1D Arrays 1¶
Agenda¶
- Introduction to Arrays
- Reading Input
- Indexing and Properties
- Sum of all elements
- Frequency of k in array
- Max of all elements
Example¶
Let's say we need to read four inputs for our programme. We can use the below approach.
Code¶
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a, b, c, d;
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
a = scanner.nextInt();
b = scanner.nextInt();
c = scanner.nextInt();
d = scanner.nextInt();
}
Code¶
public static void main(){
for(int i = 1; i <= 4;i ++ ){
int a = sc.nextInt();
}
}
a in each iteration due this a would be set to the last input value provided.
Concept of Arrays¶
- In above example what is instead of four there are hundreds of value to store. It would be manually infeasible to declare and set hundreds of variables.
- Therefore to overcome above problem we use arrays
Array¶
It is a data structure that can hold fixed number of values of same data type.
Syntax¶
datatype name[] = new datatype[size]
// example
float f[] = new float[10]
int arr[] = new int[10]
// Various ways
datatype[] name = new datatype[size]
datatype []name = new datatype[size]
Question¶
Correct way to create an Array containing 5 int values in Java?
Choices¶
- int[] ar = new int[5]
- int[] ar = new int[4]
- int[] ar = int new[5]
Explanation¶
Since size is 5 and datatype is int using above provided syntax rules: int[] ar = new int[5]
Indexing and Properties¶
- Indexing in array starts from 0.
| index | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
- Accessing an element at ith index in an array can be done as follows:-
nameOfArray[i]

Question¶
int[] ar = new int[6];
How can we access last position element ?
Choices¶
- ar[5]
- ar[6]
- ar[4]
- ar[7]
Explanation¶
Since size is 6 indexing would be like :-
| index | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| arr | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
last element would be at index 5
Question¶
int[] ar = new int[10];
How can we access last position element ?
Choices¶
- ar[9]
- ar[10]
- ar[7]
- ar[8]
Explanation¶
Since size is 10 indexing would be like :-
| index | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ar | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
last element would be at index 9
Question¶
Say int[] ar = new int[N] How to access first element and last element ?
Choices¶
- ar[0] ar[N-1]
- ar[0] ar[N]
- ar[1] ar[N]
Explanation¶
By observing previous questions we can generalize the idea that :-
* Last element in array 'arr' of size 'N' is accessed as arr[N-1].
* First element in array 'arr' of size 'N' is accessed as arr[0].
Question¶
What is the Output of
public static void main(String args[]) {
int[] arr = new int[10];
int n = arr.length;
System.out.println(n);
}
Choices¶
- 10
- 9
- 8
- By default values in an array of type
intare intialized with '0'
Question¶
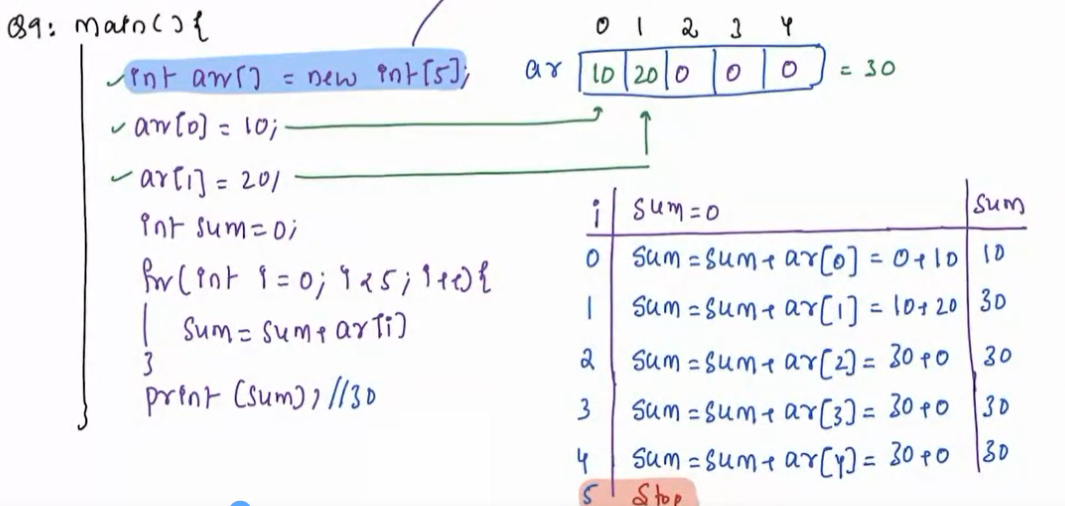
What will be the output?
