If Else 1¶
Agenda¶
- Contest Details
- Introduction to If
- If Examples
- If / Else examples
- If / Else if examples
Some abbreviations that will be used in this class: * System.out.print - SOP * System.out.println - SOPln
Success
There are a lot of quizzes in this session, please take some time to think about the solution on your own before reading further.....
The following questions serve as an introduction to the topic.
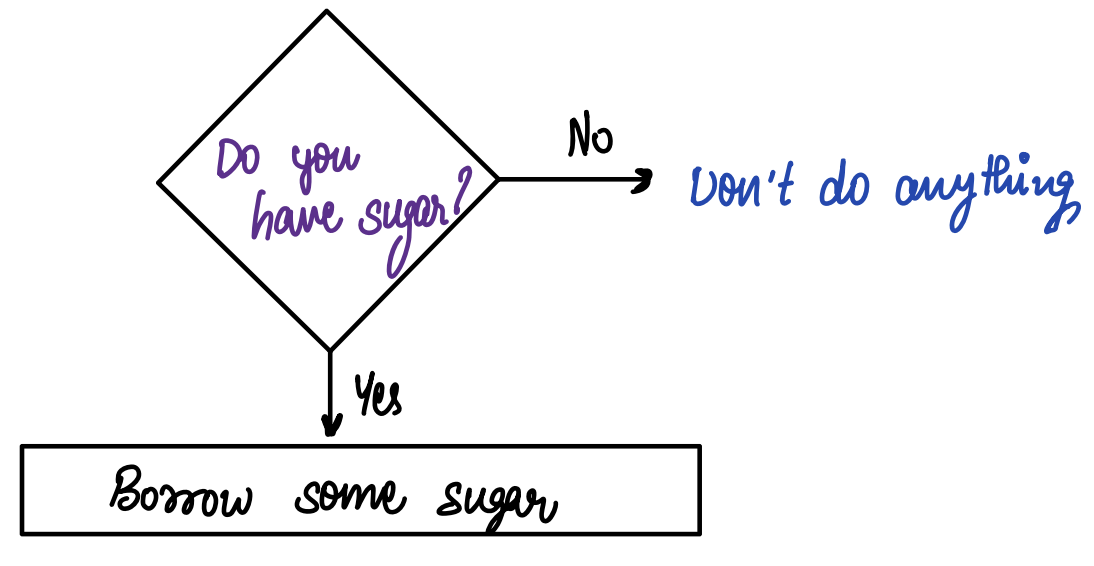
Q1. Sravan loves drinking tea. But he is out of sugar. Sravan is asking his neighbour Karthik?
A1. Look at the following diagram:
Q2. Eligibility criteria for voting.
Question¶
Correct logic to check whether you are eligible to vote.
Choices¶
- age > 180
- age != 17
- age == 18
- age >= 18
Explanation¶
Look at the following diagram.
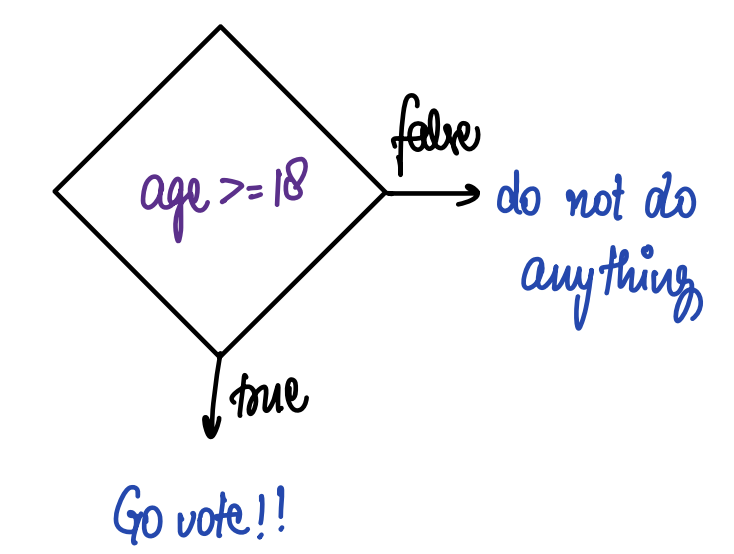
Note: Some students may ask why are we drawing diagrams. Just mention that it's easy to visualize.
