Problems on Arrays:¶
Agenda¶
- Count of Pairs with sum = K
- Elements having at least 1 element greater than it
- Given a mat[][] and row num, return sum of that row
- Given a mat[][] and col num, return sum of that col"
- Given two matrices and return sum of mat[][]
- Return an arraylist with all unique element
- Return unique of elements from every row
Problem Statement¶
Given an array arr and a value k, find the count of pairs (i, j) such that arr[i] + arr[j] == k where i != j.
Note 1: i & j are indices of array.
Note 2: (i, j) is the same as (j, i).
Example 1¶
Input: arr = [2, 4, 2, 5, 1, 3], k = 6
Output: 3
(0, 1) -> arr[0] + arr[1] = 2 + 4 = 6
(1, 2) -> arr[1] + arr[2] = 4 + 2 = 6
(3, 4) -> arr[3] + arr[4] = 5 + 1 = 6
Hence, the answer is 3.
Question¶
Given ar[5] = {5 3 2 3 6} k = 8
no of pairs (i , j) are there such that ar[i] + ar[j] = k ?
Choices¶
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
Explanation¶
Following pairs satisfy the condition-
(0, 1) -> arr[0] + arr[1] = 5 + 3 = 8
(0, 3) -> arr[0] + arr[3] = 5 + 3 = 8
(2, 4) -> arr[2] + arr[4] = 2 + 6 = 8
Hence, the answer is 3.
Solution 1¶

One way to solve this problem is to use a brute force approach, which involves checking every possible pair of elements in the array to see if their sum is equal to k. Here are the steps involved in this approach:
- Initialize a variable count to 0 to keep track of the count of pairs.
- Traverse the array arr using two nested loops, comparing each pair of elements in the array to see if their sum is equal to k.
- Return count/2, since (i, j) & (j, i) are considered as same.
Pseudocode¶
public static int countPairs(int[] arr, int k) {
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length; j++) {
if (i!=j && arr[i] + arr[j] == k) {
count++;
}
}
}
return count / 2;
}
Solution 2¶
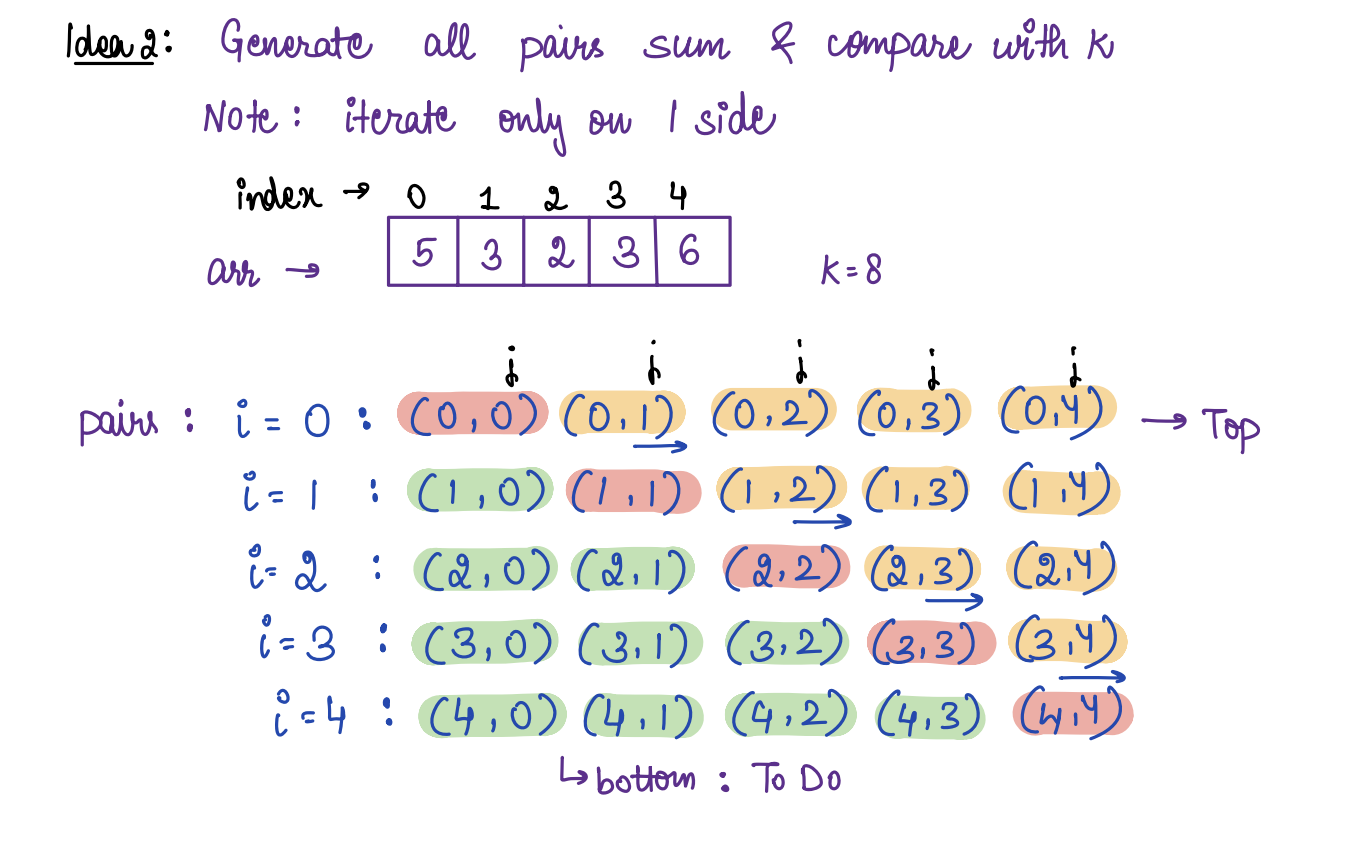
If we notice, in the above solution we are counting (i, j) & (j, i) both. If we not consider one of the pair initially only, then it will not get added to the count. To achieve this, we will always start the inner loop from one index greater than the outer loop.
Pseudocode¶
public static int countPairs(int[] arr, int k){
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++){
for (int j = i+1; j < arr.length; j++){
if (arr[i] + arr[j] == k){
count++;
}
}
}
return count;
}
Problem:¶
Given a 2D array and a row index, return sum of that particular row.
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
row index =1, 5 + 6 + 7 + 8, output=26
Question¶
Given a matrix, row index =0, return sum of that particular row.
1 2 3 4
5 6 7 8
9 10 11 12
Choices¶
- 10
- 4
- 26
- 6
Pseudocode¶
static int rowSum(int[] mat, int i){
int n = mat.length;
int m = mat[0].length;
int sum=0;
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++){
sum=sum+mar[i][j];
}
return sum;
}
¶
static int rowSum(int[] mat, int i){
int n = mat.length;
int m = mat[0].length;
int sum=0;
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++){
sum=sum+mar[i][j];
}
return sum;
}
Problem:¶
Given a 2D array and a column index, return sum of that particular column.
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
column index =2, 3 + 7 + 11, output=21
Ask the students to do it yourself.
Add two matrices¶
Write a function to add two matrix of same dimension and return the resultant
Testcase 1¶
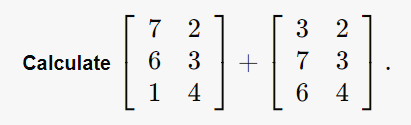
Solution with explaination¶
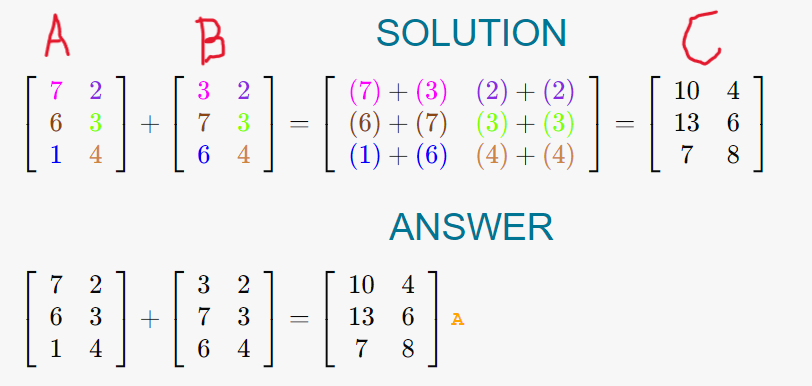
- Matrix are of same dimension i.e. they have same number of rows and columns.
- The values that are present at same row number and same column number in both matrix are to be added together inorder to get the resultant.
- In above solution number with same colors are present at same row number and same column number in both matrix.
- So inorder to get element at c[0][0] we add A[0][0] i.e 7 and B[0][0] i.e. 3 and so on.
Testcase 2¶
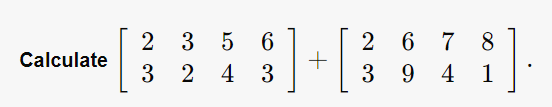
Solution¶

Question¶
Can we add a 3x4 matrix with a 3x4 matrix?
Choices¶
- Yes
- No
- Maybe
Question¶
Can we add a 3x4 matrix with a 3x3 matrix ?
Choices¶
- Yes
- No
- Maybe
Observation¶
- On oberserving both the cases we can give generalized formula for sum of matrix having same dimensions as:-
Warning
SumMat[i][j] = Mat1[i][j] + Mat2[i][j]
Code¶
static int[][] addMatrix(int[][] A, int[][] B) {
int m = A.length;
int n = A[0].length;
int[][] ans = new int[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
ans[i][j] = A[i][j] + B[i][j];
}
}
return ans;
}
Problem Statement¶
Given an ArrayList of integers, return all the unique numbers in the ArrayList.
Note: An element with frequency 1 is known as unique element.
Example 1¶
Input = 10 7 32 10 32 48 56 12 48 19 11 32
Output = 7 56 12 19 11
Question¶
ar[] = {6 10 8 2 8 10 11} Return all unique elements
Choices¶
- 6 2 11
- 6 2 10
- 10 8 11
- None of the above
Solution¶
Iterate on each element, check if frequency is 1 then add element to ans arrayList.
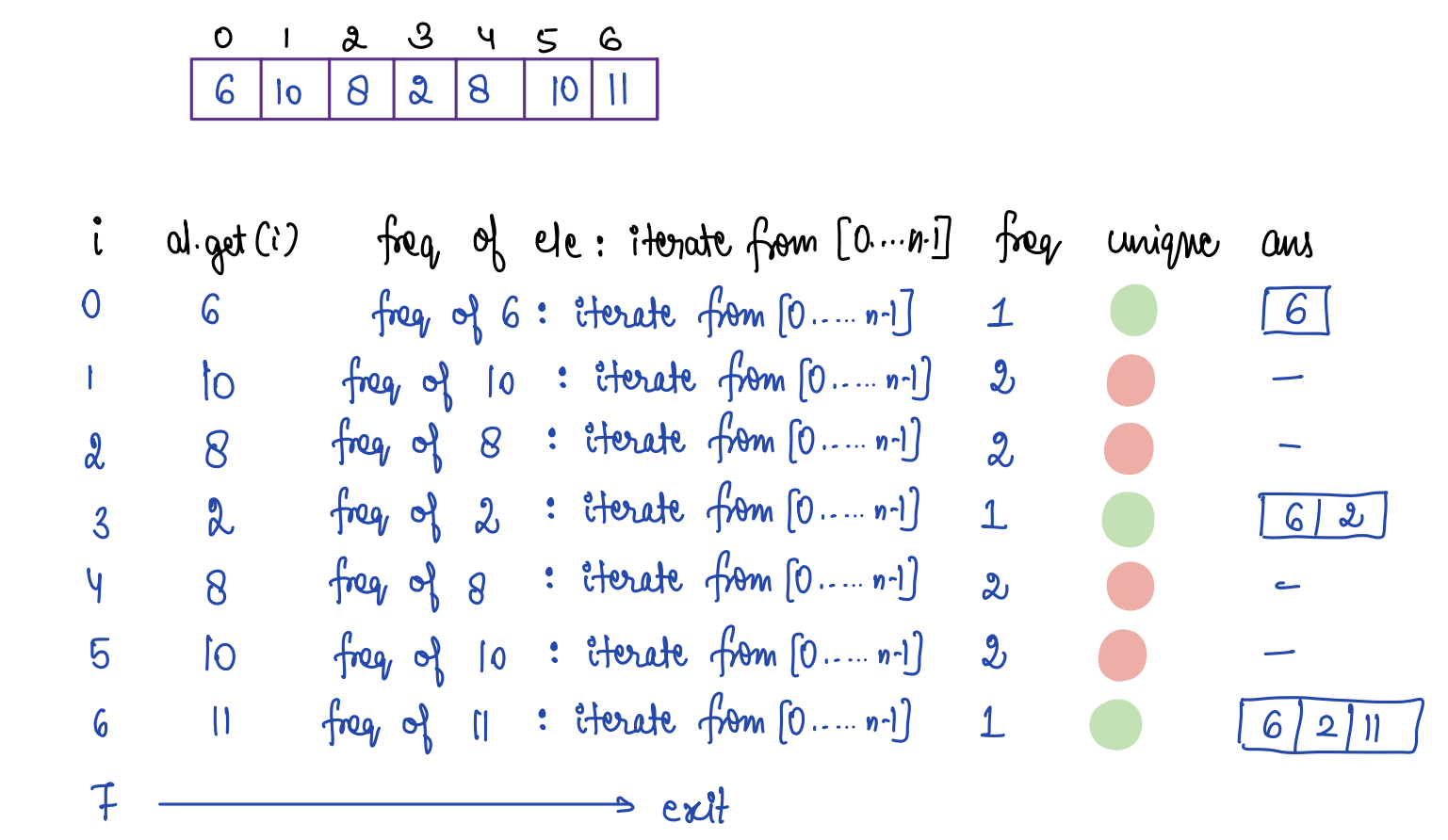
Pseudocode¶
static ArrayList<Integer> getUniqueNumbers(ArrayList<Integer> list) {
ArrayList<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
int num = list.get(i);
int freq = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < list.size(); j++) {
if (num == list.get(j)) {
freq++;
}
}
if (freq == 1) {
ans.add(num);
}
}
return ans;
}
Even numbers¶
Given a 2D ArrayList, return a 2D ArrayList which contains unique elements from every row.
Example 1¶
A =[ [1, 2, 3, 4, 1],
[5, 8, 7, 8, 8],
[9, 4, 3, 2, 4] ]
ans= [ [2, 3, 4],
[5, 7],
[9, 3, 2] ]
Example 2¶
A = [ [3, 2],
[2, 4] ]
ans= [ [3, 2],
[2, 4] ]
Observation¶
We will traverse every element in ArrayList and insert unique elements in output.
Pseudocode¶
public int freq(ArrayList<Integer>list,int k) {
int count = 0;
for(int i=0; i < list.size();i++) {
if(list.get(i) == k) {
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> solve(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> A) {
int n = A.size();
int m = A.get(0).size();
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>ans = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0; i < n;i++) {
ArrayList<Integer>temp = new ArrayList<>();
for(int j=0; j < m;j++) {
int ele = A.get(i).get(j);
if(freq(A.get(i),ele) == 1) {
temp.add(ele);
}
}
ans.add(temp);
}
return ans;
}
¶
public int freq(ArrayList<Integer>list,int k) {
int count = 0;
for(int i=0; i < list.size();i++) {
if(list.get(i) == k) {
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> solve(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> A) {
int n = A.size();
int m = A.get(0).size();
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>>ans = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i=0; i < n;i++) {
ArrayList<Integer>temp = new ArrayList<>();
for(int j=0; j < m;j++) {
int ele = A.get(i).get(j);
if(freq(A.get(i),ele) == 1) {
temp.add(ele);
}
}
ans.add(temp);
}
return ans;
}
Problem:¶
Given an array A of N integers. Count the number of elements that have at least 1 elements greater than itself.
Example1:¶
A = [3, 1, 2]
Output:
2
Example 2:¶
A = [-17, 15, 6, 3, 15, 7, -19, 15]
Output:
8-3 = 5
¶
Output:
8-3 = 5
TODO:
- Find the max in array using 1 loop.
- Count the frequency of max in array using 1 loop.
- ans= total no of elements(ar.length)- count
