String¶
A string can be defined as a sequence of characters or in other words we can say that it is an array of characters.
Example Below are the examples of string:
"Welcome to Scaler"
"Hello World!"
"". All the characters of string must be inside this quote.
Character
A character is a single symbol that represents a letter, number, or other symbol in a computer's character set. Characters are used to represent textual data, and they are typically represented using its ASCII value.
Example
'a'
'B'
'1'
'_'
Computer store everything in binary. So, how do we store strings in computer?
Each character has corresponding decimal value associated to it which is known as ASCII value.
'A' to 'Z' have ASCII from 65 to 90
'a' to 'z' have ASCII from 97 to 122
'0' to '9' have ASCII from 48 to 57
Each character '?', '!', '*', ... has a corresponding ASCII associated with it.
Some Operations:¶
Note:
Characters can also be printed using its ascii value. for example, the ascii value of 'A' is 65, so it can be printed as
char ch = (char)65;
print(ch);
/*
character 'A' gets printed; we are assigning Integer to Char,hence in some languages typecasting will be required.
*/
char ch = (char)('a' + 1);
/*
When we do arithmetic operations on characters, automatically computations happen on their ASCII values.
*/
print(ch); //'b' will get printed
int x = 'a';
/*
No need to typecast since we are assigning Char to Int (smaller data type to bigger, so it will not overflow)
*/
print(x); //97 will be printed
Question 1 : Switch cases¶
Given a string consisting of only alphabets(either lowercase or uppercase). Print all the characters of string in such a way that for all lowercase character, print its uppercase character and for all uppercase character, print its lowercase character.
TestCase
Input
"Hello"
Output
"hELLO"
Explanation
Here, there is only one uppercase character present in the string i.e, 'H' so convert it to lowercase character. All other characters are in lowercase, hence they are converted into uppercase characters.
Question¶
What is the output for String = "aDgbHJe" ?
Choices
- ADGBHJE
- aDgbHJe
- AdGBhjE
- adgbhje
Warning
Please take some time to think about the solution approach on your own before reading further.....
Observation
The key observations are:
- Lowercase characters can be changed into uppercase by subtracting 32 from its ASCII values.
- Uppercase charactes can be changed into lowercase by adding 32 from its ASCII values.
The above points are derived from the fact that for every alphabet, the difference between its ascii value in lowercase and uppercase is 32.
Pseudocode¶
Function toggle(char s[]) {
int n = s.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (s[i] >= 65 and s[i] <= 91) {
print(s[i] + 32);
} else {
print(s[i] - 32);
}
}
}
Complexity¶
Time Complexity- O(N).
Space Complexity- O(1).
Substring¶
A substring is a contiguous sequence of characters within a string. A substring concept in string is similar to subarray concept in array.
A substring can be:
- Continous part of string.
- Full string can be a substring.
- A single character can also be a subsring.
Example
Suppose, we have a string as
"abc"
There are total 6 substring can be formed from the above string. All substrings are
"a"
"b"
"c"
"ab"
"bc"
"abc"
Question¶
How many total substrings will be there for the String "bxcd" ?
Choices
- 7
- 8
- 10
- 9
Explanation:
All the substrings are as follows-
"b", "x", "c", "d", "bx", "xc", "cd", "bxc", "xcd", "bxcd"
We can also find the count using n*(n+1)/2.
Question 2 Check Palindrome¶
Check whether the given substring of string s is palindrome or not. A palindrome is the sequence of characters that reads the same forward and backward.for example, "nayan", "madam", etc.
TestCase
Input
s = "anamadamspe"
start = 3
end = 7
Output
true
Explanation
The substring formed from index 3 to 7 is "madam" which is palindrome.
Question 2 Approach¶
Approach¶
Below is the simple algorithm to check whether the substring is palindrome or not: * Initialize two indices start and end to point to the beginning and end of the string, respectively. * While start is less than end, do the following: * If the character at index start is not equal to the character at index end, the string is not a palindrome. Return false. * Else, increment start and decrement end. * If the loop completes without finding a non-matching pair, the string is a palindrome. Return true.
Pseudocode¶
function ispalindrome(char s[], int start, int end) {
while (start < end) {
if (s[start] != s[end]) {
return false;
} else {
start++;
end--;
}
}
return true;
}
Complexity¶
Time Complexity- O(N).
Space Complexity- O(1).
Question 3 : Longest Palindromic substring¶
Given a string s, calculate the length of longest palindromic substring in s.
TestCase
Input
"anamadamm"
Output
5
Explanation
The substring "madam" of size 5 is the longest palindromic substring that can be formed from given string.
Question¶
What is the length of longest palindromic substring within string "feacabacabgf" ?
Choices
- 6
- 3
- 7
- 10
Question¶
What is the length of longest palindromic substring within string "a d a e b c d f d c b e t g g t e" ?
Choices
- 6
- 3
- 9
- 10
Warning
Please take some time to think about the brute force solution approach on your own before reading further.....
Question 4 Brute Force Approach¶
The naive approach is to for all the substring check whether the string is palindrome or not. if it is palindrome and its size is greater than the previous answer(which is initially 0), then update the answer.
