If Else : 2¶
Content¶
- Revision Quizzes
- Categorize triangle
- Max of three
- Fizz Buzz
- Nested If Else
- Categorize into positive, negative and zero
Success
There are a lot of quizzes in this session, please take some time to think about the solution on your own before reading further.....
Recap¶
Some abbreviations that will be used in this class:
- System.out.print - SOP
- System.out.println - SOPln
Question¶
What will be the output of the following code?
int a = 10,b = 10;
if(a >= 10 && b >= 10){
System.out.print(a+b);
}
Choices¶
- 10
- 20
- 30
- None
Question¶
What will be the output of the following code?
int a = 10;
int b = 10;
if( ++ a >= 12 && ++ b >= 12 ){
System.out.println("Hello");
}
System.out.println(a + b);
Choices¶
- Hello
10 - 22
- 21
- None
Question¶
What will be the output of the following code?
int a = 10;
int b = 10;
if( ++ a >= 11 || ++ b >= 12 ){
System.out.println("Hello");
}
System.out.println(a + b)
Choices¶
- 20
- 22
- Hello
21 - None
Question¶
What will be the output of the following code?
int a = 10;
int b = 10;
if( ++ a >= 12 || ++ b >= 12 ){
System.out.println("Hello");
}
System.out.println(a + b);
Choices¶
- 20
- 21
- 22
- None
Question¶
What will be the output of the following code?
int N = 5;
if(N > 2)
System.out.println("Yayay");
else
System.out.println("Blahblah!!");
Choices¶
- Yayay
- Blahblah!!
Question¶
What will be the output of the following code?
int N = 5;
if(N > 2)
System.out.println("Yayay");
System.out.println("Hmmmm");
else
System.out.println("Blahblah!!");
System.out.println("Blahblah!!");
Choices¶
- Error :(
- No Error, this code rocks! :D
- Yayay Hmmmm
- Blahblah!!
Question¶
What will be the output of the following code?
int marks = 80;
if(marks > 70) {
System.out.print("Distinction ");
System.out.print("Congrats ");
} else if(marks > 35) {
System.out.print("Pass ");
} else
System.out.print("Fail ");
System.out.print("Good luck");
Choices¶
- Distinction Congrats Good luck
- Good luck
- Error
- Distinction Congrats
Categorize Triangles¶
Categorize triangle on the basis of the length of the sides
Equilateral: When the length of the all the sides are equal.
Isosceles: When the length of any two sides are equal.
Scalene: When the length of all sides are different.
Let a, b, c be the length of the three sides of a triangle. Given in each case they take some values, tell the category of the triangle. It is the given that the input values for a, b, c are positive integer values.
a = 20, b = 20, c = 20
-- Output = Equilaterial
a = 7, b = 12, c = 9
-- Output = Scalene
a = 5, b = 13, c = 5
-- Output = Isosceles
a = 12, b = 7, c = 7
-- Output = Isosceles
The equivalent code for implementing the above logic is as follows:
if(a == b && b == c){
SOPln("Equilateral");
}
else if(a == b || b == c || a == c){
SOPln("Isosceles");
}
else{
SOPln("Scalene");
}
Max of three¶
Ques: Given three numbers, print the maximum among them.

Note that a, b, c can take any integer values.
Stress on the point that a, b, c can also take equal values. The three test case demonstrates this point.
For example,
- a = 7, b = 20, c = 50 ==> max = 50
- a = 10, b = 9, c = 10 ==> max = 10
- a = 3, b = 3, c = 3 ==> max = 3
The equivalent code for implementing the above logic is as follows:
if(a >= b && a >= c){
SOPln("a");
}
else if(b >= c){
SOPln("b");
}
else{
SOPln("c");
}
Fizz-Buzz¶
Ques: Given a number,
- print "Fizz" if the number is divisible by 3.
- print "Buzz" if the number is divisible by 5.
- print "Fizz-Buzz" if the number is divisble by both 3 and 5.
