Stacks 2: Nearest Smaller/Greater Element¶
Problem 1 Nearest smallest element on left¶
Given an integer array A, find the index of nearest smallest element on left for all i index in A[].
Formally , for all i find j such that A[j] < A[i], j < i and j is maximum.
Example:
A[] = [8, 2, 4, 9, 7, 5, 3, 10]
Answer = [-1, -1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 1, 6]
For each element in the input array, the output indicates the index of the nearest smaller element on the left side of that element. If there's no smaller element on the left, it's represented by -1.
| Element | Nearest Smaller Element | Index of Nearest Smaller Element |
|---|---|---|
| 8 | NA | -1 |
| 2 | NA | -1 |
| 4 | 2 | 1 |
| 9 | 4 | 2 |
| 7 | 4 | 2 |
| 5 | 4 | 2 |
| 3 | 2 | 1 |
| 10 | 3 | 6 |
Question¶
Given N array elements, find the nearest smaller element on the left side for all the elements. If there is NO smaller element on left side, return -1. (Assume all elements are positive).
A = [4, 6, 10, 11, 7, 8, 3, 5]
Choices
- [-1, 4, 6, 10, 4, 7, -1, 3]
- [-1, 4, 6, 10, 6, 6, -1, 3]
- [-1, 4, 6, 10, 6, 7, -1, 3]
Question¶
Given N array elements, find the nearest smaller element on the left side for all the elements. If there is NO smaller element on left side, return -1. (Assume all elements are positive).
A = [4, 5, 2, 10, 8, 2]
Choices
- [4, 4, -1, 2, 2, -1]
- [-1, 4, -1, 2, 2, -1]
- [-1, 4, 4, 2, 2, -1]
- [-1, 4, 2, 2, 2, 2]
Warning
Please take some time to think about the solution approach on your own before reading further.....
Nearest smallest element on left Brute Force¶
For each element in the array, iterate through all the elements to its left.
Pseudocode¶
result[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int nearestSmaller = -1;
for (int j = i - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
if (arr[j] < arr[i]) {
nearestSmaller = j;
break;
}
}
result[i] = nearestSmaller;
}
return result;
Time Complexity¶
This approach has a time complexity of \(O(n^2)\) because for each element, it requires checking all elements to its left. It is inefficient for large input arrays.
Question¶
If A = [8, x, x, x, x, 5, x, x, x, x...]
For any element > 5 can the element 8 become nearest smaller element on left?
Choices
- Yes
- No
Explanation¶
Not really since 5 will be the answer for them.
Nearest Smallest Element Optimized Approach¶
Observation/Intuition:¶
When iterating through the array from left to right, we want to find the nearest smaller element on the left for each element efficiently.
- Using a stack helps us keep track of potential candidates for the nearest smaller element as we move from left to right. The stack stores the indices of elements that have not yet found their nearest smaller element.
- When we encounter a new element, we check if it is smaller than the element at the top of the stack (the most recent candidate for the nearest smaller element). If it is, we know that the element at the top of the stack cannot be the nearest smaller element for any future elements because the new element is closer and smaller. Therefore, we pop elements from the stack until we find an element that is smaller than the current element or until the stack becomes empty.
- The popped elements from the stack are assigned as the nearest smaller elements on the left for the corresponding indices.
- By doing this, we efficiently find the nearest smaller element for each element in the array without the need for nested loops or extensive comparisons, resulting in a linear time complexity of O(n).
Optimized Approach:¶
- Create an empty stack to store the indices of elements.
- Initialize an empty result array with -1 values.
- Iterate through the input array from left to right.
- For each element, while the stack is not empty and the element at the current index is less than or equal to the element at the index stored at the top of the stack, pop elements from the stack and update the result array for those popped elements.
- After the loop, the stack will contain indices of elements that haven't found their nearest smaller element. These elements have no smaller element on the left side.
- The result array will contain the index of the nearest smaller element for all other elements.
- Return the result array.
Nearest Smallest Element Optimized Approach Dry Run¶
- Initialize an empty stack and an empty result array of the same length as A filled with -1s.
- Start iterating through the array from left to right:
| i | Element | Pop index | Stack | Nearest Smaller Element | Push index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 8 | NIL | EMPTY | NA | 0 |
| 1 | 2 | 0 | EMPTY | NA | 1 |
| 2 | 4 | NIL | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 9 | NIL | 1, 2 | 4 | 3 |
| 4 | 7 | 3 | 1, 2 | 4 | 4 |
| 5 | 5 | 4 | 1, 2 | 4 | 5 |
| 6 | 3 | 5, 2 | 1 | 2 | 6 |
| 7 | 10 | NIL | 1, 6 | 3 | 7 |
Code:
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// While the stack is not empty and the element at the current index is less than or
// equal to the element at the index stored at the top of the stack, pop elements from
// the stack and update the result array.
while (!stack.isEmpty() && arr[i] <= arr[stack.peek()]) {
stack.pop();
}
// If the stack is not empty, the top element's index is the nearest smaller element on the left.
if (!stack.isEmpty()) {
result[i] = stack.peek();
}
// Push the current index onto the stack.
stack.push(i);
}
return result;
Complexity¶
Time Complexity: O(N)
Space Complexity: O(N)
Nearest Smallest Element related questions¶
Question-2¶
For all i, find nearest smaller or equal element on left
ANS:
For this question, we need to change the sign from <= to < in the above code of the approach in line number 5.
