Heaps 2: Problems¶
Problem 1 Sort an Array¶
We want to sort an array in increasing order using a heap.
Idea¶
We can use min-heap, and we need to call extract-min()/remove() repeatedly many times, extract-min() will every time give the minimum element among all the available elements.
- Build a min-heap.
extract-min()and store the returned value in theansarray until all the elements are not deleted.
Question¶
What is the time Complexity to convert an array to a heap?
Choices
- O(1)
- O(log n)
- O(n)
- O(nlog(n))
Question¶
Root element in a heap is ?
Choices
- min element of the array
- max element of the array
- either min or max depending upon whether it is min or max heap
- random element of the array
Explanation:
Either min or max depending upon whether it is min or max heap. Min-Heap has minimum element at the root node, where as Max-Heap has maximum element at the root node.
Sort an Array Complexity and Solution Approach¶
Complexity of sorting an array using heap¶
- Build a min-heap -> Complexity:
O(n) extract-min()and store the returned value in theansarray until all the elements are not deleted.- Complexity of
extract-min()isO(logn)and we are callingNtimes, so the overall complexity isO(NlogN).
Complexity¶
- Time Complexity: O(NlogN)
- Space Complexity: O(N), as we are using another array for building the heap.
Can we optimize the space complexity?¶
Hint: Try to solve by usingmax-heap.
- Let us take an example of
max-heap
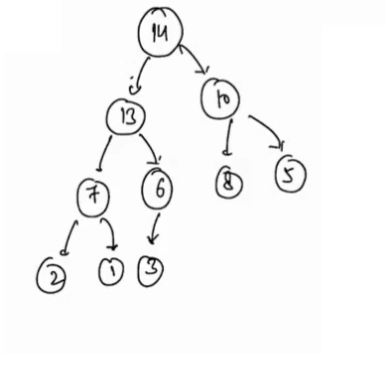
- Create an array for this max-heap.
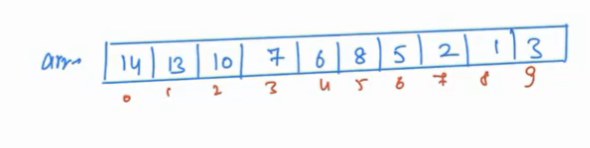
- Say, we extract an element, which element will we get? The Maximum! Now, the maximum element can be swapped with the last index. This way, maximum element will come at its correct position in sorted array.
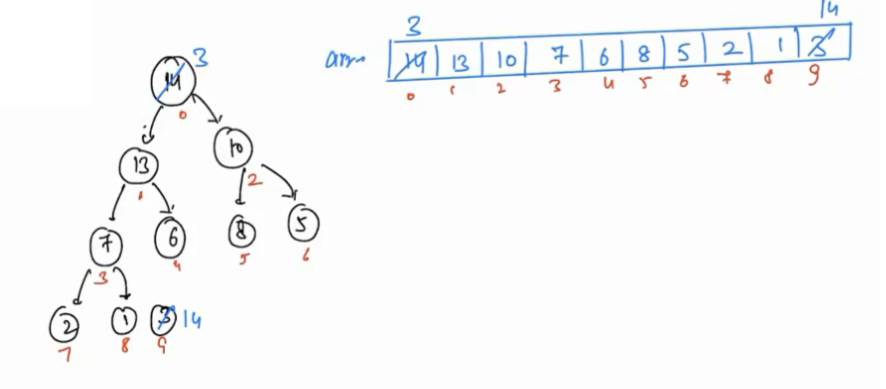
-
Now we will virtually remove the last element, which means we consider an array till the second last element of an array.
-
Now, since the tree is not satisfying the heap order property, so we will call
heapify()for index 0. -
So when we call
heapify(), firstly 3 is swapped with 13(maximum of 13 and 10).