For example,
- n = 39, O/p = Fizz
- n = 25, O/p = Buzz
- n = 15, O/p = Fizz-Buzz
- n = 13, O/p =
No output
**How to implement this? **
The following code shows a wrong implementation of the above logic:
if(n % 3 == 0){
SOPln("Fizz");
}
else if(n % 5 == 0){
SOPln("Buzz");
}
else{
SOPln("Fizz-Buzz");
}
The above code prints "Fizz-Buzz" for n = 11, but this is wrong as n is neither divisble by 3 nor 5. So there should have no output for this number.
Another wrong implementation is as follows:
if(n % 3 == 0){
SOPln("Fizz");
}
else if(n % 5 == 0){
SOPln("Buzz");
}
else if(n % 3 == 0 && n % 5 == 0){
SOPln("Fizz-Buzz");
}
The above code prints "Fizz" for n = 15, but this is wrong as n is divisble by 3 and 5 both. So the correct output should be "Fizz-Buzz".
So finally, the correct implementation of this logic is as follows:
if(n % 3 == 0 && n % 5 == 0){
SOPln("Fizz-Buzz");
}
else if(n % 3 == 0){
SOPln("Fizz");
}
else if(n % 5 == 0){
SOPln("Buzz");
}
Nested If Else¶
Syntax:
Statement 1
if(cond1){
Statement 2
if(cond2){
Statement 3
}
else{
Statement 4
}
Statement 5
}
else{
Statement 6
if(cond3){
Statement 7
}
else{
Statement 8
}
Statement 9
}
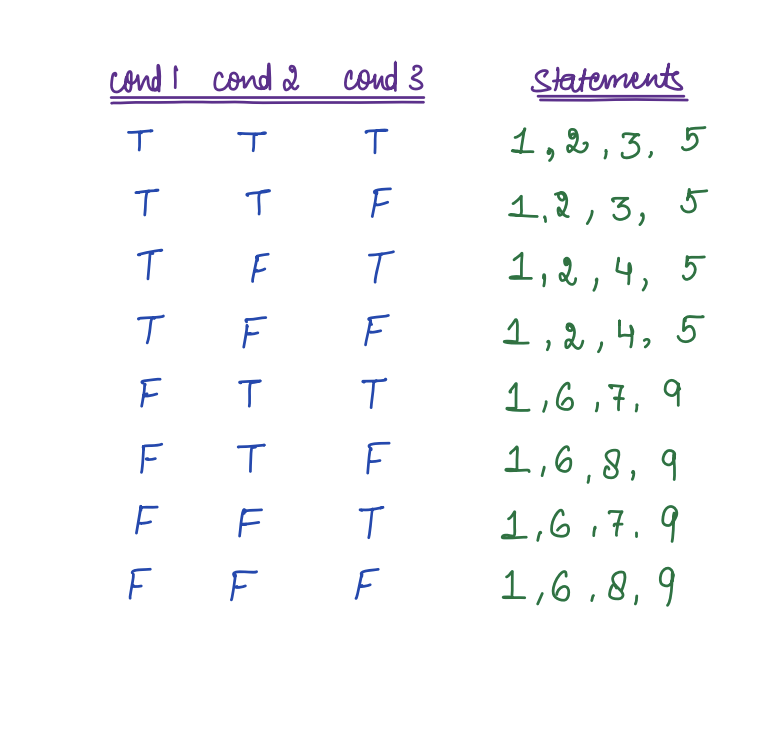
Question¶
Predict the output of the following code?
int a = 10, b = 15;
if(a > 8) {
if(a < b || b == 9) {
System.out.println("Hi");
}
else {
System.out.println("Bye");
}
}
else {
System.out.println("Good Bye");
}
Choices¶
- Hi
- Bye
- Good Bye
- None
Question¶
Predict the output of the following code?
int a = 10, b = 15;
if(a > 8) {
if(a == b || b < a) {
System.out.println("Hi");
}
else {
System.out.println("Bye");
}
}
else {
System.out.println("Got it");
}
Choices¶
- Hi
- Bye
- Got it
- None
Question¶
Predict the output of the following code?
if(true) {
if(true) {
if(false) {
System.out.println("Hey there");
}
}
else {
System.out.println("Hello");
}
}
else {
System.out.println(10 / 0);
}
Choices¶
- Hey there
- Hello
- No output
- Error
Explanation:
We are not getting an error because the inner if statement with the false condition is not executed due to the if condition being false. Therefore, the else block following it is also not executed. The program simply moves on to the next line, which is outside of any control structures and executes the statement System.out.println("Hello"); as expected.