Question-3¶
For all i, find nearest greater element on left
ANS:
For this question, we need to change the sign from <= to >= in the above code of the approach.
Question-4¶
For all i, find nearest greater or equal element on left.
ANS:
For this question, we need to change the sign from <= to > in the above code of the approach.
Question-5¶
For all i, find nearest smaller element on right.
ANS:
For this question, the for loop iterates through the input array arr in reverse order (from right to left), and it finds the nearest smaller element on the right for each element using a stack.
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
// While the stack is not empty and the element at the current index is less than or
// equal to the element at the index stored at the top of the stack, pop elements from
// the stack and update the result array.
while (!stack.isEmpty() && arr[i] <= arr[stack.peek()]) {
stack.pop();
}
// If the stack is not empty, the top element's index is the nearest smaller element on the right.
if (!stack.isEmpty()) {
result[i] = stack.peek();
}
// Push the current index onto the stack.
stack.push(i);
}
return result;
Question-6¶
For all i, find nearest smaller or equal element on right.
ANS:
For this question, we need to change the sign from <= to > in the above code of the approach.
Question - 7¶
For all i, find nearest greater element on right.
ANS:
For this question, we need to change the sign from <= to >= in the above code of the approach.
Question-8¶
For all i, find the nearest greater or equal element on right.
ANS:
For this question, we need to change the sign from <= to > in the above code of the approach.
Problem 2 Largest Rectangle in histogram¶
Given an integer array A, where
A[i] = height of i-th bar.
Width of each bar is = 1.
Find the area of the largest rectangle formed by continious bars.
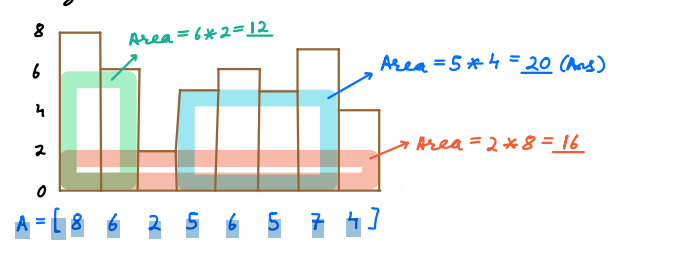
Given Array (heights): [8, 6, 2, 5, 6, 5, 7, 4]
The goal is to find the largest rectangle that can be formed using continuous bars from this array. In this example, the largest rectangle is formed by bars with heights 5, 6, 5, and 7. The width of each bar is 1, so the area of this rectangle is 5 (height) * 4 (width) = 20.
Sure, here is a brief MCQ based on finding the largest rectangle formed by continuous bars in an integer array representing bar heights:
Question¶
Find the area of the largest rectangle formed by continious bars.
bars = [1, 2, 3, 2, 1]
Choices
- 5
- 9
- 7
- 6
- 3
Explanation:
The largest rectangle is formed from [2, 3, 2] whose contribution is [2, 2, 2] thus the area of the largest rectangle is 6.
Largest Rectangle Brute Force¶
Brute - Force Approach Pseudo Code:
function findMaxRectangleArea(hist):
maxArea = 0
for i from 0 to len(hist) - 1:
// Consider each bar as a potential starting point
minHeight = hist[i]
for j from i to len(hist) - 1:
// Iterate through bars to the right
minHeight = min(minHeight, hist[j])
width = j - i + 1
area = minHeight * width
maxArea = max(maxArea, area)
return maxArea
The brute-force approach involves nested loops and has a time complexity of O(n2) because it considers all possible combinations of starting and ending points for rectangles.
Warning
Please take some time to think about the optimised approach on your own before reading further.....
Optimized Approch¶
Mathematical Representation:
- Let a[i] represent the height of the bar at index i.
- We use j to represent the index of the nearest smaller bar to the left of i.
- Similarly, we use k to represent the index of the nearest smaller bar to the right of i.
- The area of the rectangle that can be formed with the bar at index i as its base is given by
a[i] * (k - j - 1).
Observation/Intuition:
- The key insight here is that for each potential base (represented by indices in the stack), we can efficiently calculate the area of the rectangle by finding the width between the current index and the index at the top of the stack.
- By using a stack, we maintain a list of potential bases and calculate the area of rectangles as we encounter new heights, ensuring we consider all possible rectangles efficiently.
