Introduction to Document Object Model¶
Definition¶
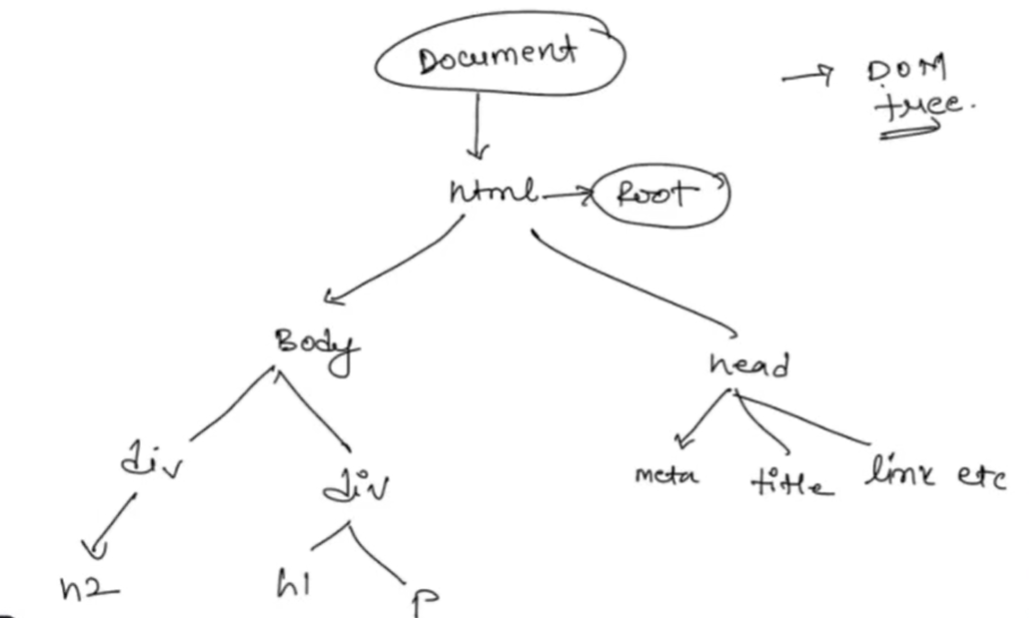
Dom is a tree structure in which every HTML element is arranged in heirarchical order.
Example¶
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang = "en">
<head>
<meta charset = "UTF - 8">
<meta name = "viewport" content = "width = device - width, initial - scale = 1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<h1>This is heading 2</h1>
</div>
<div>
<h1>This is heading 1</h1>
<p>This is Paragraph</p>
</div>
</body>
</html>
Output¶
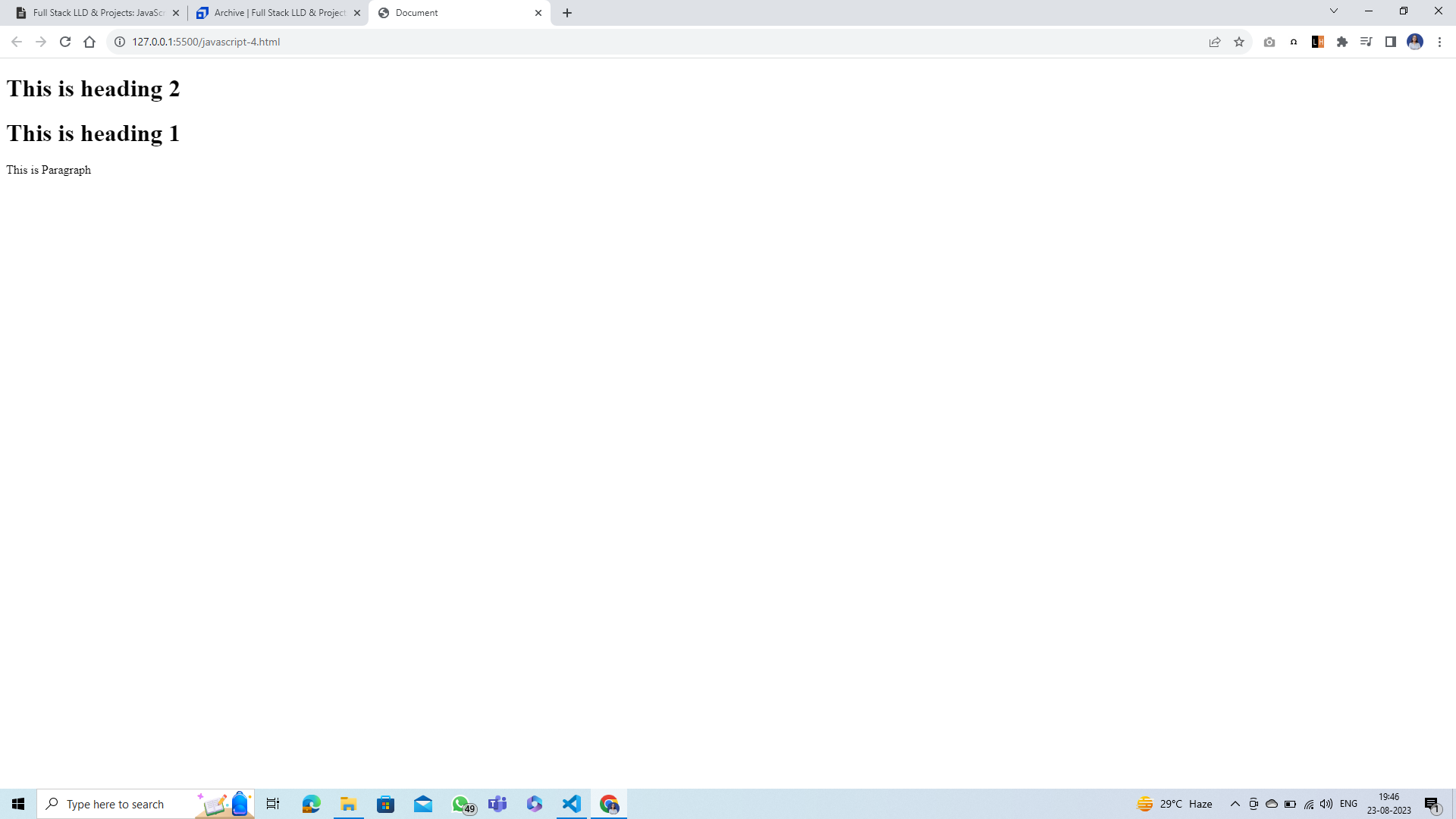
DOM tree visualization of above example¶
Note:
- We will be uisng javascript to put the interactivity in our web apps or websites.
- JavaScript is used to put interactivity in DOM elements.
Question¶
On clicking the button append hello to the page.
Solution¶
Step 1: Slecting html element
To select oe identify a particular html element we have methods.
- getElementById
- QuerySelector
- QuerySelectorAll
Code: Using getElementById
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang = "en">
<head>
<meta charset = "UTF - 8">
<meta name = "viewport" content = "width = device - width, initial - scale = 1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<button id = "btn - 1"> Say Hello </button>
<script>
// on clicking the button append hello to the page
let btn = document.getElementById('btn-1')
console.log(btn)
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output:
Code: Using getElementsByClassName
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang = "en">
<head>
<meta charset = "UTF - 8">
<meta name = "viewport" content = "width = device - width, initial - scale = 1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<button class = "btn - 1"> Say Hello </button>
<script>
// on clicking the button append hello to the page