public static void main(String args[]) {
int[] arr = new int[5];
arr[0] = 10;
arr[1] = 20;
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 5;i ++ ) {
sum += arr[i];
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
Choices¶
- 30
- error
- 20
- 43
Explanation¶
By observing previous questions we can generalize the idea that :-
* Last element in array 'arr' of size 'N' is accessed as arr[N-1].
* First element in array 'arr' of size 'N' is accessed as arr[0].
Solution¶
Question¶
public static void main(String args[]) {
int[] arr = new int[5];
System.out.println(arr[0]);
}
Choices¶
- 0
- error
- random number
- 43
Question¶
public static void main(String args[]) {
int[] ar = new int[3];
ar[0] = 10;
ar[1] = 20;
ar[2] = 30;
System.out.print(ar[0] + ar[3]);
}
Choices¶
- error
- 0
- 40
- 60
Question¶
public static void main(String args[]) {
int[] ar = new int[3];
ar[0] = 10;
ar[1] = 20;
ar[2] = 30;
System.out.print(ar[0] + ar[2]);
}
Choices¶
- 40
- 0
- error
- 60
Question¶
public static void main(String args[]) {
int[] ar = new int[3];
ar[0] = 10;
ar[1] = 20;
ar[2] = 30;
System.out.print(ar[-1] + ar[3]);
}
Choices¶
- error
- 0
- 40
- 60
We can reassign an array to replace the previous value it was referencing.
Code:
public static void main(){
int[] ar = new int[6];
ar= new int[2];
S.O.Pln(arr.length);
}
2
- We can directly store elements into an array
Code:
int ar[] = {10,20,30};
Creating and Reading an array¶
Create an array of size 4 and print sum of all it's element :-¶
- Let's create an array of size 4 and take input.
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int[] arr = new int[4];
arr[0] = sc.nextInt();
arr[1] = sc.nextInt();
arr[2] = sc.nextInt();
arr[3] = sc.nextInt();
}
- In above approach we have to take input for each index manually which is not a good idea.
- So How can we take inputs efficiently ?
- Solution :- We use a loop.
- But how to apply loop to take array input ?
- On observing above approach we will find that only index changes each time we take an input.
- In each iteration we change the index number.
- We iterate starting from 0 till last index i.e. array size -1.
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int[] arr = new int[4];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++ ) {
arr[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
Passing Array to Functions¶
Create a Function Which Takes arr[] as A Parameter and Print the Array¶
- We need to declare a function which takes array as parameter to function.
- It can be done like :-
Function nameOfFunction(dataType anyName[]){} - '
[]' are important for distinguishing array type parameter from other variable type parameters. - How can we access the length of array from function ?