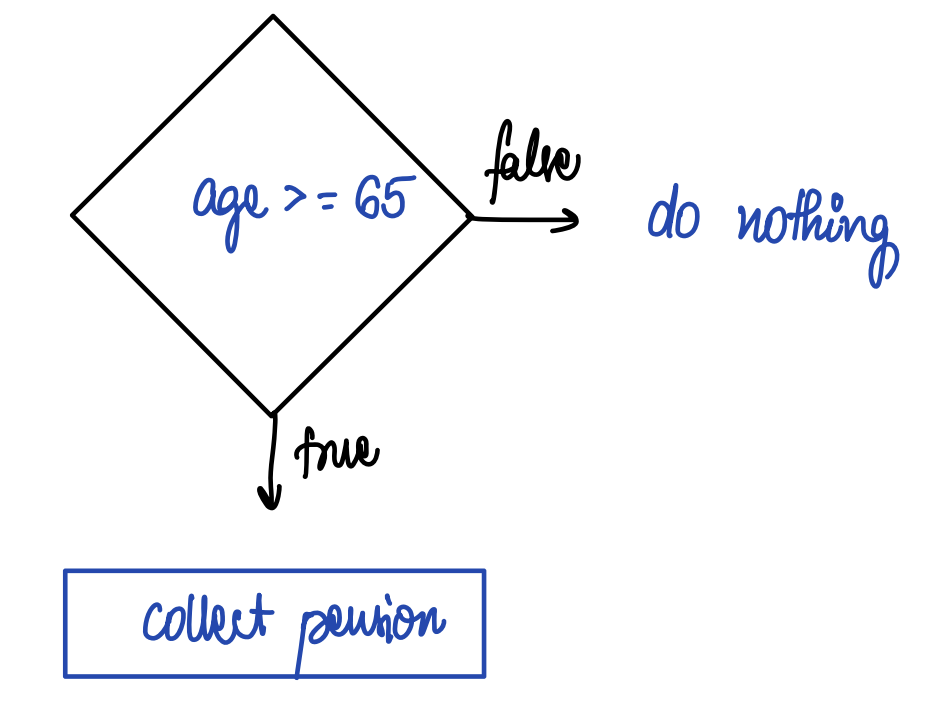
Q3. Check person is senior citizen or not.
If age >= 65, then they can collect pension.
A. Look at the following diagram.
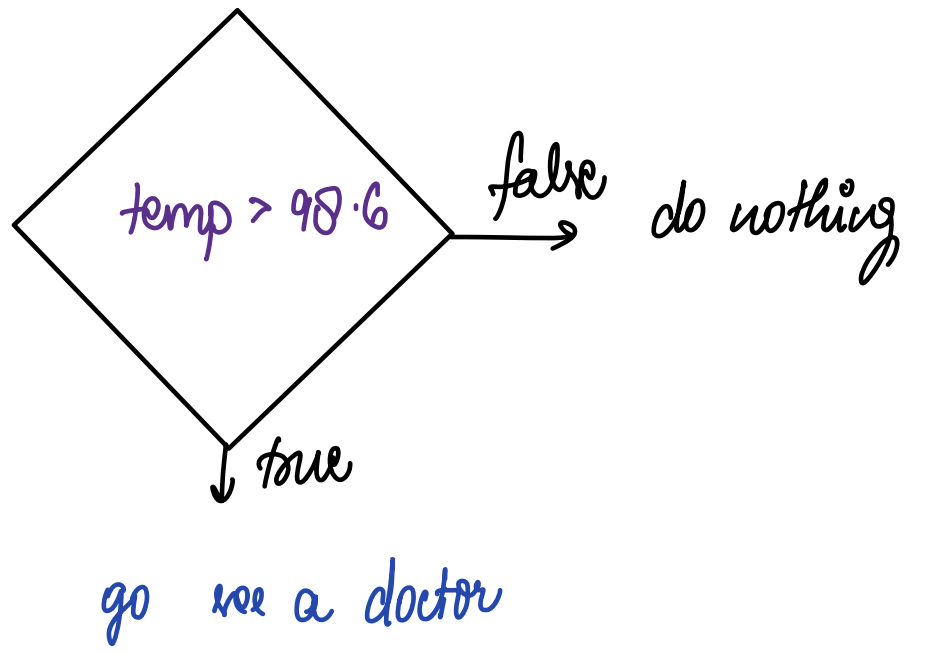
Q4. Check whether person is suffering from fever or not.