let btn = document.getElementsByClassName('btn - 1')
console.log(btn)
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output:
Code: Using querySelector by ID
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang = "en">
<head>
<meta charset = "UTF - 8">
<meta name = "viewport" content = "width = device - width, initial - scale = 1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<button id = "btn - 1"> Say Hello </button>
<script>
// on clicking the button append hello to the page
let btn = document.querySelector('#btn - 1')
console.log(btn)
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output:
Code: Using querySelector by class
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang = "en">
<head>
<meta charset = "UTF - 8">
<meta name = "viewport" content = "width = device - width, initial - scale = 1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<button id = "btn - 1"> Say Hello </button>
<button class = "btn - 1"> Say Bye </button>
<script>
// on clicking the button append hello to the page
let btn = document.querySelector('.btn-1')
console.log(btn)
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output:
Code: Using querySelector by elements
The document method querySelector() returns the first element within the document that matches the specified selector, or group of selectors. If no matches are found, null is returned.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang = "en">
<head>
<meta charset = "UTF-8">
<meta name = "viewport" content = "width = device - width, initial - scale = 1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<button id = "btn - 1"> Say Hello </button>
<script>
// on clicking the button append hello to the page
let btn = document.querySelector('button')
console.log(btn)
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output:
Step 2: hello should get appended
What is an event?