Optimized Approach Pseudo Code:
function findMaxRectangleArea(hist):
stack = [] // Initialize an empty stack to store indices of bars.
maxArea = 0
for i from 0 to len(hist) - 1:
while (stack is not empty and hist[i] < hist[stack.top()]):
// Pop elements from the stack and calculate areas
// with their heights as the potential bases.
height = hist[stack.pop()]
width = (i - stack.top() - 1) if stack is not empty else i
area = height * width
maxArea = max(maxArea, area)
stack.push(i) // Push the current index onto the stack.
while (stack is not empty):
// Process the remaining elements in the stack.
height = hist[stack.pop()]
width = (len(hist) - stack.top() - 1) if stack is not empty else len(hist)
area = height * width
maxArea = max(maxArea, area)
return maxArea
Mathematical Representation of the Answer:
- The answer (maximum area) is given by the formula:
- \(ans ~=~ max(a[i] * (nearest~smaller~right[i] * nearest~smaller~left[i] - 1))\)
- Where a[i] is the height of the bar at index i.
nearest_smaller_right[i]is the index of the nearest smaller bar to the right of i.nearest_smaller_left[i]is the index of the nearest smaller bar to the left of i.- We subtract 1 from the product of
nearest_smaller_right[i]andnearest_smaller_left[i]to account for the width of the rectangle.
Problem 3 Sum of (Max-Min) of all subarrays¶
Giver an integer array with distinct integers, for all subarrays find (max-min) and return its sum as the answer.
Example:
Given Array: [2, 5, 3]
The goal is to find the sum of the differences between the maximum and minimum elements for all possible subarrays.
- Subarray [2]: Max = 2, Min = 2, Difference = 0
- Subarray [5]: Max = 5, Min = 5, Difference = 0
- Subarray [3]: Max = 3, Min = 3, Difference = 0
- Subarrays of length 2:
- [2, 5]: Max = 5, Min = 2, Difference = 3
- [5, 3]: Max = 5, Min = 3, Difference = 2
- Subarray [2, 5, 3]: Max = 5, Min = 2, Difference = 3
The sum of all differences is 0 + 0 + 0 + 3 + 2 + 3 = 8.
Warning
Please take some time to think about the solution approach on your own before reading further.....
Sum of (Max-Min) of all subarrays Brute force approach¶
Brute-Force Approach Pseudo Code:
function sumOfDifferences(arr):
result = 0
for start from 0 to len(arr) - 1:
for end from start to len(arr) - 1:
// Find the maximum and minimum elements within the subarray
maxElement = arr[start]
minElement = arr[start]
for i from start to end:
maxElement = max(maxElement, arr[i])
minElement = min(minElement, arr[i])
// Calculate the difference between the maximum and minimum elements
difference = maxElement - minElement
// Add this difference to the result
result += difference
return result
Complexity¶
Time Complexity: O(N * N)
Space Complexity: O(1)
Question¶
Giver an integer array, A with distinct integers, for all subarrays find (max-min) and return its sum as the answer.
A = [1, 2, 3]
Choices
- 4
- 6
- 5
- 0
Explanation:¶
The goal is to find the sum of the differences between the maximum and minimum elements for all possible subarrays.
Subarrays of length 1:
- [1]: Max = 1, Min = 1, Difference = 0
- [2]: Max = 2, Min = 2, Difference = 0
- [3]: Max = 3, Min = 3, Difference = 0
Subarrays of length 2:
- [1, 2]: Max = 2, Min = 1, Difference = 1
- [2, 3]: Max = 3, Min = 1, Difference = 1
Subarrays of length 3:
- [1, 2, 3]: Max = 3, Min = 1, Difference = 2
The sum of all differences is 0 + 0 + 0 + 1 + 1 + 2 = 4.
Sum of (Max-Min) of all subarrays Optimized approach¶
Optimized Approach¶
Intuition:
- The contribution technique eliminates redundant calculations by efficiently counting the number of subarrays in which each element can be the maximum or minimum element.
- By tracking the elements that are greater or smaller than the current element in both directions, we can calculate their contributions to the sum of (max - min) differences without repeatedly considering the same subarrays.
Optimized Approach Pseudo code:
function sumOfDifferences(arr):
n = length of arr
left = new array of size n
right = new array of size n
max_stack = empty stack
min_stack = empty stack
result = 0
// Initialize left and right arrays
for i from 0 to n - 1:
left[i] = (i + 1) * (n - i)
right[i] = (i + 1) * (i + 1)
// Calculate left contributions
for i from 0 to n - 1:
while (not max_stack.isEmpty() and arr[i] > arr[max_stack.top()]):
max_stack.pop()
if (max_stack.isEmpty()):
left[i] = (i + 1) * (i + 1)
else:
left[i] = (i - max_stack.top()) * (i + 1)
max_stack.push(i)
// Calculate right contributions
for i from n - 1 to 0:
while (not min_stack.isEmpty() and arr[i] < arr[min_stack.top()]):
min_stack.pop()
if (min_stack.isEmpty()):
right[i] = (n - i) * (n - i)
else:
right[i] = (min_stack.top() - i) * (n - i)
min_stack.push(i)
// Calculate the sum of (max - min) differences
for i from 0 to n - 1:
contribution = (right[i] * left[i]) * arr[i]
result += contribution
return result
Complexity¶
Time Complexity: O(N)
Space Complexity: O(N)
