1D Array - 2¶
Agenda¶
- Revision
- Implement Function
- Increasing Order [increasing and non-decreasing]
- Drawbacks of Array
- Right shift of the array
- Array List introduction
- Functions [add, get, set, remove, size, sort]
- ArrayList functions via code
- Write a function which takes arrayList as input and update all values by 1
- Return an arraylist with all even numbers
Revision¶
Let us revise what we discussed in the last class wit the help of quizzes.
Question¶
What will be output for this program ?
int[] myArray = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
System.out.println(myArray[2]);
Choices¶
- 2
- 3
- 4
Question¶
What will be output for this program ?
int[] myArray = new int[3];
System.out.println(myArray[1]);
Choices¶
- 0
- Null
- Error
Question¶
What will be output for this program ?
int[] myArray = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
System.out.println(myArray.length);
Choices¶
- 4
- 0
- 5
Question¶
What will be output for this program ?
int[] myArray = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
myArray[2] = 6;
System.out.println(myArray[2]);
Choices¶
- 6
- 3
- 3
- Error
Return arr[] Syntax¶
Implement Function¶
Given N, create an array of size N, which should contain all elements in increasing order from 1 to N.
Example¶
N = 3
arr[3] = { 1, 2, 3 }
N = 5
arr[5] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 }
Question¶
Given N = 6, create an array of size N containing all elements in increasing order from 1 to N.
Choices¶
- 0 1 2 3 4 5 6
- 1 2 3 4 5 6
- 6 5 4 3 2 1
Implement Function Code¶
Pseudocode¶
static int[] num(int N){
int arr = new int[N];
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++){
arr[i] = i + 1;
}
return arr;
}
Increasing Order¶
Numbers arranged from smallest to largest. Note: If elements are equal then no issues
Scritly Increasing Order¶
Arrangement of numbers such that the next number is always greater than the previous number.
Question¶
Check whether the given numbers are in increasing order?
3, 4, 4, 4, 4, 5, 5, 7, 9, 18, 18, 26
Choices¶
- yes
- no
- maybe
Question¶
Check whether the given numbers are in increasing order?
-1, -2, -3, -4, -5
Choices¶
- Yes
- No
- Maybe
Question¶
Check whether the given numbers are in strictly increasing order?
3, 9, 16, 24, 29, 29, 34, 50
Choices¶
- Yes
- No
- Maybe
Checking Strictly Increasing Array¶
Given an integer N, create an array of size N containing elements in increasing order from 1 to N. Check if the created array is strictly increasing (each element is greater than the previous element).
Example¶
For N = 5, the array arr will be {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}, and it is strictly increasing.
For N = 5, the array arr will be {1, 2, 2, 4, 5}, and it is not strictly increasing.
Question¶
Check whether the given numbers are in strictly increasing order?
21, 39, 46, 97, 105
Choices¶
- Yes
- No
- Maybe
If Array Is Strictly Increasing Code¶
Note to instructor: Explain logic of implementing this in code format here
Pseudocode¶
static boolean isStrictlyIncreasing(int N) {
int[] arr = new int[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
arr[i] = i + 1;
}
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
if (arr[i] < arr[i - 1]) {
return false; // Array is not strictly increasing
}
}
return true; // Array is strictly increasing
}
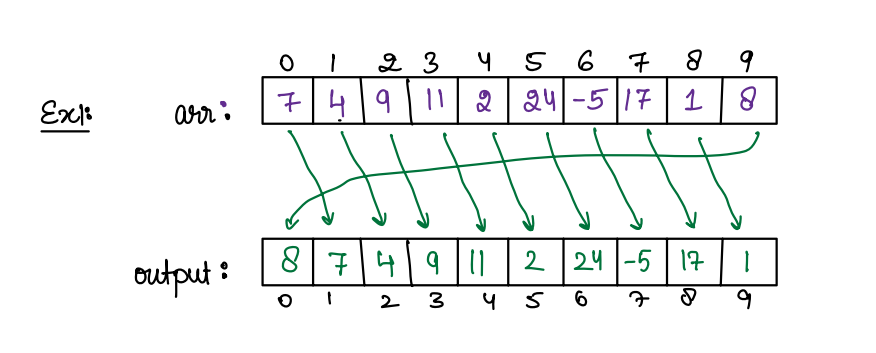
Right Shift of An Array¶
Given an array of size N, shift all the elements to the right by 1 and move the last element to the beginning of array
Example 1¶
N = 10
arr[10] = { 7, 4, 9, 11, 2, 24, -5, 17, 1, 8 }
Ans =
arr[10] = { 8, 7, 4, 9, 11, 2, 24, -5, 17, 1}
Question¶
Right shift the given array
arr[] = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60}
Choices¶
- 60, 50, 40, 30, 20, 10
- 0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60
- 60, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50
Right Shift of An Array Idea and Code¶
Idea¶
- Store last element of original array in a temp variable for future use (
temp = arr[n - 1]) - Traverse from end to first index and do
arr[i] = arr[i - 1] - Till here all indexes are updated with their new value except 0th index. Finally do
arr[0] = temp
Pseudocode¶
static int[] rotateByone(int arr[]){
int n = arr.length
int temp = arr[n - 1]
for(int i = n - 1; i >= 1; i--){
arr[i] = arr[i - 1]
}
arr[0] = temp;
return ans;
}
Drawbacks of Arrays¶
Once array size is fixed, it cannot be changed.