A.
Syntax of If¶
Idea: When we want to do something when condition is True.
Syntax:
if (condition) {
// Statements we want to be executed
// if above condition is True.
}
Imp point: condition should be a boolean expression. A boolean expression is an expression whose value can only be true or false.
Question¶
Which of the following is NOT a boolean expression?
Choices¶
- true
- 4 == 5
- 4 + 5
- 4 < 5
- false
- Read a number and If person is eligible, print "eligible to vote".
Run the below code on IDE and explain.
public static void main() {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int age = sc.nextInt();
if (age >= 18) {
System.out.print("Eligible to vote");
}
}
Question¶
Which data type should be used to store temperature of a patient?
Choices¶
- int
- double
- boolean
- String
Explanation¶
Explain with the following code:
psv main() {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
double temp = sc.nextDouble();
if (temp >= 98.6) {
System.out.print("Go to doctor!");
}
}
Question¶
Predict the output:
int a = 10;
if(a >= 10){
System.out.println("Yo");
}
System.out.println("Yo");
Choices¶
- YoYo
- Yo
Yo - Error
Question¶
Predict the output:
int a = 18,b = 16;
if(a >= 18){
System.out.println("a is major");
}
if(b >= 18){
System.out.println("b is major");
}
System.out.println("Blab");
Choices¶
- a is major
b is major
Blab - a is major
b is major - b is major
Blab - a is major
Blab
Question¶
Predict the output:
int a = 50,b = 50;
if(a >= 50){
System.out.println("a scored half");
a = a + 1;
}
if(b >= 50){
System.out.println("b scored half");
b = b + 1;
}
System.out.print(a + b);
Choices¶
- a scored half
101 - a scored half
b scored half
101 - b scored half
102 - a scored half
b scored half
102
Question¶
Predict the output:
if(5 > 4) {
System.out.println("First if");
}
if(10 >= 6) {
System.out.println("Second if");
}
Choices¶
- First if
Second if - First if
- Second if
- Error
Question¶
Predict the output:
if(5 > 10) {
System.out.println("First if");
}
if(10 >= 16) {
System.out.println("Second if");
}
System.out.println("Oops!! Nothing will get printed..");
Choices¶
- First if
- Second if
- First if
Second if
Oops!! Nothing will get printed.. - Oops!! Nothing will get printed..
Question¶
Predict the output:
if(true) {
System.out.println("1");
}
if(true) {
System.out.println("2");
}
if(true) {
System.out.println("3");
}
Choices¶
- 1
2
3 - 1
- 2
- Error
Check if someone has normal temperature: Normal temp = [98.0 to 98.9]
Ex:
- 98.1 -> Normal temperature
- 99 -> Not normal temperature
- 97.9 -> Not normal temperature
Explain -> _______98.0________98.9_______
- 96.8 -> Not normal temperature
- 98.5 -> Normal temperature
Q. What is the Java code for this?
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
double temp = sc.nextDouble();
if (temp >= 98.0 && temp >= 98.9) {
System.out.println("Normal temperature");
}
Note: Logical operators are used to combine conditions.
Now, we want to do something or the other accordingly when the condition is true or false.
Syntax of If / Else¶
if (condition) {
// Statements to run, when above condition True
}
else {
// Statements to run, when above condition False
}
Flow 1¶
if (condition) {
Statement 1
}else{
Statement 2
}
Q2: Condition False: Statement 2
Flow 2¶
Statement 1
if (condition) {
Statement 2
}else{
Statement 3
}
Statement 4
A. Condition True: Statement 1, 2 4
Condition False: Statement 1, 3, 4
Example 1¶
Read age of a person, check if person is at retirement age, or still have few years left to work. Retirement age is 65.
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int age = sc.nextInt();
if (age > 65) {
System.out.println("Retired");
}else{
System.out.println("Few more years of service.");
}
Question¶
Predict the output:
if(9 > 5){
System.out.println("If block");
}
else{
System.out.println("Else block");
}
Choices¶
- If block
- If block
Else block - Error
Question¶
Predict the output:
if(false){
System.out.println("Line 1");
} else {
System.out.println("Line 2");
}
Choices¶
- Line 1
- Line 2
- Line 1
Line 2 - Error
Modulus Operator¶
Modulus operator (%) -> Gives remainder
System.out.println(17 % 4) -> Remainder = 1
System.out.println(24 % 2) -> Remainder = 0
System.out.println(97 % 2) -> Remainder = 1
System.out.println(82 % 2) -> Remainder = 0
Explain even and odd numbers.