Anything that happens depending on some other thins is an event. Let's say you are clicking on button then something will happen (hello is getting printed).
Method - addEventListener: We can add any event to any of our elements with using addEventListener method.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang = "en">
<head>
<meta charset = "UTF - 8">
<meta name = "viewport" content = "width = device - width, initial - scale = 1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<button id = "btn - 1"> Say Hello </button>
<script>
// on clicking the button append hello to the page
let btn = document.querySelector('#btn-1')
console.log(btn)
btn.addEventListener('click', function(e){
// console.log(e)
let divElem = document.createElement('div')
divElem.innerText = 'Hello'
let body = document.querySelector('body')
body.appendChild(divElem)
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output:
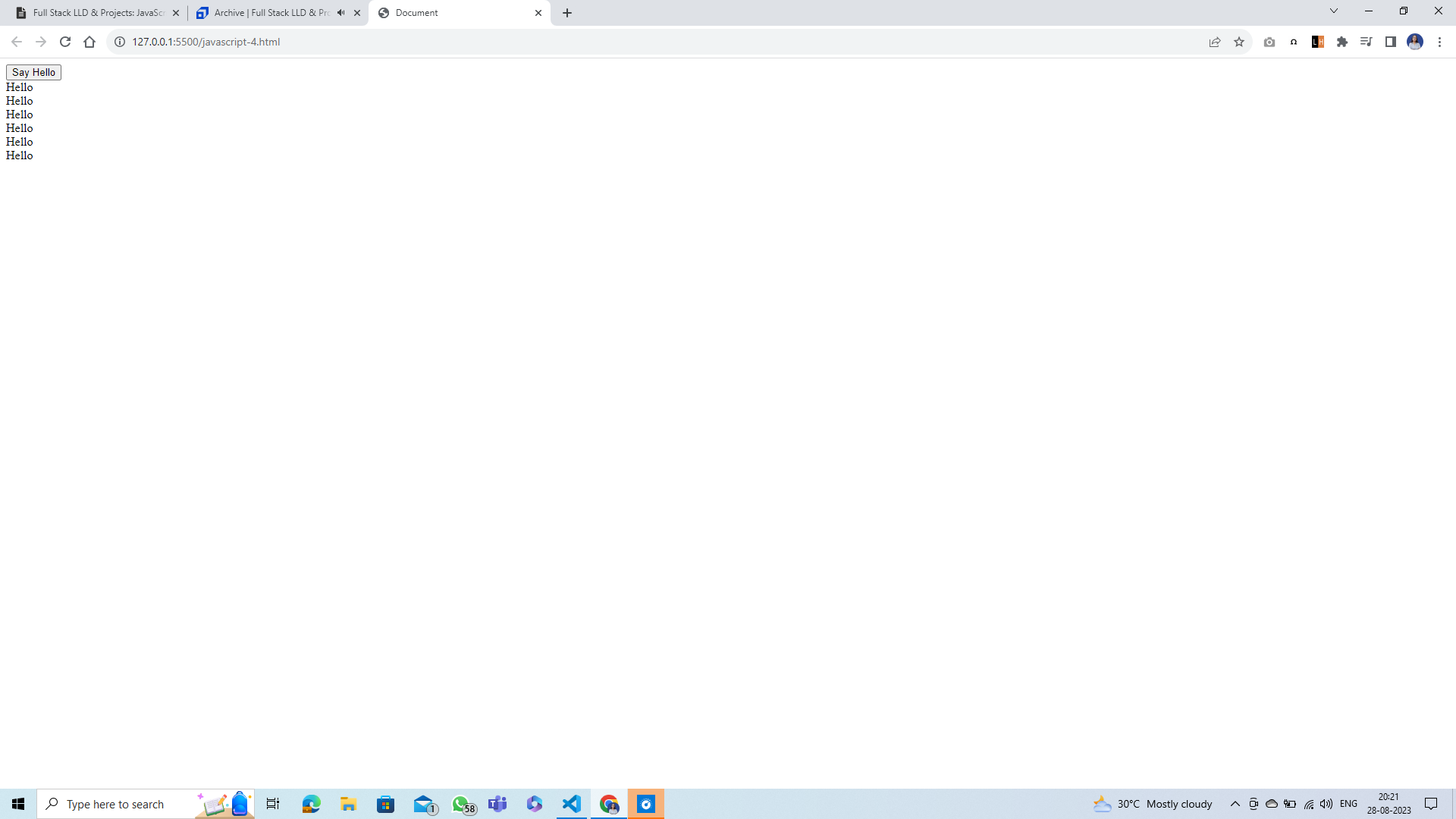
Append Hello DOM Tree¶

Question¶
Fix the list by inserting the missing element using querySelectorAll and insertBefore
Solution¶