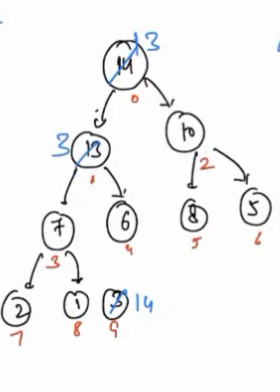
- Now again 3 is swapped with 7.
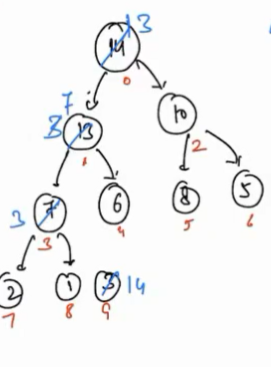
- Now 3 is the maximum among 3, 2 and 1. Hence, no further swaps are needed. Now we have an array,
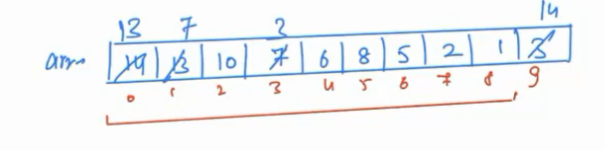
- As we know now a maximum of all available elements is present at root, call
extract-max(), swap maximum element with the last index element(index 8) and then we will call heapify for the value 1.
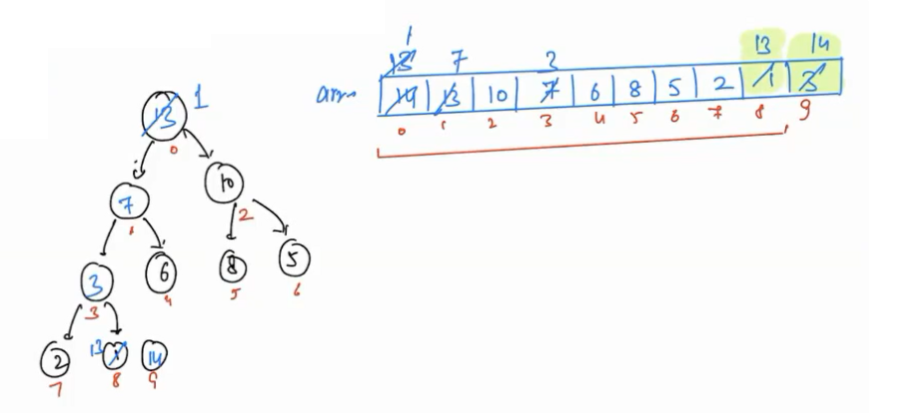
- 1 is swapped with 10, then swapped with 8, after that 1 will reach to its correct position.
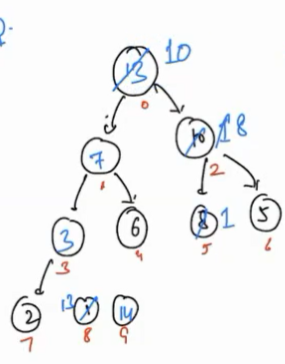
- Again extract the maximum and swap it with the last(7th) index element. Then call Heapify for it.
In this way, repeat these steps we completed with all the elements of the tree.
Sort an Array PseudoCode¶
PseudoCode¶
Build max - heap-- -> TC: O(N)
j = N - 1;
while (j > 0) {
swap(A[0], A[j]);
j--;
heapify(0, arr[], j)
}
Complexity¶
- Time Complexity: O(NlogN)
- Space Complexity: O(1), we are not taking an extra array, we are converting the max heap into sorted array.
Is heap sort an in-place sorting algorithm?¶
Answer: Yes it is in-place as we are sorting an array using heap sort in constant time in the above question.
Is heap sort a stable sorting algorithm?¶
Answer: No heap sort is not stable.
Explanation: Heap sort is not stable because operations in the heap can change the relative order of equivalent keys.
Problem 2 kth Largest Element¶
Given arr[N], find the kth largest element.
