HTML (Lists , Tables and Forms)
List¶
In HTML you can structure your content in a more readable and organized manner using lists. There are two types of lists such as
1. Ordered lists <ol> and,
2. Unordered lists <ul>
1. Ordered List¶
An ordered list is used to create a list of items that have a specific sequence or order. Each item in an ordered list is typically numbered, and the numbers usually increment in a sequential manner.
Each list item is defined with the <li> (list item) element, this will be more clear further in this article.
An ordered list can store content in two ways as well: 1. Non-alphabetically ordered 2. Alphabetically ordered
1.1 Ordered List¶
In the following code you can clearly see that the output generated is not structured alphabetically but listed in an orderely fashion
Pseudocode¶
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>List Examples</title>
</head>
<body>
<ol>
<li>Banana</li>
<li>Apple</li>
<li>Strawberry</li>
</ol>
</body>
</html>
Output:¶

1.2. Alphabetical Ordered List¶
In order to structure list in alphabetical fashion we can use type = "A" between <ol> tags
Pseudocode¶
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Alphabetical Ordered List</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Alphabetical Ordered List Example</h1>
<ol type = "A">
<li>Banana</li>
<li>Apple</li>
<li>Strawberry</li>
</ol>
</body>
</html>

2. Unordered List¶
Use <ul> tags for displaying a list with the help of symbols/shapes. In this case we're considering shapes.
Pseudocode¶
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>List Examples</title>
</head>
<body>
<ul type = "circle">
<li>Banana</li>
<li>Apple</li>
<li>Strawberry</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>
Output:¶

Tables in HTML¶
We gnerally tables are used to organize and display data in a structured format. Tables consist of rows and columns, where each cell is capable of storing data in form of text, images, links, or other HTML elements. But in-order to create tables in HTML one needs to be familiar with certain tags and attributes used such as:
<table: tag is used to define the beginning of a table 2.<td>: tag represents a table cell that contains data<tr>: tag represents a table row<th>: tag represents a table header and is used to label columns or provide additional information about the data<thead>: tag is used to group the header content in a table. It typically contains one or more<tr>elements with<th>elements inside.<tbody>: tag groups the body content of the table.<caption>: tag is used to provide a title or caption for the table. It is placed immediately after the opening<table>tag.- border attribute: is used to specify the thickness of the border around the table and its cells.
Pseudocode¶
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>List Examples</title>
</head>
<body>
<table border style = "text-align: center;">
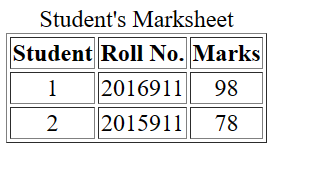
<caption>Student's Marksheet</caption>
<thead>
<th>Student</th>
<th>Roll No.</th>
<th>Marks</th>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td>1</td>
<td>2016911</td>
<td>98</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>2</td>
<td>2015911</td>
<td>78</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</body>
</html>
Output:¶
HTML Forms.¶
Just like any other forms are used to collect information, in context of HTML it collects user input on a web page. They allow users to enter data, make selections, and submit that information to a server for processing. HTML forms are created using a combination of form-related tags and input elements such as
<form>: tag defines the beginning of a form and contains the elements that make up the form, such as text fields, checkboxes, and buttons. It has several attributes, including action (specifying the URL to which the form data should be submitted) and method (specifying the HTTP request method, usually "GET" or "POST")-
<input>: The<input>tag is used to create various types of form input fields. The type attribute specifies the type of input field to be displayed. Common type values include: -
text: Creates a single-line text input.
- password: Creates a password input field (text is masked for security).
- checkbox: Creates a checkbox for binary (true/false) choices.
- radio: Creates a radio button for selecting one option from a group.
- submit: Creates a submit button to send the form data.
- button: Creates a generic button.
- file: Allows users to upload files.
-
date, email, number, and more: Various input types for specific data formats.
-
<label>: tag is used to associate a label with a form element, making the form more accessible and user-friendly. The for attribute of the<label>tag should match the id attribute of the form element it labels. <select>: tag creates a dropdown list, allowing users to select one option from a list of choices. It contains one or more<option>elements.<option>: tag defines an individual item in a<select>dropdown list. The value attribute specifies the value that will be sent to the server when the form is submitted.<button>: acts as an input element in HTML and is used for various purposes in a form including the submission of a form. We have different types of input elements as well such as checkboxes<input type = "checkbox">, radio buttons<input type = "radio">, and other input elements as needed to gather user input
Pseudocode¶
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>List Examples</title>
</head>
<body>
<form>
<label>Name</label>
<input type = "text">
<label>Email</label>
<input type = "email">
<label>Phone</label>
<input type = "number" maxlength = "10">
<label>age</label>
<input type = "number" min = "1" max = "100">
<label>Birthday</label>
<input type = "date" min = "1905 - 06 - 18" max = "2002 - 06 - 10">
<p>Food</p>
<label>Apple</label>
<input type = "checkbox">
<label>Orange</label>
<input type = "checkbox">
<label>Banana</label>
<input type = "checkbox">
<p>Gender</p>
<label>Male</label>
<input type = "radio">
<label>Female</label>
<input type = "radio">
<label for = "">Eyecolor</label>
<select>
<option>Blue</option>
<option>Black</option>
<option>Red</option>
</select>
</form>
</body>
</html>
Output:¶

Inline Elements¶
In HTML, elements are categorized as either block-level elements or inline elements. Inline elements do not create new block-level containers and flow within the content of surrounding elements. The <span>element is one such common inline element used for various purposes. It's a generic inline container that is often used to apply styles or attributes to a specific portion of text within a larger block of content.
Pseudocode¶
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Span in Inline Element Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Inline Element with Span</h1>
<p>This is a <strong><span style = "color: red;">red</span></strong> word.</p>
</body>
</html>
Output:¶

