Carry Forward & Subarrays¶
Problem 1 : Count of Pairs ag¶
Given a string s of lowercase characters, return the count of pairs (i,j) such that i < j and s[ i ] is 'a' and s[ j ] is 'g'.
Example 1¶
String s = "abegag"
Ans = 3
Explanation:¶
Here, [i,j] such that i<j and s[i] is 'a' and s[j] is 'g' are [0,3], [0,5] and [4,5]. So ans would be 3.
Question¶
What is the count of a,g pairs in the array:- s = "acgdgag"
Choices
- 4
- 3
- 5
- 2
Explanation:¶
Here, [i,j] such that i<j and s[i] is 'a' and s[j] is 'g' are [0,2], [0,4], [0,6] and [5,6]. So ans would be 4.
Question¶
How many ag pairs are in this string? s = "bcaggaag"
Choices
- 5
- 4
- 3
- 6
Explanation:¶
Here, [i,j] such that i<j and s[i] is 'a' and s[j] is 'g' are [2,3], [2,4], [2,7], [5,7] and [6,7]. So ans would be 5.
Warning
Please take some time to think about the brute force approach on your own before reading further.....
Problem 1 : Brute Force Solution¶
For every 'a', we need to find the count of g's on the right side of a. So, we need to have nested loops.
Pseudocode
int count_ag(string s) {
int result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (s[i] == 'a') {
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
if (s[j] == 'g') {
result++;
}
}
}
}
return result;
}
Time and Space Complexity¶
Time Complexity : O(n^2)
Space Complexity : O(1)
Problem 1 Optimised solution¶
Observation:¶
- For every 'g', we need to know the count of 'a' on left side of 'g'.
- We will store the count of 'a' and whenever 'g' is encountered, we will add the count of 'a' to the result.
Dry Run¶
Example: "acbagkagg"
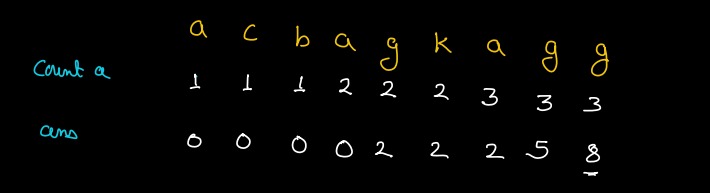
Pseudocode¶
int count_ag(string s) {
int result = 0;
int count_a = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (s[i] == 'a') {
count_a++;
} else if (s[i] == 'g') {
result += count_a;
}
}
return result;
}
Time and Space Complexity¶
What will be T.C and S.C for this approach?
Time Complexity : O(n)
Space Complexity : O(1)
Introduction to Subarrays¶
Definition¶
A subarray is a contiguous part of an array. It is formed by selecting a range of elements from the array. A subarray can have one or more elements and must be a contiguous part of the original array.
Example¶
Consider the following array of integers:
| 4 | 1 | 2 | 3 | -1 | 6 | 9 | 8 | 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
2, 3, -1, 6is a subarray of length 4.9is a subarray of single element.4, 1, 2, 3, -1, 6, 9, 8, 12is a subarray consisting of all the array elements.4, 12is not a subarray because loop does not count as subarray.1, 2, 6is not a subarray beacuse the array elements must be contiguous.3, 2, 1, 4is not a subarray because order of the elements in a subarray should be same as in the array.
Question¶
A[] = { 2, 4, 1, 6, -3, 7, 8, 4}
Which of the following is a valid subarray?
Choices
- {1, 6, 8}
- {1, 4}
- {6, 1, 4, 2}
- {7, 8, 4}
Explanation:¶
{1, 6, 8} & {1, 4} are not contiguous parts of array. {6, 1, 4, 2} is not in the same order as in original array. Only {7, 8, 4} is a valid subarray.
Representation of a Subarray¶
Representation of a Subarray¶
A Subarray can be uniquely represented in following ways:
- By specifying the
startandendindex of the subarray. - By specifying the
startindex andlengthof the subarray.
If we consider the same array from the above example,
| 4 | 1 | 2 | 3 | -1 | 6 | 9 | 8 | 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
The subarray 2, 3, -1, 6 can be represented as
- the range of elements starting at index
2and ending at index5(0-based indexing). - the range of elements having length of
4with start index as2.
Question¶
How many subarrays of the following array start from index 0
[4, 2, 10, 3, 12, -2, 15]
Choices
- 6
- 7
- 21
- 36
[4] (starting from index 0)
[4, 2]
[4, 2, 10]
[4, 2, 10, 3]
[4, 2, 10, 3, 12]
[4, 2, 10, 3, 12, -2]
[4, 2, 10, 3, 12, -2, 15]
Therefore, there are a total of 7 subarrays that start from index 0.
Question¶
How many subarrays of the following array start from index 1
[4, 2, 10, 3, 12, -2, 15]
Choices
- 6
- 7
- 21
- 36
[2] (starting from index 1)
[2, 10]
[2, 10, 3]
[2, 10, 3, 12]
[2, 10, 3, 12, -2]
[2, 10, 3, 12, -2, 15]
Therefore, there are a total of 6 subarrays that start from index 1.
Formula to count no. of subarrays¶
No. of subarrays starting from index 0 = n
No. of subarrays starting from index 1 = n-1
No. of subarrays starting from index 2 = n-2
No. of subarrays starting from index 3 = n-3
...........
...........
No. of subarrays starting from index n-1 = 1
So, Using the formula for the sum of an arithmetic series, total number of subarrays = n + (n-1) + (n-2) + (n-3) + . . . . . . + 3 + 2 + 1 = n(n+1)/2.
total = n(n + 1) / 2
Print the subarray of the array that starts from the start index and ends at the end index¶
Problem Statement¶
Given an array of integers and two indices, a start index and an end index, we need to print the subarrays of the array that starts from the start index and ends at the end index (both inclusive).
Solution¶
To solve this problem, we can simply iterate over the elements of the array from the start index to the end index (both inclusive) and print each element.
Pseudocode¶
void printSubarray(int arr[], int start, int end) {
for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) {
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
Time and Space Complexity¶
What will be T.C and S.C for the above approach?
Time Complexity : O(n)
Space Complexity : O(1)
Print all possible subarrays of the array¶
Problem Statement:
Given an array of integers, we need to print all possible subarrays of the array.
Example
Input: [1, 2, 3]
Output:
[1]
[1, 2]
[1, 2, 3]
[2]
[2, 3]
[3]
Solution¶
To solve this problem, we can generate all possible subarrays of the array using two nested loops.
- The outer loop iterates over the starting index of the subarray.
- The inner loop iterates over the ending index of the subarray.
- At each iteration, we print the subarray from the starting index to the ending index.
Pseudocode¶
void printSubarrays(int arr[], int n) {
// Generate all possible subarrays
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = i; j < n; j++) {
// Print the current subarray
for (int k = i; k <= j; k++) {
cout << arr[k] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
}
Time and Space Complexity¶
Time Complexity : O(N^3)
Space Complexity : O(1)
Problem 2 : Max And Min¶
Given an array of N integers, return the length of smallest subarray which contains both maximum and minimum element of the array.
Question¶
What is the length of the smallest subarray which has both, the max and the min of the array?
| 2 | 2 | 6 | 4 | 5 | 1 | 5 | 2 | 6 | 4 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Choices
- 4
- 5
- 2
- 3
Here, minimum element is 1 and maximum is 6. Smallest subarray which contains both is from index 8 to index 10 which is of length 10-8+1=3.
Another Example
A[ ] = { 1, 2, 3, 1, 3, 4, 6, 4, 6, 3}
Ans = 4
Explanation:
Here, minimum element is 1 and maximum is 6. Smallest subarray which contains both is from index 3 to index 6 which is of length 6-3+1=4.
Warning
Please take some time to think about the brute force approach on your own before reading further.....
Problem 2 : Brute Force Solution¶
Check all subarrays and find the answer.
Time Complexity : O(N^3)
Space Complexity : O(1)
Note: It can be reduced to O(n^2) since we can check miniumum and maximum in a subarray in second loop itself.
Problem 2 : Optimised Solution Observation¶
- The answer subarray must have exactly one instance of minimum element and one instance of maximum element since we want the length to be minimum.
- The minimum and maximum value must be present at the corners of the subarray.
- So, basically we are looking for subarray which starts with maximum value and ends with closest minimum value or which starts with minimum value and ends with closest maximum value.
NOTE:
- We can search a min for a max or vice versa, only in a single direction.
- We don't have to consider all the pairs of min and max but look for closest pair, since we want to find smallest such subarray.
- So we can keep track of the last found min and a last found max index.
Dry Run¶
A[ ] = { 2, 2, 6, 4, 5, 1, 5, 2, 6, 4, 1 }
Initially,
last_min_index = -1
last_max_index = -1
ans = INT_MAX
minValue = 1
maxValue = 6
| i | A[i] | last_min_index | last_max_index | ans |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2 | -1 | -1 | INT_MAX |
| 1 | 2 | -1 | -1 | INT_MAX |
| 2 | 6 | -1 | 2 | INT_MAX |
| 3 | 4 | -1 | 2 | INT_MAX |
| 4 | 5 | -1 | 2 | INT_MAX |
| 5 | 1 | 5 | 2 | 5-2+1 = 4 |
| 6 | 5 | 5 | 2 | 4 |
| 7 | 2 | 5 | 2 | 4 |
| 8 | 6 | 5 | 8 | 4 |
| 9 | 4 | 5 | 8 | 4 |
| 10 | 1 | 10 | 8 | 10-8+1 = 3 |
So final ans would be 3.
Pseudocode¶
int minSubarray(int A[], int n) {
// find maximum and minimum
// values in the array
int minValue = minOfArray(A);
int maxValue = maxOfArray(A);
int last_min_index = -1, last_max_index = -1, ans = INT_MAX;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if (A[i] == minValue) {
last_min_index = i;
if (last_max_index != -1) {
ans = min(ans, i - last_max_index + 1);
}
}
if (A[i] == maxValue) {
last_max_index = i;
if (last_min_index != -1) {
ans = min(ans, i - last_min_index + 1);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
Time and Space Complexity¶
What will be T.C and S.C for this approach?
Time Complexity : O(N)
Space Complexity : O(1)
