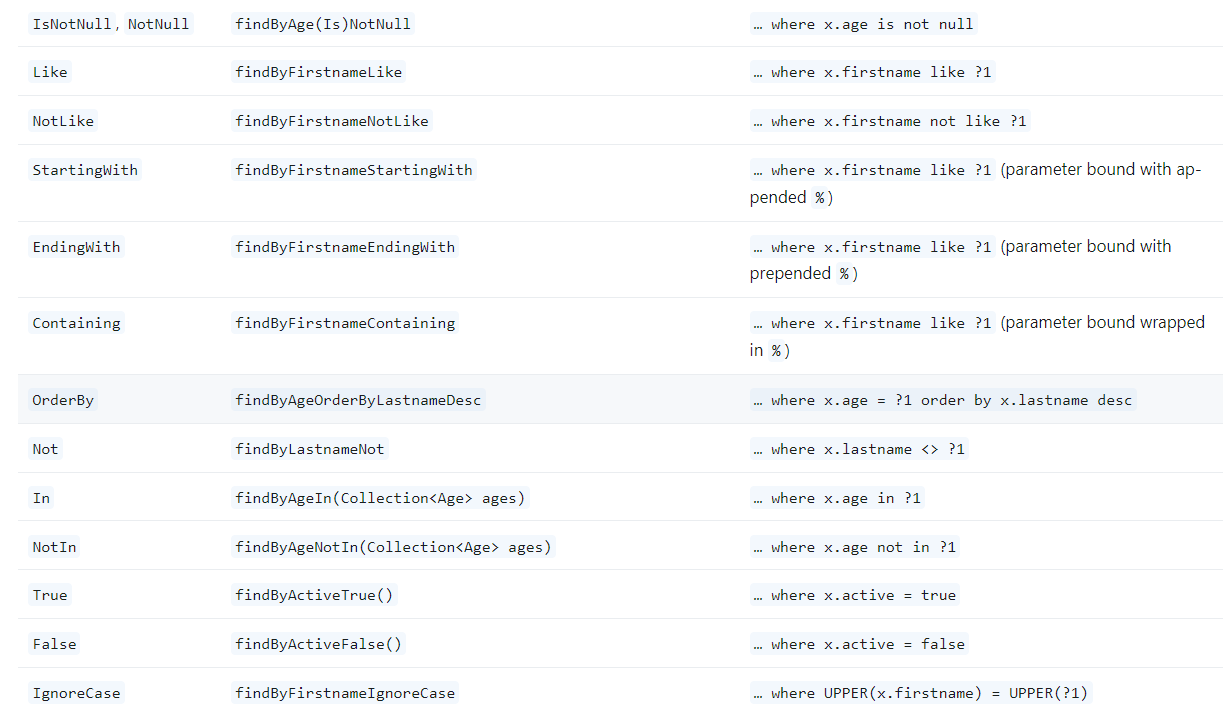
Detailed Explanation of Query Keywords¶
-
Query Method Keywords:
-
JPA query methods can incorporate various keywords to refine the query generated by the ORM framework. Understanding these keywords is essential for writing precise and efficient data retrieval methods.
-
Distinct:
- Ensures that the result set contains unique records.
- Example:
findDistinctByName(String name)retrieves all unique products with the specified name.
- And:
- Combines multiple conditions, both of which must be true for a record to be included in the result.
- Example:
findByIdAndName(long id, String name)returns products that match both the ID and name.
- Or:
- Combines multiple conditions, where at least one must be true.
- Example:
findByIdOrName(long id, String name)returns products that match either the ID or the name.
- Is, Equals:
- Used to check equality between values.
- Example:
findByIsAvailable(boolean available)checks whether the availability status of products matches the given boolean value.