Example
Input:
arr[] = [8, 5, 1, 2, 4, 9, 7]
k = 3
Output:
7
Explanation:
In the above array,
- First largest element = 9
- Second largest element = 8
- Third largest element = 7
We need to return the third largest element.
Question¶
What is the 5th largest element of an array [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]?
Choices
- 5
- 3
- 1
- 2
Explanation
In the above array,
- First largest element = 5
- Second largest element = 4
- Third largest element = 3
- Fourth largest element = 2
- Fifth largest element = 1
We need to return the fifth largest element.
kth Largest Element solution approach¶
Warning
Please take some time to think about the solution approach on your own before reading further.....
 Idea 1 (by sorting)¶
Idea 1 (by sorting)¶
Sort an array and simply return arr[N-K].
Example:
arr[] = [8, 5, 1, 2, 4, 9, 7]
k = 3
Solution
Sort an array, [1, 2, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9]
Now return arr[N-K] element i.e. arr[7-3] = arr[4] = 7
Time Complexity: O(NlogN), Space Complexity: O(1).
 Idea 2 (Using binary search)¶
Idea 2 (Using binary search)¶
We can find the kth largest element by applying binary search just like we have used in the kth smallest element.
Time Complexity: O(Nlog(max-min))
 Idea 3 (Using heap sort)¶
Idea 3 (Using heap sort)¶
- Build a max-heap.
- Call extract-max() k-1 times to remove K-1 elements(for first largest we need zero removals, for second largest we need 1 removal, in this way for kth largest we need k-1 removals)
Complexity¶
Time Complexity: O(N + KlogN)
Space Complexity: O(1)
kth Largest Element Using min-heap¶
 Idea 4 (Using min-heap)¶
Idea 4 (Using min-heap)¶
Let us take an example, we want to create a cricket team of 4 batsmen and we have 8 batsmen i.e. b1, b2, b3, b4, b5, b6, b7 and b8, and every batsman is given only 1 over and everyone tries to achieve maximum run in that over.
Firstly, 4 batsmen played and scored
| b1 | b2 | b3 | b4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 12 | 8 | 4 | 6 |
We have recently incorporated four batsmen into our team with respective scores of 12, 8, 4, and 6. When batsman B5 joins, scoring 7, we opt to replace the player with the lowest score to maintain team quality. Since we use a min heap to track scores, we remove the batsman with a score of 4 and include B5, updating our heap to [12, 8, 7, 6].
Later, batsman B6 arrives, earning 3 runs. However, his score doesn't surpass our team's minimum, so he isn't added. Then, batsman B7 steps in, scoring a notable 10 runs. Outperforming our lowest score, B7's addition leads us to drop the current minimum scorer and update the heap to [12, 8, 7, 10].
Following this, batsman B8 enters with a score of 9. Exceeding the lowest score in our lineup, we incorporate B8 by removing the now lowest scorer, refining our heap to [12, 8, 9, 10].
Thus, in this dynamic team selection process, the minimum element in our heap represents the fourth-highest score among our players.
Example:¶
To find the 3rd largest element in an array using a min-heap of size 3:
Given array: arr = [8, 5, 1, 2, 4, 9, 7] and k=3.
- Initialize an empty min-heap.
- Add the first three elements of the array to the heap: [8, 5, 1].
- Iterate over the remaining elements. If an element is greater than the heap's minimum, remove the minimum and insert the new element.
- After processing elements 2, 4, 9, and 7, the heap evolves as follows:
- [8, 5, 2] (after adding 2)
- [8, 5, 4] (after adding 4)
- [8, 5, 9] (after adding 9)
- [8, 7, 9] (after adding 7)
- The 3rd largest element is the minimum in the heap: 7.
PseudoCode¶
Build min-heap with first k elements. -> O(K)
Iterate on the remaining elements. -> (N-K)
for every element, check
if(curr element > min element in heap){
extractMin()
insert(current element)
}
ans = getMin()
Complexity¶
- Time Complexity: O(K+(N-K)logK)
- Space Complexity: O(K)

Problem 2 kth Largest Element for all windows¶
Find the kth largest element for all the windows of an array starting from 0 index.