If we want to change, we need to create a new array.
int[] ar=new int[4];
This can only store 4 elements, if we want to store 1 more element we cannot update the size. We have to create a new array only.
Arraylist¶
Definition¶
ArrayList is a class that provides a resizable array implementation that is similar to an ordinary array, but with the added benefit of being able to resize dynamically as elements are added or removed. An ArrayList can store objects of any type, including primitives.
Syntax¶
The general syntax for creating an ArrayList in Java is as follows:
ArrayList<DataType> listName = new ArrayList<DataType>();
- DataType is the data type of the elements that will be stored in the list (e.g. Integer, String, Object).
- listName is the name given to the ArrayList object.
Note: There is no need to mention size in Arraylist, an empty Arraylist is created.
Example¶
Here's an example that creates an ArrayList of integers and adds the values 10, 20, 30, and 50 to it:
// Create an ArrayList of integers
ArrayList<Integer> al = new ArrayList<>(); // size = 0
// Add integers to the list
al.add(10); // size = 1
al.add(20); // size = 2
al.add(30); // size = 3
al.add(50); // size = 4
Some Methods in Arraylist¶
- Adding an element at the end -
We can add an element at the end of Arraylist using the add(value) method:
al.add(10)
Task: Find out how to add a new value at a particluar index in an ArrayList.
- Total elements -
We can get the size of the Arraylist using the size() method:
int n = al.size(); // Returns the number of elements in the list
- Access ith index element of an Arraylist -
We can access ith index element of an Arraylist using the get(index) method:
int element = al.get(2); // Returns the element at second index
¶
int element = al.get(2); // Returns the element at second index
Question¶
ArrayList<Integer> al = new ArrayList<>();
al.add(10);
al.add(20);
al.add(30);
al.add(40);
System.out.print(al.get(2));
Choices¶
- 10
- 20
- 30
- 40
- Error
Explanation:¶
We first created an empty arraylist al. We then added 10, 20, 30 & 40 to it, the list becomes al = [10, 20, 30, 40]. The element at 2nd index is 30. Hence, answer is 30.
Question¶
ArrayList<Integer> al = new ArrayList<>();
al.add(10);
al.add(20);
al.add(30);
al.add(40);
System.out.print(al.get(4));
Choices¶
- 40
- 20
- Error
- 10
Explanation:¶
We first created an empty arraylist al. We then added 10, 20, 30 & 40 to it, the list becomes al = [10, 20, 30, 40]. The size of the array is 4 with indexes from 0 - 3. There is no index 4. Hence, the code gives an error.
ArrayList¶
- Update existing element -
We can update the existing element of an Arraylist using the set(index, value) method:
// myList = [10, 20, 30, 50]
myList.set(2, 40); // Updates the element at second index with value 40
// updated myList = [10, 20, 40, 50]
myList.set(6, 60); // Gives error because index 6 does not exist
- Remove an element -
We can remove an element from the Arraylist using the remove(index) method:
// myList = [10, 20, 40, 50]
myList.remove(2); // Removes the element at 2nd index from array
// updated myList = [10, 40, 50]
- Sort the arraylist -
We can sort the Arraylist using the Collections.sort(arraylist_name) method:
// myList = [10, 20, 40, 50]
myList.remove(2); // Removes the element at 2nd index from array
// updated myList = [10, 40, 50]
Note: Here is the link to example code snippet for practice.
Question¶
What will be the output of the following code?
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> ar = new ArrayList<>();
ar.add(1);
ar.add(2);
ar.add(3);
ar.set(1, 5);
ar.set(2, ar.get(0) + ar.get(1));
System.out.println(ar);
}
Choices¶
- [1, 5, 3]
- [1, 7, 3]
- [1, 5, 6]
- [1, 6, 3]
Question¶
Predict the output
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> ar = new ArrayList<>();
ar.add(-5);
ar.add(20);
ar.add(19);
ar.add(50)
ar.remove(1);
System.out.println(ar);
}
Choices¶
- [-5, 19, 20]
- [20, 19, 50]
- [-5, 20, 50]
- [-5, 20, 19, 50]
Question¶
What will be the output?
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> ar = new ArrayList<>();
ar.add(5);
ar.add(2);
ar.add(9);
ar.add(1);
Collections.sort(ar);
System.out.println(ar);
}
Choices¶
- [5, 2, 9, 1]
- [9, 5, 2, 1]
- [1, 2, 5, 9]
- [2, 1, 5, 9]
Problem Statement¶
Write a function which takes arrayList as input and update all values by 1
Example 1¶
temp : [20, 15, 8, 25, 21]
ans : [21, 16, 9, 26, 22]
Pseudo Code:¶
static ArrayList<Integer> increaseByOne(ArrayList<Integer> al){
//iterate over the ArrayList
int n = al.size();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
//access ith index element : al.get(i)
int num = al.get(i);
al.set(i, num + 1);
}
return al;
}
Problem Statement¶
Given an ArrayList of integers, return all the even numbers in the ArrayList.
Example 1¶
Input = 10 13 7 14 16 19 22 9 11
Output = 10 14 16 22
Example 2¶
Input = 4 9 1 10 22 21 45
Output = 4 10 22
Solution¶
Iterate on the arrayList and check if element is even. If yes add it to ans arrayList.
Pseudocode¶
public static ArrayList<Integer> getEvenNumbers(ArrayList<Integer> list) {
ArrayList<Integer> evenNumbers = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
int num = list.get(i);
if (num % 2 == 0) {
evenNumbers.add(num);
}
}
return evenNumbers;
}