- We use
array.lengthfor this purpose. - We can pass array parameter to function call like:
functionName(arrayName) - We only need to pass array name.
static void printArray(int[] ar) {
int n = ar.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) {
System.out.print(ar[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int[] arr = new int[4];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++ ) {
arr[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
printArray(arr);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = new int[4]; // creates an array of size 4
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++ ) {
arr[i] = scanner.nextInt();
}
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++ ) {
sum += arr[i]; // add element at ith index to sum variable
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
Problem 1¶
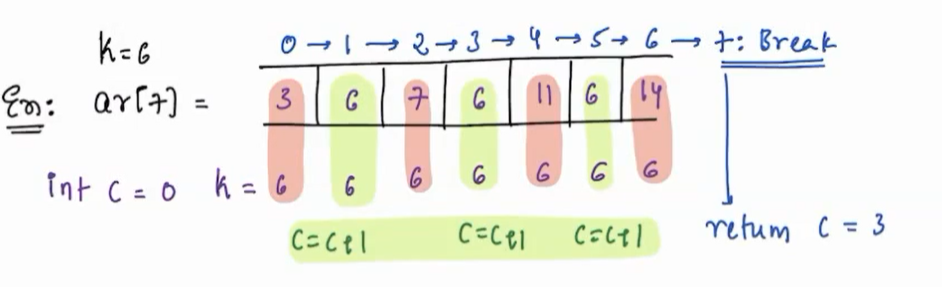
Given an array and k. Write a function to return the frequency of k in array?
Testcase¶
arr[7] = [3,6,7,6,11,6,14]
k = 6
solution¶
ans = 4
Warning
Please take some time to think about the solution approach on your own before reading further.....
Approach¶
- We need to create a function and pass array and k as parameters to the function.
- Inside the function :-
- Maintain a count variable which is intialised to 0.
- Iterate over the array:-
- If element at current index equals k increament count by 1.
- Return count.
Trace¶
Solution¶
Pseudeocode¶
static int frequencyK(int[] ar, int k) {
int n = ar.length;
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) {
if (ar[i] == k) {
count ++ ;
}
}
return count;
}
Problem 2¶
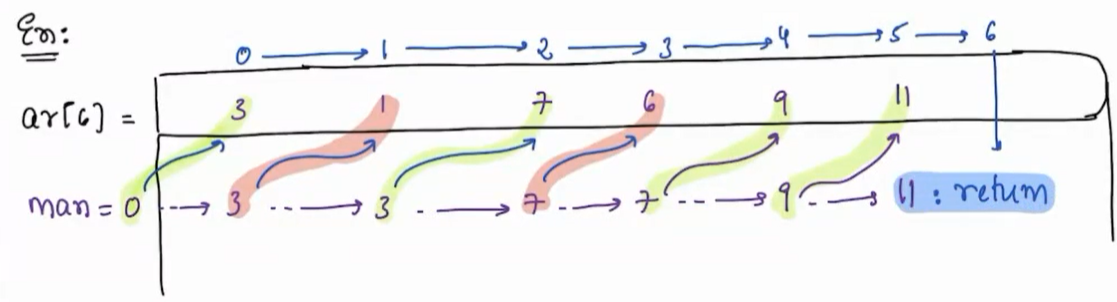
Given an array . Write a function to return the maximum element present in array?
Testcase 1¶
arr[6] = [3,1,7,6,9,11]
solution¶
ans = 11
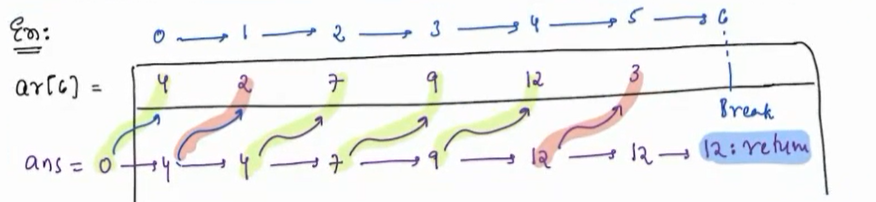
Testcase 2¶
arr[6] = [4,2,7,9,12,3]
solution¶
ans = 12
Warning
Please take some time to think about the solution approach on your own before reading further.....
Approach 1¶
- We need to create a function and pass array as parameters to the function.
- Inside the function :-
- Maintain a max variable which is intialised to 0.
- Iterate over the array:-
- If element at current index is greater than max then set max to current element.