Example
Input:
arr[] = [10, 18, 7, 5, 16, 19, 3]
k = 3
Solution:
- We need atleast 3 elements in a window, so we will consider first window from index 0 to k-1, we have elements in that
[10, 18, 7]; third largest is 7, ans=[7]. - Window 0 to 3
[10, 18, 7, 5],third largest = 7, ans=[7, 7]. - Window 0 to 4
[10, 18, 7, 5, 16],third largest = 10, ans=[7, 7, 10]. - Window 0 to 5
[10, 18, 7, 5, 16, 19],third largest = 16, ans=[7, 7, 10, 16]. - Window 0 to 6
[10, 18, 7, 5, 16, 19, 3],third largest = 16, ans=[7, 7, 10, 16, 16].
Question¶
Find the kth largest element for all the windows of an array starting from 0 index.
arr[] = [5, 4, 1, 6, 7]
k = 2
Choices
- [4, 4, 5, 6]
- [6, 6, 6, 6]
- [5, 4, 1, 6]
- [4, 1, 6, 7]
Explanation:
To find the second largest element in each window of a given size in an array:
- Start with the first window (from index 0 to k-1). For example, in [5, 4], the second largest is 4. Answer array starts as [4].
- Shift the window one element at a time and find the second largest in each new window.
- Window [5, 4, 1] gives second largest 4. Answer array becomes [4, 4].
- Window [5, 4, 1, 6] gives second largest 5. Answer array becomes [4, 4, 5].
- Window [5, 4, 1, 6, 7] gives second largest 6. Answer array becomes [4, 4, 5, 6].
kth Largest Element for all windows Idea¶
To find the k-largest elements in an array using a min-heap:
- Initialize Min-Heap: Start with a min-heap and add the first k elements from the array to it.
- Compare and Update: For each remaining array element, if it's larger than the heap's minimum, replace the minimum with this element.
- Track Minimums: After each update, record the heap's minimum. This shows the evolving k-th largest element.
Pseudocode¶
Build min-heap with first K elements. -> O(K)
ans.add(extractMin())
Iterate on the remaining elements. -> (N-K)
for every element, check {
if(curr element > min element in heap){
extractMin()
insert(current element)
ans.add(extractMin())
}
}
Problem 3 Sort the nearly sorted array¶
Given a nearly sorted array. You need to sort the array.
Nearly sorted array definition - Every element is shifted away from its correct position by at most k-steps.
Example
Sorted array can be [11, 13, 20, 22, 31, 45, 48, 50, 60]
We are given,
Input:
arr[] = [13, 22, 31, 45, 11, 20, 48, 60, 50]
k = 4
Every element is not more than 4 distance away from its position.
Warning
Please take some time to think about the solution approach on your own before reading further.....
 Idea 1(Sorting)¶
Idea 1(Sorting)¶
Sort an Array
Time Complexity: O(NlogN)
 Idea 2¶
Idea 2¶
An element can be shifted by at most k steps, so the element at index 0 can only be shifted till index (k), so the minimum element lies from index 0 to k.
- So we need to choose a minimum of first k+1 elements.
- We will take a min-heap of size k+1.
- Add first k+1 elements into a heap, heap =
[13, 22, 31, 45, 11]. - extractMin()(heap =
[13, 22, 31, 45]) will give a first element of a sorted array, ans =[11], now add the next element from an input array, into a heap, heap =[13, 22, 31, 45, 20]. - Again extractMin(), it will give a second of a sorted array, ans =
[11, 13], again add the next element of the input array, again extractMin(), in this way do until we reach the last index, and then remove minimum element from array one-by-one and add it to ans array.
PseudoCode¶
1. build min-heap with the first (k + 1) elements.
2. for(i = k + 1 ; i < N ; i ++){
extractMin(); -> put it into ans[] array
insert( arr[i] )
}
while(minHeap is not empty){
extractMin() -> put it into ans[] array
}
3. return ans;
Compexity¶
Time Complexity: O(K + N.logK)
Space Complexity: O(K)
Flipkart's Delivery Time Estimation Challenge¶
Flipkart is currently dealing with the difficulty of precisely estimating and displaying the expected delivery time for orders to a specific pin code.
The existing method relies on historical delivery time data for that pin code, using the median value as the expected delivery time.
As the order history expands with new entries, Flipkart aims to enhance this process by dynamically updating the expected delivery time whenever a new delivery time is added. The objective is to find the expected delivery time after each new element is incorporated into the list of delivery times.
End Goal: With every addition of new delivery time, requirement is to find the median value.
Why Median ?
The median is calculated because it provides a more robust measure of the expected delivery time
The median is less sensitive to outliers or extreme values than the mean. In the context of delivery times, this is crucial because occasional delays or unusually fast deliveries (outliers) can skew the mean significantly, leading to inaccurate estimations.
Problem 4 Find the median¶
Given an infinite stream of integers. Find the median of the current set of elements
Median¶
Median is the Middle element in a sorted array.
The median of [1, 2, 5, 4, 3, 6]
First, we need to sort an array [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
We have two middle values as the size of the array is even i.e. 3, 4.
So to find the median, we need to take the average of both middle values, median = (3+4)/2 = 3.5
Question¶
The median of [1, 2, 4, 3]
Choices
- 2
- 4
- 3
- 2.5
Explanation:
The median of [1, 2, 4, 3]
First, we need to sort an array [1, 2, 3, 4]
We have two middle values as the size of the array is even i.e. 2, 3.
So to find the median, we need to take the average of both middle values,
Median = (2+3)/2 = 2.5
Find the median Brute Force Approach¶
Warning
Please take some time to think about the solution approach on your own before reading further.....
Understanding the question¶
We have an infinite stream of elements.
- First we have one element. 6, then median = 6.
- Next element if 3 6, 3, then median = 4.5
- 6, 3, 8, then median = 6
- 6, 3, 8, 11, then median = 7
- 6, 3, 8, 11, 10 then median = 8
Brute Force Idea¶
For every incoming value, include the value and sort an array. Find the middle point/average of 2 middle points.
Time Complexity: O(N2logN)
Find the median solution approach¶
Idea(Using Insertion Sort)¶
Every time find the correct position of the upcoming element i.e. Insertion Sort
Time Complexity: O(N2)
Idea(Using heap)¶
To find the median in an array by dividing it into two parts - one with smaller elements and the other with larger elements:
Consider an array, for example, [6, 3, 8, 11]. We divide it such that 6, 3 are on the smaller side and 8, 11 on the larger side, as shown in the image:
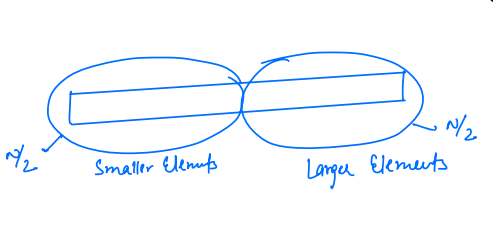
To find the median:
- If both sides have an equal number of elements, take the average of the largest element on the smaller side and the smallest element on the larger side.
- If the sizes are unequal, choose the largest element from the smaller side if it's larger, or the smallest from the larger side otherwise.
The key is to use two heaps: a min-heap for the larger elements and a max-heap for the smaller elements. This approach maintains a balanced partition of the array for efficient median calculation.