Step 1: creating node list
Note: Node list is an array like structure which will have your elements in indexed form stored.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang = "en">
<head>
<meta charset = "UTF - 8">
<meta name = "viewport" content = "width = device - width, initial - scale = 1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<li>1</li>
<li>2</li>
<li>3</li>
<li>4</li>
<li>5</li>
<li>6</li>
<li>8</li>
<li>9</li>
<li>10</li>
</ul>
<script>
// Fix the list by inserting the missing element using querySelectorAll and insertBefor
let allItems = document.querySelectorAll('li');
console.log(allItems);
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output:
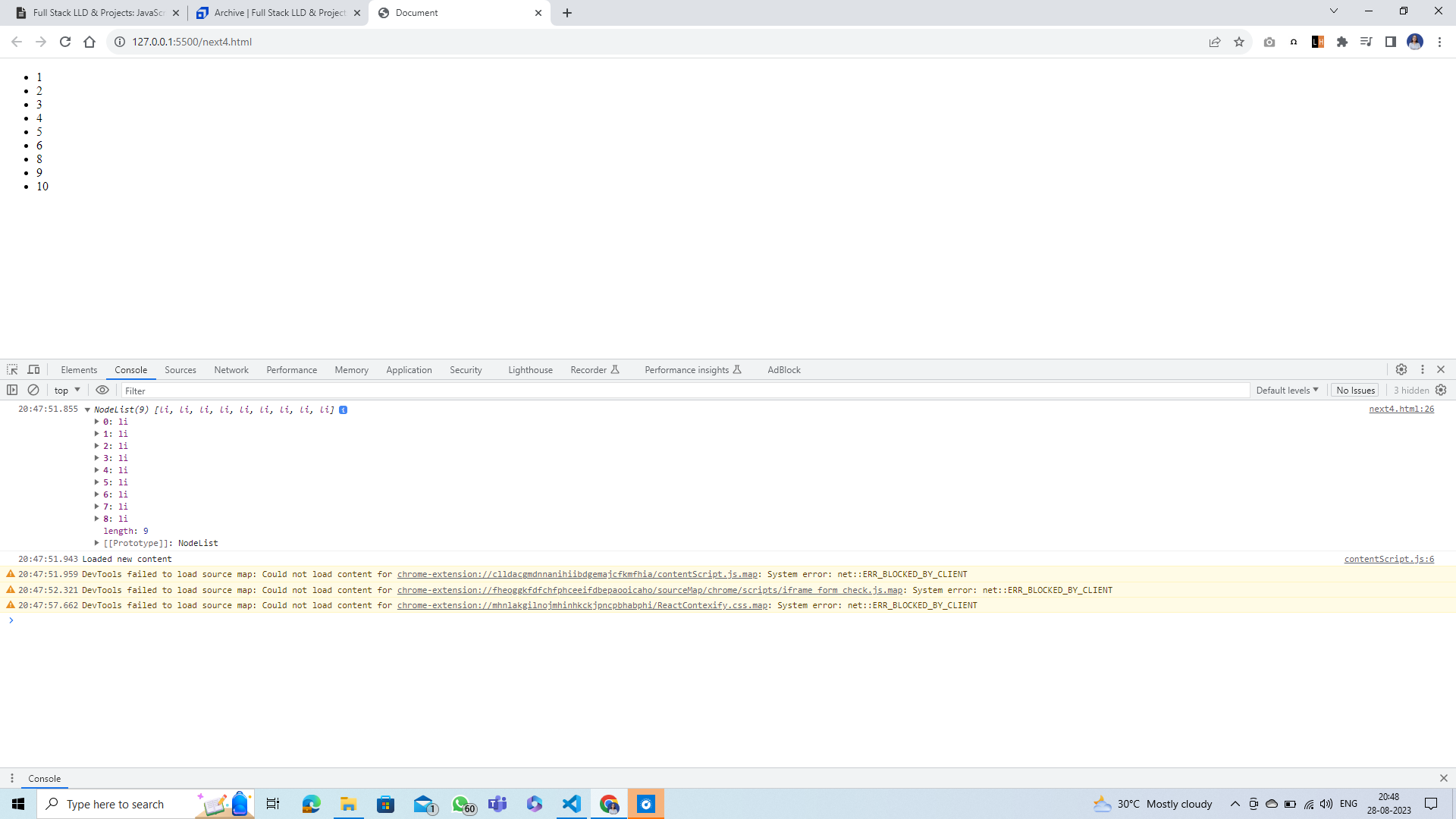
Step 2: adding element
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang = "en">
<head>
<meta charset = "UTF - 8">
<meta name = "viewport" content = "width = device - width, initial - scale = 1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<li>1</li>
<li>2</li>
<li>3</li>
<li>4</li>
<li>5</li>
<li>6</li>
<li>8</li>
<li>9</li>
<li>10</li>
</ul>
<script>