-
-
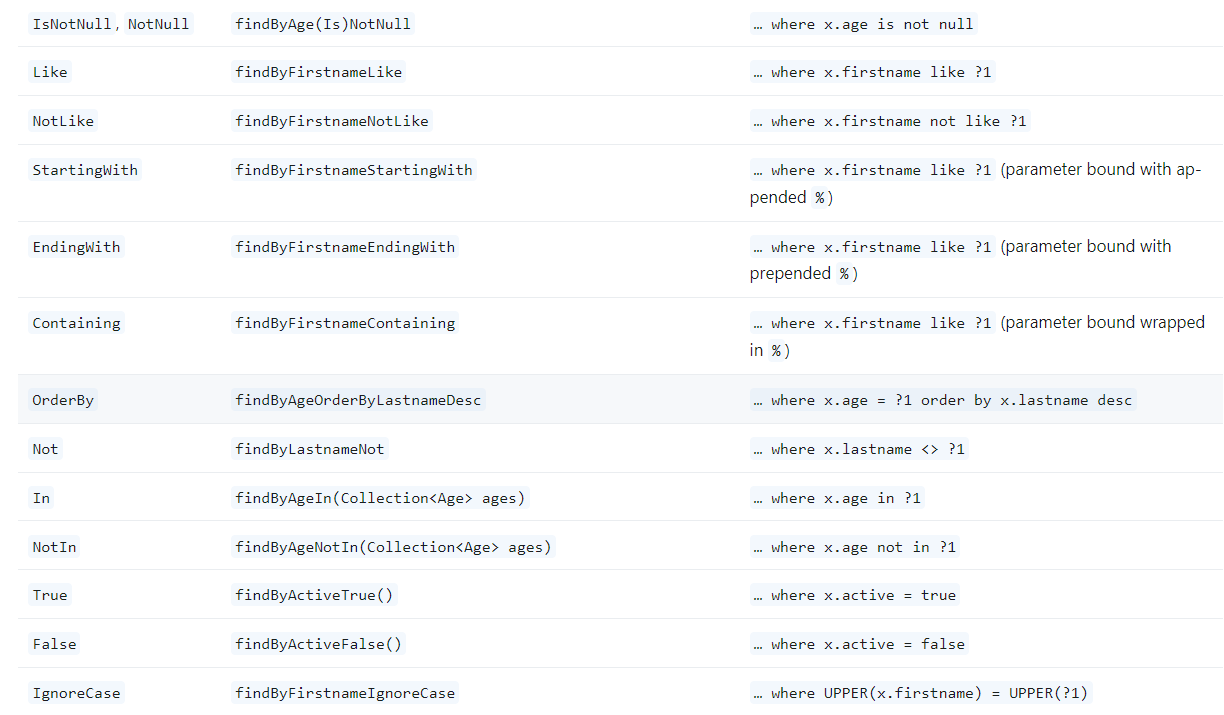
Repository Query Keywords:
- The following keywords are used to further refine and define JPA query methods. Understanding these will help you craft specific queries that return the desired results efficiently.

- IsNull:
- Checks if a particular field is null.
- Example:
findByCategoryIsNull()retrieves all products that do not have a category assigned.
- IsNotNull:
- Checks if a particular field is not null.
- Example:
findByCategoryIsNotNull()retrieves all products that have an assigned category.
- IsTrue:
- Checks if a boolean field is true.
- Example:
findByIsAvailableTrue()retrieves all products that are currently available.
- IsFalse:
- Checks if a boolean field is false.
- Example:
findByIsAvailableFalse()retrieves all products that are currently unavailable.