Example
arr = [6, 3, 8, 11, 20, 2, 10, 8, 13, 50, _ _ _ ]
Take two heaps, min-heap and max-heap
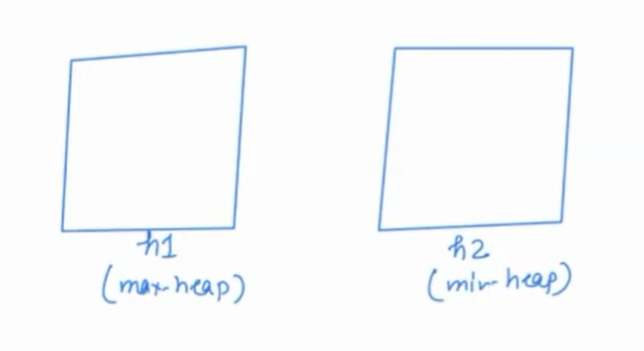
Smaller side elements are stored in max-heap and Greater side elements are stored in min-heap
- First element is 6, simply add it in max-heap
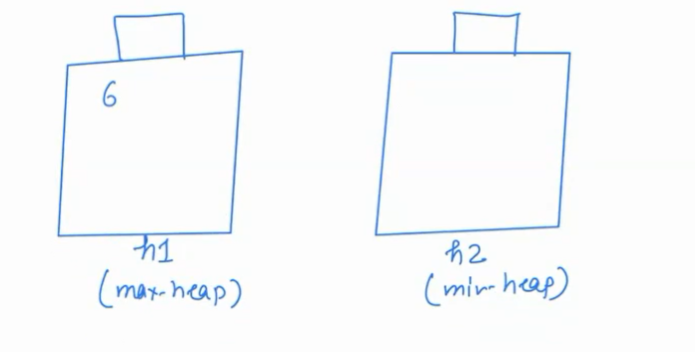
The median is 6.
- Second element is 3; compare with h1.getMax(), if 3<6 then it must be included in h1.
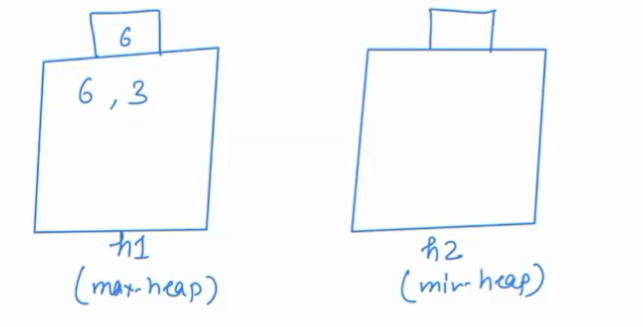
but now both the heaps do not have half-half elements. Remove the maximum element from max-heap and insert it into h2.
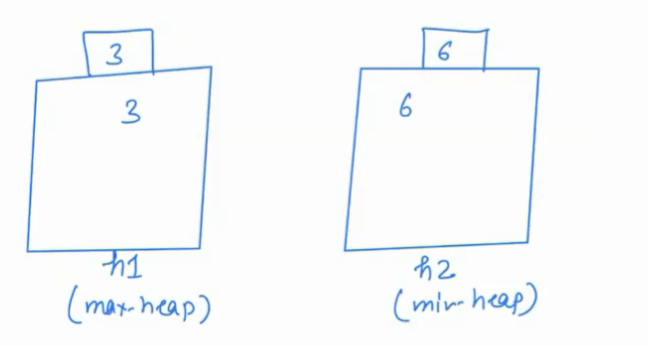
Now we have an equal number of elements in both heaps, so the median is the average of the largest value of h1 and the smallest value of h2.
Median is 4.5
- Next element is 8. Compare it with h1.getMax(), 8>3 so 8 will go to h2.
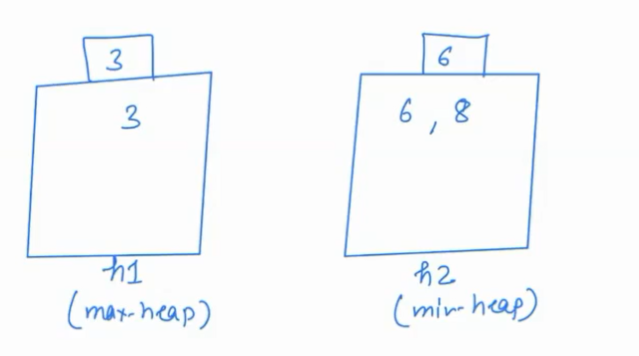
size(h2) is greater by 1 Median is 6
- Next element is 11.
Compare it with h1.getMax(), 11>3 so 11 will go to h2.
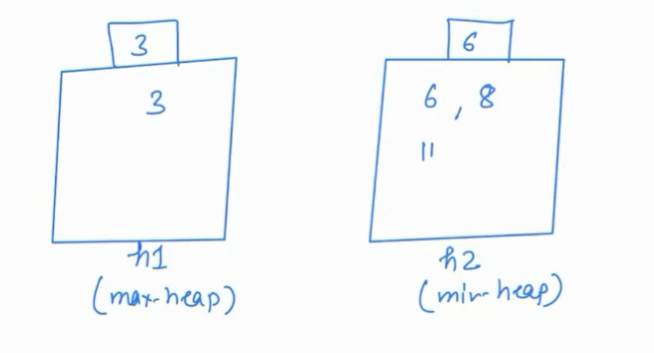
But now both heap does not have nearly half elements.
So remove the minimum element and add it to h1.
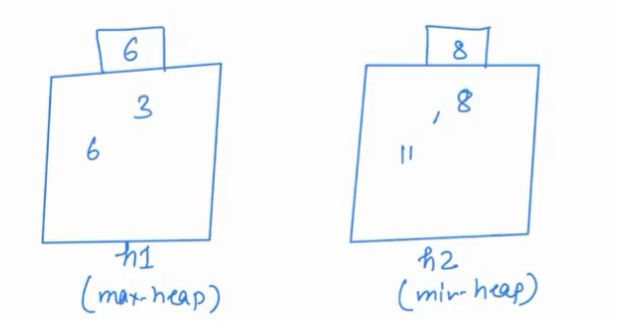
Median is average of 6,8 = (6+8)/2 = 7
- Next element is 20.
Compare it with h1.getMax(), 20>6 so 20 will go to h2.
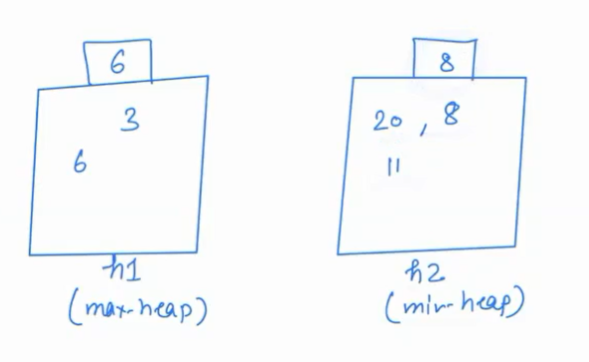
size(h2) is greater by 1
The median is 8.
In this way we will do for all the elements of an array, and find the median at every step, we need to take care that the |h1.size()-h2.size()|<=1.
After adding all the medians in an array, we will get an answer: [6, 4.5, 6, 7, 8, 7, 8, 8, 8, _ _ _ ]
PseudoCode¶
h1, h2
h1.insert(arr[0])
print(arr[0])
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
if (arr[i] > h1.getMax()) {
h2.insert(arr[i]);
} else {
h1.insert(arr[i]);
}
diff = | h1.size() - h2.size() |
if (diff > 1) {
if (h1.size() > h2.size()) {
h2.insert(h1.getMax());
} else {
h1.insert(h2.getMin());
}
}
if (h1.size() > h2.size()) {
print(h1.getMax());
} else if (h2.size() > h1.size()) {
print(h2.getMin())
} else {
print((h1.getMax() + h2.getMin()) / 2.0);
}
}
Complexity¶
Time Complexity: O(NlogN)
Space Complexity: O(N)