Even numbers: Numbers which are divisible by 2. Eg: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12.. When we divide the number with 2, remainder = 0 Odd numbers: Numbers which are not divisible 2. Eg: 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11.. When we divide the number with 2, remainder = 1
Example 1¶
Read a number and check if number is odd or even.
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int a = sc.nextInt();
if (a % 2 == 0) {
System.out.println("Number is even");
}else{
System.out.println("Number is odd");
}
Example 2¶
Check if a number is divisible by 5.
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int a = sc.nextInt();
if (a % 5 == 0) {
System.out.println("Number is divisible by 5");
}else{
System.out.println("Number is not divisible by 5");
}
Example 3¶
Check if a number is divisible by 2 or 3.
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int a = sc.nextInt();
if (a % 2 == 0 || a % 3 == 0) {
System.out.println("Number is divisible by 2 or 3");
}else{
System.out.println("Number is not divisible by 2 and 3 both");
}
Question¶
Can we have if without an else block?
Choices¶
- Yup!!
- Nope!!
- Don't know
Question¶
Can we have else without an if block?
Choices¶
- Yup!!
- Nooo!!
- Maybe
Read 2 numbers and print max of 2 numbers.
Examples:
a = 5 , b = 10
Max of a and b = 10
a = 15 , b = 10
Max of a and b = 15
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int a = sc.nextInt();
int b = sc.nextInt();
if (a > b) {
System.out.println(a);
}else{
System.out.println(b);
}
Question¶
Predict the output:
For input: 45 45
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int a = sc.nextInt();
int b = sc.nextInt();
if(a > b){
System.out.print(a);
}
else{
System.out.print(b);
}
Choices¶
- Error
- 45
45 - 45
Categorize Number¶
Given an integer n0, categorize it into positive, negative or zero.
Category:
n = 10: n > 0: print "positive number" n = -27: n < 0: print "negative number" n = 0: n == 0: print "zero"
Give some more examples.
Idea:
public static void main() {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int a = scn.nextInt();
if (a > 0) {
System.out.println("positive number");
}
if (a < 0) {
System.out.println("negative number");
}
if (a == 0) {
System.out.println("zero");
}
}
Q. Is the above logic correct?
A. Yes
Dry run the above code for some examples.
Explain the problem in the above approach. It's the wastage of comparisions.
Syntax:
if (cond_1) {
// Statements if cond_1 is true
}
else if (cond_2) {
// Statements if cond_1 is false and cond_2 is true
}else{
// Statements if cond_1 is false and cond_2 is false
}
Note: "else" is optional.
Flow¶
Statement 1
if (cond_1) {
Statement 2
}
else if (cond_2) {
Statement 3
}
else{
Statement 4
}
Statement 5
Explain the above flow according to below table.
| Conditions which are true | Statements executed |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1 2 5 |
| 2 | 1 3 5 |
| All false | 1 4 5 |
| 1 2 | 1 2 4 |
Note: If a condition is true, it will execute and will come out of If/Else block and execute remaining statements.
Note: We can have multiple "else if()" blocks.
Back to Categorize number problem,
public static void main() {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int a = scn.nextInt();
if (a > 0) {
System.out.println("positive number");
}
else if (a < 0) {
System.out.println("negative number");
}
else{
System.out.println("zero");
}
}
Example¶
Is the below code correct or not?
int a = 10;
else if (a > 5) {
System.out.println("Number is more than 5");
}
else{
System.out.println("Number is not more than 5");
}
We cannot write any else if() without if() block.
Question¶
What will be the output of the following:
if(true) {
System.out.println("1");
}
else if(true) {
System.out.println("2");
}
else if(true) {
System.out.println("3");
}
Choices¶
- 1
- 1
2
3 - 2
- 3
Question¶
Can there be an else if block without a if block
Choices¶
- Yes
- No
- Maybe
Question¶
Can there be an else if block without an else block
Choices¶
- Yes
- No
- Maybe