// Fix the list by inserting the missing element using querySelectorAll and insertBefore
let ourList = document.querySelector('ul');
console.log(ourList);
let allItems = document.querySelectorAll('li');
console.log(allItems);
let indexThatHas8 = allItems[6];
let sevenElement = document.createElement('li')
sevenElement.innerText = '7'
ourList.insertBefore(sevenElement, indexThatHas8)
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output:
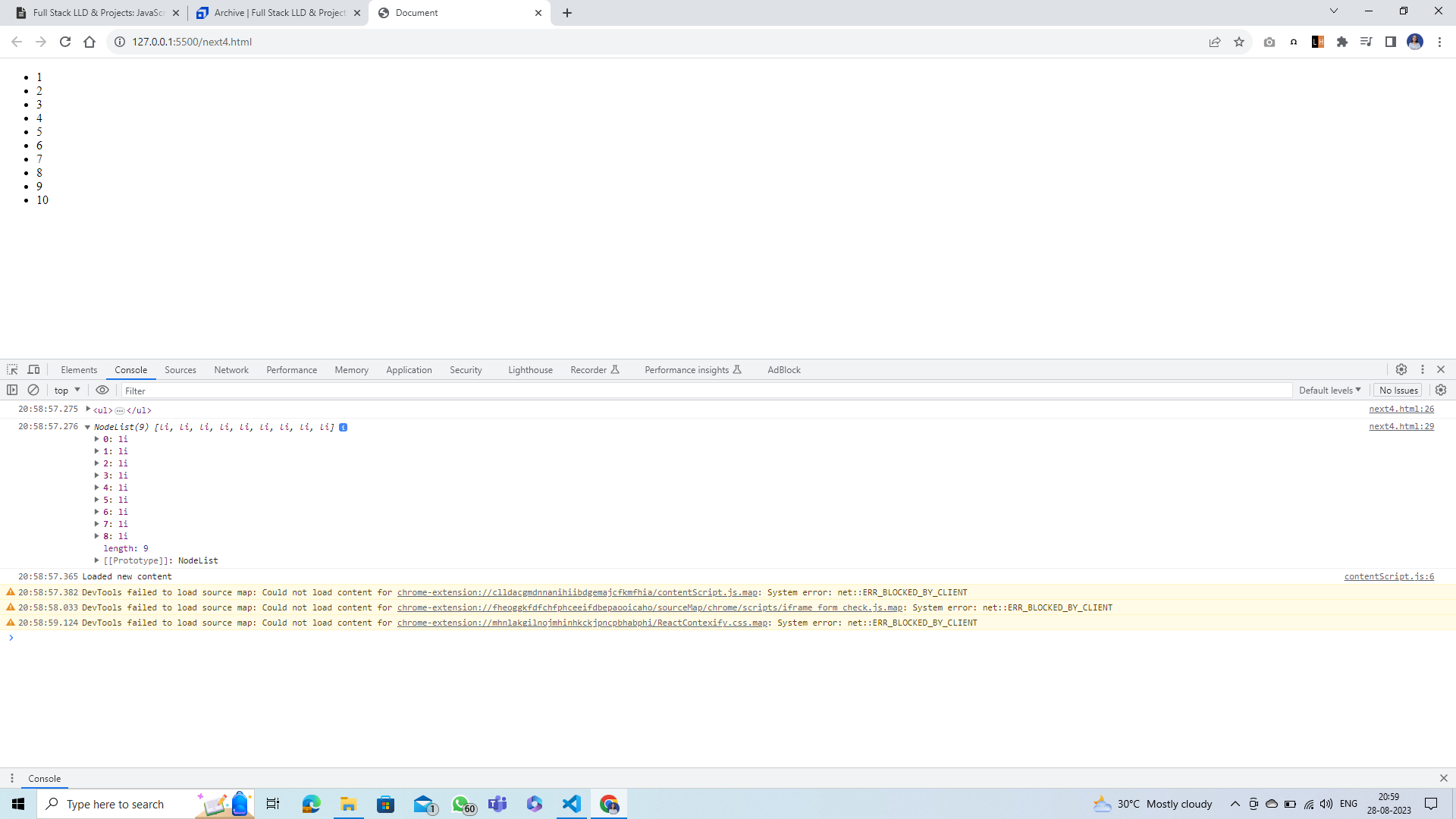
Question¶
Fix the mathmatical problem using JS
Solution¶
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang = "en">
<head>
<meta charset = "UTF - 8">
<meta name = "viewport" content = "width = device - width, initial - scale = 1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- Q. Fix the mathmatical problem usng JS <br> -->
<p>2 + 2 = 22</p>
<script>
let para = document.querySelector('p')
para.innerText = `2 + 2 = 4`
</script>
</body>
</html>
Output:
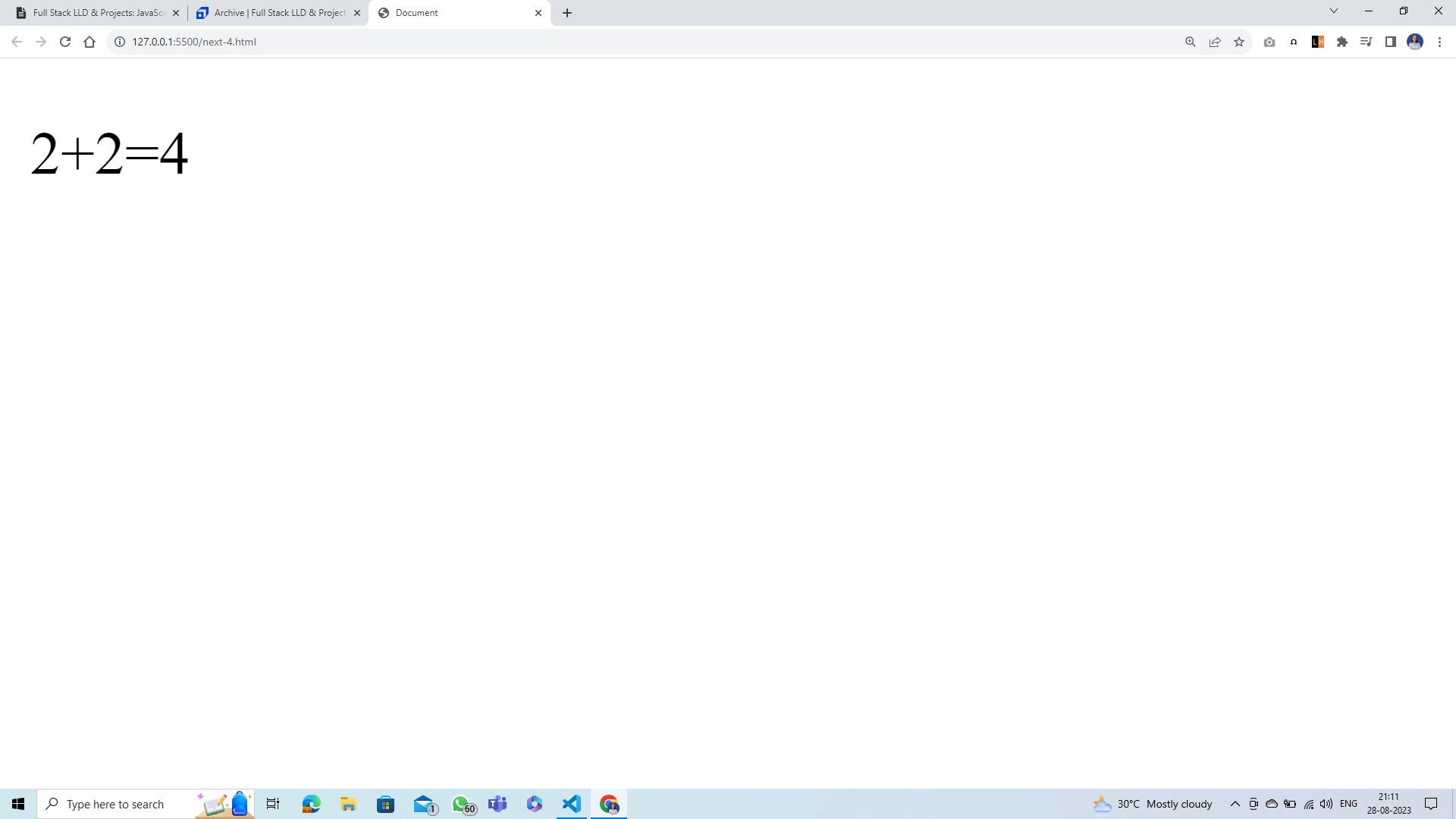
Question¶
Write a script which fetches the data-color attribute of the card and double clicking on them and attahces the fetched class to that card and also changes the data-color attribute to "used"