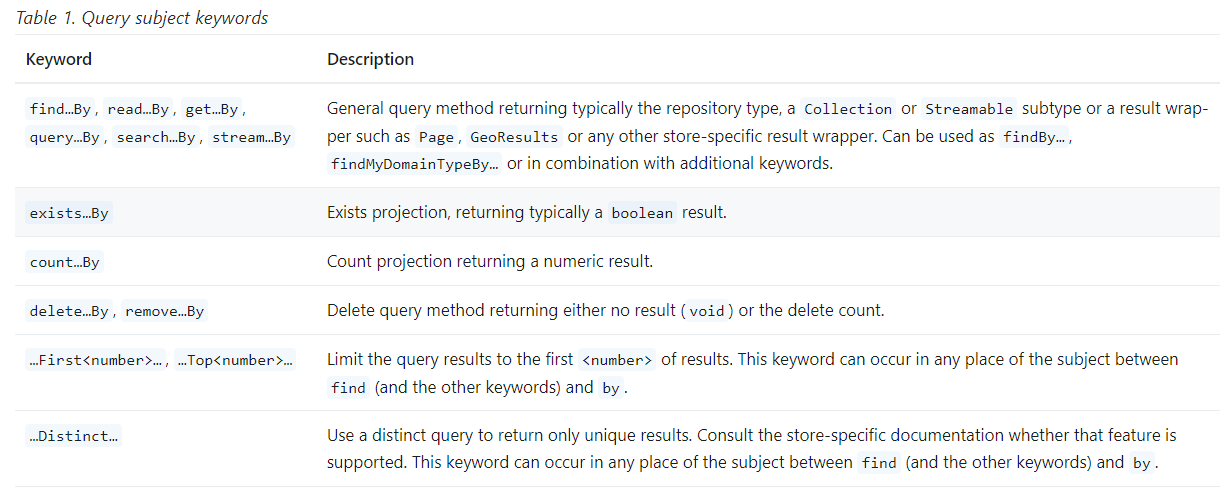
Defining Query Methods¶
-
OrderBy:
- The
OrderBykeyword is used to sort the results based on one or more fields. - Example:
findAllByOrderByPriceAsc()returns all products sorted by price in ascending order.
- The
-
Limit:
- The
Limitkeyword restricts the number of records returned by the query. - Example:
findTop5ByOrderByPriceDesc()returns the top 5 most expensive products.
- The
CRUD Operation Methods in JPA¶
-
Create:
- To add a new product to the database, use the method
Product save(Product p). This method persists the given entity to the database. - Example:
save(new Product("Laptop", 1500.00))adds a new product with the specified details to the database.
- To add a new product to the database, use the method
-
Read:
- Retrieval operations are performed using methods prefixed with
findBy,getBy,existsBy, orcountBy. - Example:
findById(long Id)retrieves a product by its ID, whilecountByCategory(String category)counts the number of products within a specific category.
- Retrieval operations are performed using methods prefixed with
-
Update:
- To update an existing product, use the
savemethod with an entity that already has an ID. The presence of an ID indicates that the entity already exists in the database, and thus, thesavemethod will update it. - Example:
save(existingProduct.setPrice(1300.00))updates the price of the product with the existing ID.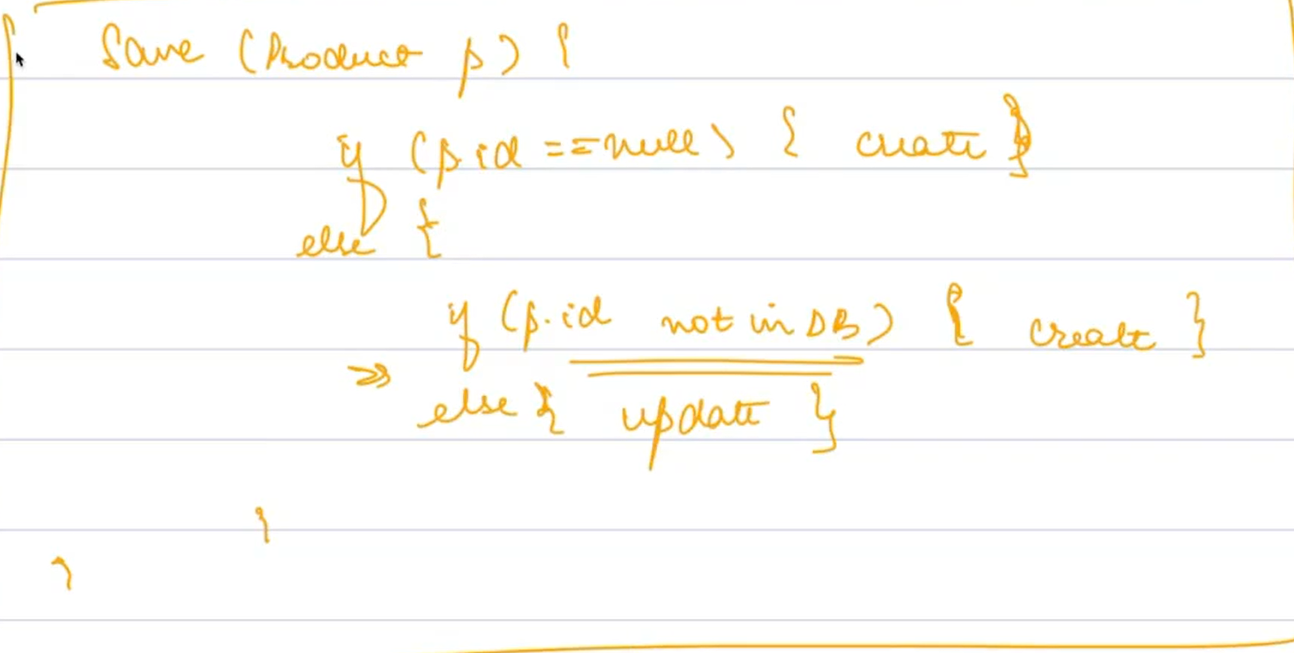
- To update an existing product, use the
-
Delete:
- Use the
deleteBymethods to remove entities from the database. - Example:
deleteById(long id)removes the product with the specified ID from the database.
- Use the
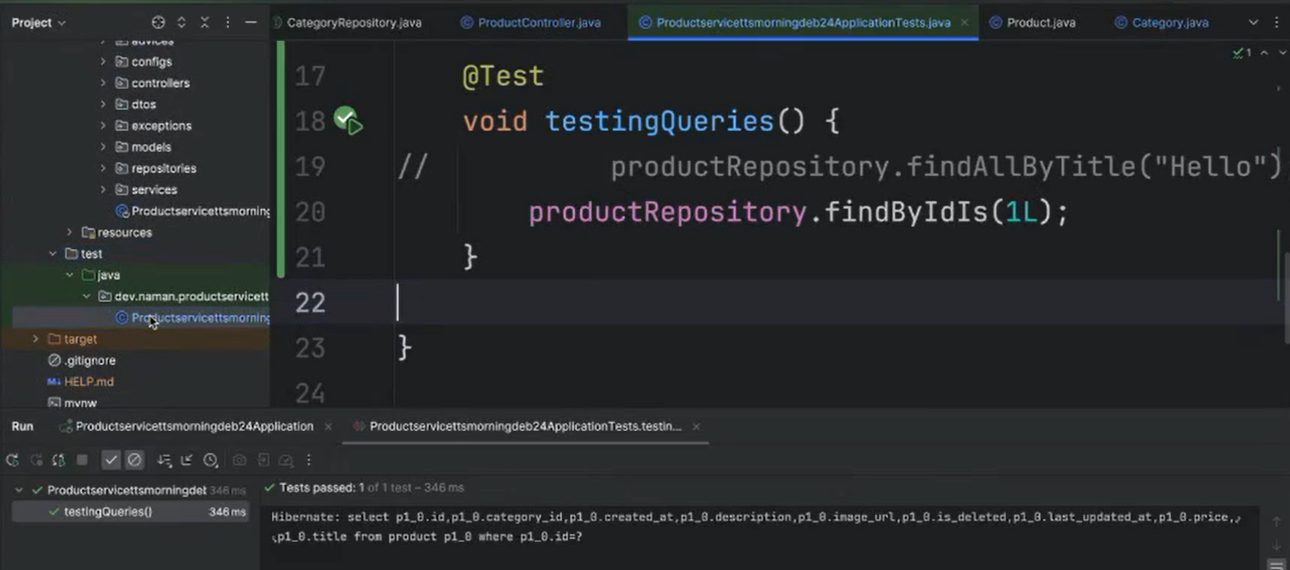
Implementation of Queries¶
-
Retrieve All Products:
- Use the method
List<Product> findAll()to retrieve a list of all products in the database.
- Use the method
-
Retrieve a Single Product:
- The method
Product findById(long Id)retrieves a single product based on its unique ID.
- The method
-
Testing the Queries:
- You can test the implemented queries using Postman, a popular API testing tool. Postman allows you to send requests to your application and observe the responses to ensure the queries work as expected.
- Additionally, Spring automatically generates a test folder, where you can write unit tests to validate the correctness of your query methods.