Functions 1¶
Content of this lecture
Factorial
- Function Intro
- Sum()
- Quizzes
- Power function
- Ceil/floor
- Assignments
Factorial¶
Given an non negative integer N, the factorial of N is defined as follows:
Factorial of N = Product of all numbers from 1 to N .
| Factorial | Output |
| 4! | 4 3 2 * 1 = 24 |
| 3! | 3 2 1 = 6 |
Question¶
What is the factorial of 5?
Choices¶
- 5
- 15
- 24
- 120
Code:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int N = scanner.nextInt();
// multiply numbers from 1 to N
int ans = 1;
for(int i = 1;i <= N;i ++ ){
ans *= i;
}
S.O.Pln(ans);
}
Dry run for N = 5:

nCr¶
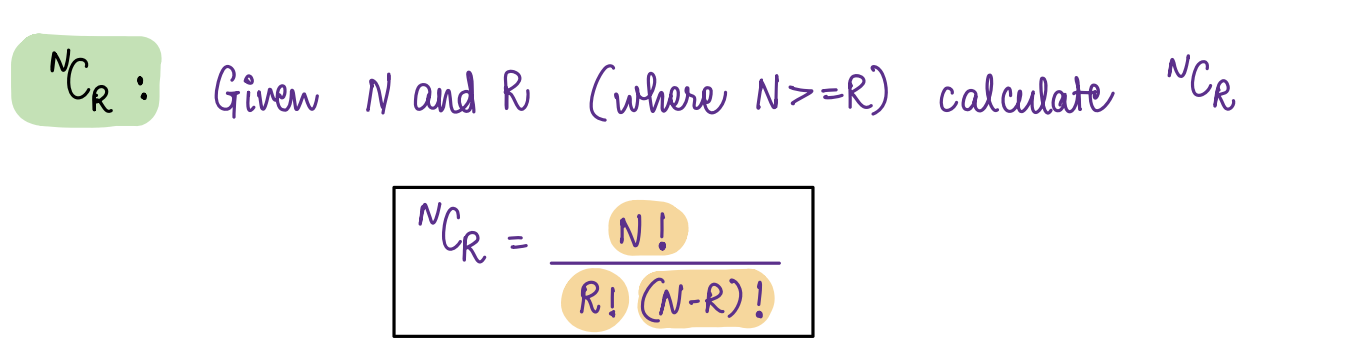

Dry Run for some values of N and R:
Question¶
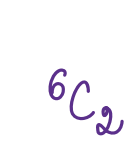
Calculate
Choices¶
- 10
- 15
- 20
- 25
Explanation:
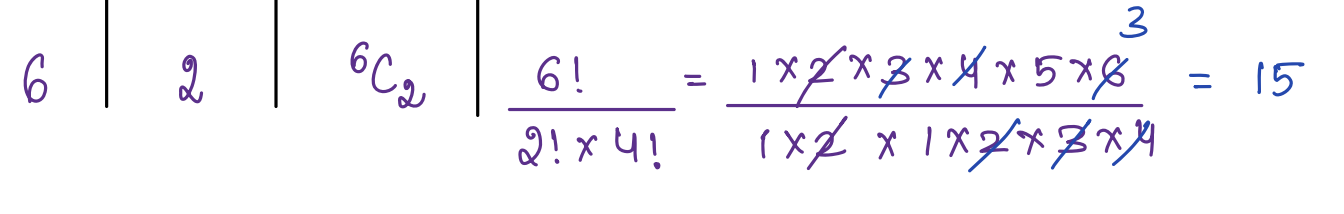
Small Question:
How many inputs are required to calculate NCR? -- Ans = 2
Code for calculating NCR:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int N = scanner.nextInt();
int R = scanner.nextInt();
int nf = 1;
// calculate N!
for(int i = 1;i <= N;i ++ ){
nf *= i;
}
// calculate R!
int rf = 1;
for(int i = 1;i <= R;i ++ ){
rf *= i;
}
// calculate (N-R)!
int nrf = 1;
for(int i = 1;i <= (N - R);i ++ ){
nrf *= i;
}
S.O.Pln(nf / (rf * nrf));
}
Functions¶
Give a real-life analogy. Suppose you need a screw-driver. First time you will buy that screw driver. From next time onwards you will use the same screw-driver.
Structure of a function:

Diagram/Flow Chart for Factorial function:

What is the need of a function?
To reuse the code, i.e., we dont need to write the same code again and again.
Syntax of a function:
output_type function_name(data_type input_name){
// function body
// i.e. the code to be executed
return ans; // the return keyword is used to return the output from the function
}
Writing the first function:
- You cannot write a function inside the main().
- Write it before public static void main() and inside the class Main{} .
- In Java, methods are also known as functions
Factorial function:
static int factorial(int a){
int ans = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= a; i ++ ){
ans = ans * i;
}
return ans;
}
Calling the factorial function from the main function:
public static void main(){
Scanner scn = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scn.nextInt();
System.out.println(factorial(5));
}
Output:
120
We cannot call non static functions from inside static functions. Since the main function is static, so to call the factorial function from inside the main function, we need to make the factorial function as static by writing the keyword static in front of it.
Write a function that returns sum of two numbers:
static int sum2(int a, int b){
int sum = a + b;
return sum;
}
Question: What will be the output of
sum2(10,5)-- Ans = 15
Code
public class MainClass {
public static int sum2(int a, int b){
int sum = a + b;
return sum;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.print(sum2(10,20));
}
}
Write a function that returns sum of three numbers:
static int sum3(int a, int b, int c){
return a + b + c;
}
Question¶
What is the output of the following code?
static int sum(int a, int b){
return a + b;
}
public static void main(String args[]){
sum(5,10);
}
Choices¶
- 15
- Error
- None
Explanation:
This is because we are not printing the answer in the code.
Question¶
What is the output of the following code?
static int sum(int a, int b){
return a + b;
}
public static void main(String args[]){
System.out.println(sum(5,10));
}
Choices¶
- Error
- 15
- No output
Write a function that returns the max of two numbers:
static void max_of_two(int a, int b){
int max = 0;
if(a > b){
max = a;
}
else{
max = b;
}
SOPln(max);
}
Calling this function:
System.out.println(max_of_two(5,9));
Output:
9
Code¶
public class MainClass {
public static void max_of_two(int a, int b){
int max = 0;
if(a > b){
max = a;
}
else{
max = b;
}
System.out.println(max);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
max_of_two(10,20);
}
}
Write a function that will print the product of two numbers:
Stress that the function needs to print the value rather than returning it.
static void product_of_two(int a, int b){
int product = a * b;
System.out.println(product);
}
The return type of the function changes from
inttovoid. void data type is used to denote that the function is not returning anything.
Calling this function:
product_of_two(5,9);
Output:
45
Question¶
What is the output of the following code?
static void sum(int a, int b){
return a + b;
}
public static void main(String args[]){
System.out.println(sum(5,10));
}
Choices¶
- Error
- 15
- No output
Explanation:
The return type of the function is wrong. You are returning an int, but the return type is set to void.
Question¶
What is the output of the following code?
static int extra(int a, int b){
return a + b + 10;
}
public static void main(String args[]){
int ans = extra(5,10);
System.out.println(ans);
}
Choices¶
- 15
- 25
- Error
- No Output
Question¶
What is the output of the following code?
static int square(int a){
return a * a;
}
public static void main(String args[]){
System.out.println(square( - 6 ));
}
Choices¶
- -36
- 36
- 6
- Error
Question¶
What is the output of the following code?
public static int square(int x){
return x * x;
}
public static int add(int x, int y){
return x + y;
}
public static void main(String args[]){
int n1 = square(3);
System.out.println(add(n1,square(9)));
}
Choices¶
- 81
- 9
- 90
- 115
Explanation:
n1 = square(3) = 9 square(9) = 81 add(9,81) = 90
Ceil Function¶
Given a number x, return smallest number >= x
- ceil(3.42) = 4
- ceil(5.67) = 6
Question
What is the value of ceil(6.5)?
Choices
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
Question¶
What is the value of ceil(6)
Choices
- 7
- 6
- 5
- 4
Question¶
What is the value of ceil(-3.4) ?
Choices¶
- -3
- -2
- -4
- -1
Question¶
What is the value of ceil(-4.5) ?
Choices¶
- -3
- -4
- -5
- -6
Floor Function¶
greatest integer that is less than or equal to a given number \(x\)
- floor(3.2) = 3
- floor(5.67) = 5
- floor(6.5) = 6
- floor(-3.4) = -4
- floor(-4.5) = -5
- floor(-7) = -7
Predefined functions¶
Functions which are already defined in the coding languages to make life simpler. Rules for using predefined functions.
- Check parameters
- Check return type
Examples:
Math.ceil()Math.floor()Math.power(a,b)
| Predefined function | Number of inputs | Return type |
| Math.ceil | 1 | double |
| Math.floor | 1 | double |
| Math.power | 2 | double |
Some more pre-defined functions:
Explain there workings with small examples
- Math.random()
- Math.abs()