Pseudocode¶
function longestPalindrome(char s[]) {
int N = s.size();
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = i; j < N; j++) {
if (ispalindrome(s, i, j)) {
ans = max(ans, j - i + 1);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
Complexity¶
Time Complexity- O(N^3).
Space Complexity- O(1).
Idea¶
The key idea here is that:
- For odd length substring, take every character as a center and expand its center and gets maximum size palindromic substring.
- For even length substring, take every adjacent character as a center and expand its center and get maximum size palindromic substring.
Pseudocode¶
function longestpalindrome(char s[]) {
int maxlength = 0;
int N = s.size();
for (int c = 0; c < N; c++) {
//odd length string
int left = c, right = c;
while (left >= 0 and right < N) {
if (s[left] != s[right]) {
break;
}
left--;
right++;
}
maxlength = max(maxlength, right - left - 1);
//even length string
left = c;
right = c + 1;
while (left >= 0 and right < N) {
if (s[left] != s[right]) {
break;
}
left--;
right++;
}
maxlength = max(maxlength, right - left - 1);
}
return maxlength;
}
Complexity¶
Time Complexity- O(N^2).
Space Complexity- O(1).
Immutability of Strings¶
In languages like Java, C#, JavaScript, Python and Go, strings are immutable, which means it's value can't be changed.
String s1 = "Hello"; // String literal
String s2 = "Hello"; // String literal
String s3 = s1; // same reference
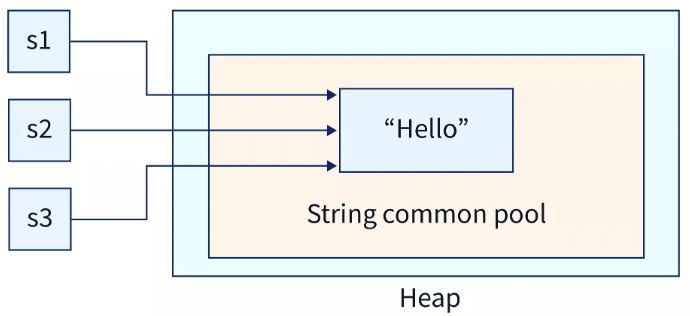
- As seen above, because strings with the same content share storage in a single pool, this minimize creating a copy of the same value.
- That is to say, once a String is generated, its content cannot be changed and hence changing content will lead to the creation of a new String.
//Changing the value of s1
s1 = "Java";
//Updating with concat() operation
s2.concat(" World");
//The concatenated String will be created as a new instance and an object should refer to that instance to get the concatenated value.
String newS3 = s3.concat(" Scaler");
System.out.println("s1 refers to " + s1);
System.out.println("s2 refers to " + s2);
System.out.println("s3 refers to " + s3);
System.out.println("newS3 refers to " + newS3);
Output
s1 refers to Java
s2 refers to Hello
s3 refers to Hello
news3 refers to Hello Scaler
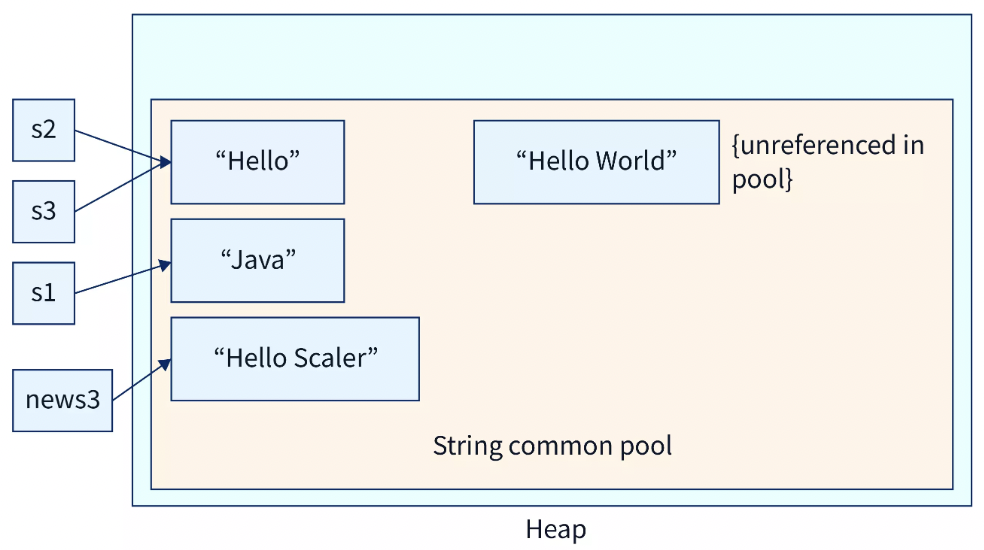
As shown above, considering the example:
- String s1 is updated with a new value and that's why a new instance is created. Hence, s1 reference changes to that newly created instance "Java".
- String s2 and s3 remain unchanged as their references were not changed to a new instance created after performing concat() operation.
- "Hello World" remains unreferenced to any object and lost in the pool as s2.concat() operation (in line number 5) is not assigned to any object. That's why there is a reference to its result.
- String newS3 refers to the instance of s3.concat() operation that is "Hello Scaler" as it is referenced to new object newS3.
Hence, Strings are immutable and whenever we change the string only its reference is changed to the new instance.