- Return max.
Trace 1¶
Trace 2¶
Code¶
static int maxElement(int array[]) {
int n = array.length;
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
// Initialize max with the smallest possible integer value
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) {
if (array[i] > max) {
max = array[i];
}
}
return max;
}
There is a flaw in above code. Let's see it with help of an testcase.
Testcase 3¶
arr[4] = [ - 8, - 4, - 3, - 5]
solution¶
ans = - 3
- Let' apply approach 1 to testcase 3
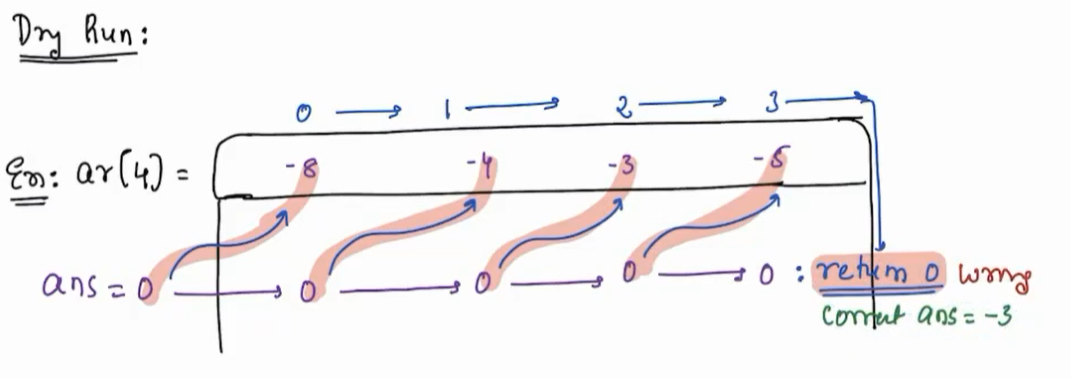
- In trace we get the answer as 0 whereas the correact answer is -3. Why ?
Issue¶
Since max/ans variable is intialised to 0 which is already greater than all elements in array therefore max/ans is not updated.
Question¶
For taking sum of N numbers we initialise our sum variable with =
Choices¶
- 0
- 9
- 1
title: Quiz 13
description:
duration: 30
Question¶
For taking product of N numbers we initialise our product variable with =
Choices¶
- 0
- 9
- 1
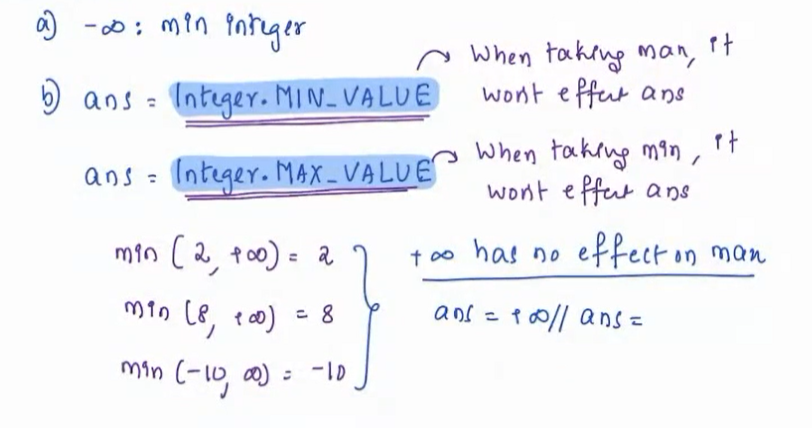
- Based upon observations from above questions we need to intialize max/ans in such a manner that it won't affect the answer.
- We intialize the ans/max variable to - ∞(negative infinity) so that it does not affect the final answer.
- We do this by Integer.MIN_VALUE
Code¶
static int maxElement(int[] ar) {
int n = ar.length;
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) {
if (ar[i] > max) {
max = ar[i];
}
}
return max;
}