The else block following the outer if statement is also not executed since the condition of the outer if statement is true, and the program again moves to the next line and executes the statement System.out.println("Hello");
Categorise the number¶
Ques: Given a number, classify it as follows:
- +ve and even
- +ve and odd
- -ve and even
- -ve and odd
Example :¶
Input:
public static void main(){
Scanner scn = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = scn.nextInt();
if(num > 0){
if(num % 2 == 0){
SOPln("Positive and even");
}
else{
SOPln("Positive and odd");
}
}
else{
if(num % 2 == 0){
SOPln("Negative and even");
}
else{
SOPln("Negative and odd");
}
}
}
Scope of a Variable¶
It defines the point till where you can use the variable. You can only use a variable till the closing bracket of the block in which it was created.
Example 1:
public static void main(){
int x;
x = 5;
int y;
y = 20
}
Scope of variable x: Line 4 to 10
Scope of variable y: Line 7 to 10
Example 2:
public static void main(){
int x = 10;
if(x == 10){
int y = 5;
SOP(y);
}
int z = 9;
}
Scope of variable x: Line 3 to 10
Scope of variable y: Line 5 to 7
Scope of variable z: Line 8 to 10
Example 3:
public static void main(){
int a = 10;
{
a = 20;
}
SOP(a);
}
Scope of variable a: Line 2 to 8
Also the code will print 20 as the changes done in the variable values are not restricted to that block in which the change is done. But the life of the variable is restricted to the block in which it was created.
Example 4:
public static void main(){
int x = 10;
{
int y = 20;
SOP(x + " " + y);
}
{
SOP(x + " " + y);
// This line will give error as y is not present in its scope
}
}
Example 5: Redefining variable error
public static void main(){
int a = 90;
{
int a = 7;
// This line will give error as variable a is already defined in this scope
SOPln(a);
}
}
Question¶
Predict the output of the following code:
public static void main(String args[]) {
int x = 10;
{
int y = 20;
System.out.println(x + " " + y);
}
{
System.out.println(x + " " + y);
}
System.out.println(x + " " + y);
}
Choices¶
- Error
- 10 20
10 20
10 20 - 10 20 10 20 10 20
Question¶
Predict the output of the following code:
public static void main(){
int x = 10, y = 20;
{
SOP(x + " " + y);
}
{
x = 15;
SOPln(x + " " + y);
}
SOPln(x + " " + y);
}
Choices¶
- 10 20
15 20
10 20 - Error
- 10 20
15 20
15 20 - inky pinky ponky
Question¶
Predict the output of the following code:
if(true){
int x = 10;
SOPln("Value of x is " + x);
x ++ ;
}
SOPln("Value of x is " + x);
Choices¶
- Value of x is 10
Value of x is 11 - Value of x is 10
Value of x is 0 - Value of x is 10
Value of x is 10 - Error
Question¶
Predict the output of the following code:
int a = 0;
{
int b = 10;
SOPln("b = " + b);
int c = a + b;
SOPln("c = " + c);
}
a = c + b;
SOPln("a = " + a);
Choices¶
- a = 20
b = 10
c = 10 - b = 10
c = 10
a = 20 - Error
Explanation: Error b and c are out of the scope
Question¶
Predict the output of the following code:
int a = 10, b = 5;
if(true){
int c = a * b;
}
SOPln(c);
Choices¶
- 50
- Error
- Need Coffee!!
Explanation: Error the variable c is out of the scope