Solution¶
classList:
An element can have multiple classes attached to it and all of those classes are collected in a structure called classList.
Example:
<div class = "card test blue"> Our card </div>
The classList for this div will be - [card, test, blue]
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang = "en">
<head>
<meta charset = "UTF - 8" />
<meta http - equiv = "X - UA - Compatible" content = "IE = edge" />
<meta name = "viewport" content = "width = device - width, initial - scale = 1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
<style>
* {
box-sizing: border-box;
}
body {
display: flex;
flex-wrap: wrap;
justify-content: space-around;
padding-top: 5rem;
}
.blue {
background-color: blue;
box-shadow: 0px 0px 6px 5px;
}
.green {
background-color: green;
box-shadow: 0px 0px 6px 5px;
}
.red {
background-color: red;
box-shadow: 0px 0px 6px 5px;
}
.card {
border: 1px solid;
height: 10rem;
width: 10rem;
margin: 2rem;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class = "card" data-color = "blue"></div>
<div class = "card" data-color = "red"></div>
<div class = "card" data-color = "blue"></div>
<div class = "card" data-color = "red"></div>
<div class = "card" data-color = "red"></div>
<div class = "card" data-color = "blue"></div>
<div class = "card" data-color = "green"></div>
<div class = "card" data-color = "blue"></div>
<div class = "card" data-color = "green"></div>
<div class = "card" data-color = "blue"></div>
<script>
// Q Write a script which fetches the data-color attribute of the card on
//double clicking on them and attaches the fetched class to that card.
// Also changes the data-color attribute to "used"
let cardsNodeList = document.querySelectorAll('.card')
console.log(cardsNodeList)
for(let i = 0 ; i < cardsNodeList.length; i ++ ){
cardsNodeList[i].addEventListener('dblclick' , function(e){
console.log(e.currentTarget)
let classTobeAttached = e.currentTarget.getAttribute('data-color')
console.log(classTobeAttached)
e.currentTarget.classList.add(classTobeAttached)
e.currentTarget.setAttribute('data-color' , 'used')
})
}
</script>
</body>
Output: