String Implementation¶
- Introduction to Characters
- ASCII Introduction
- Sum of digits in the string with characters and digits
- Replace all the characters 'x' with '$'
- Count uppercase and lower case characters
- Count number of characters of first string present in the second string
Character:¶
A character represent a single symbol.
There are different types of characters:
- Uppercase characters : ['A' - 'Z']
- Lowercase characters : ['a' - 'z']
- Numeric characters: ['0' - '9']
- Special characters: ['@', '#', '$', '%', '&'...]
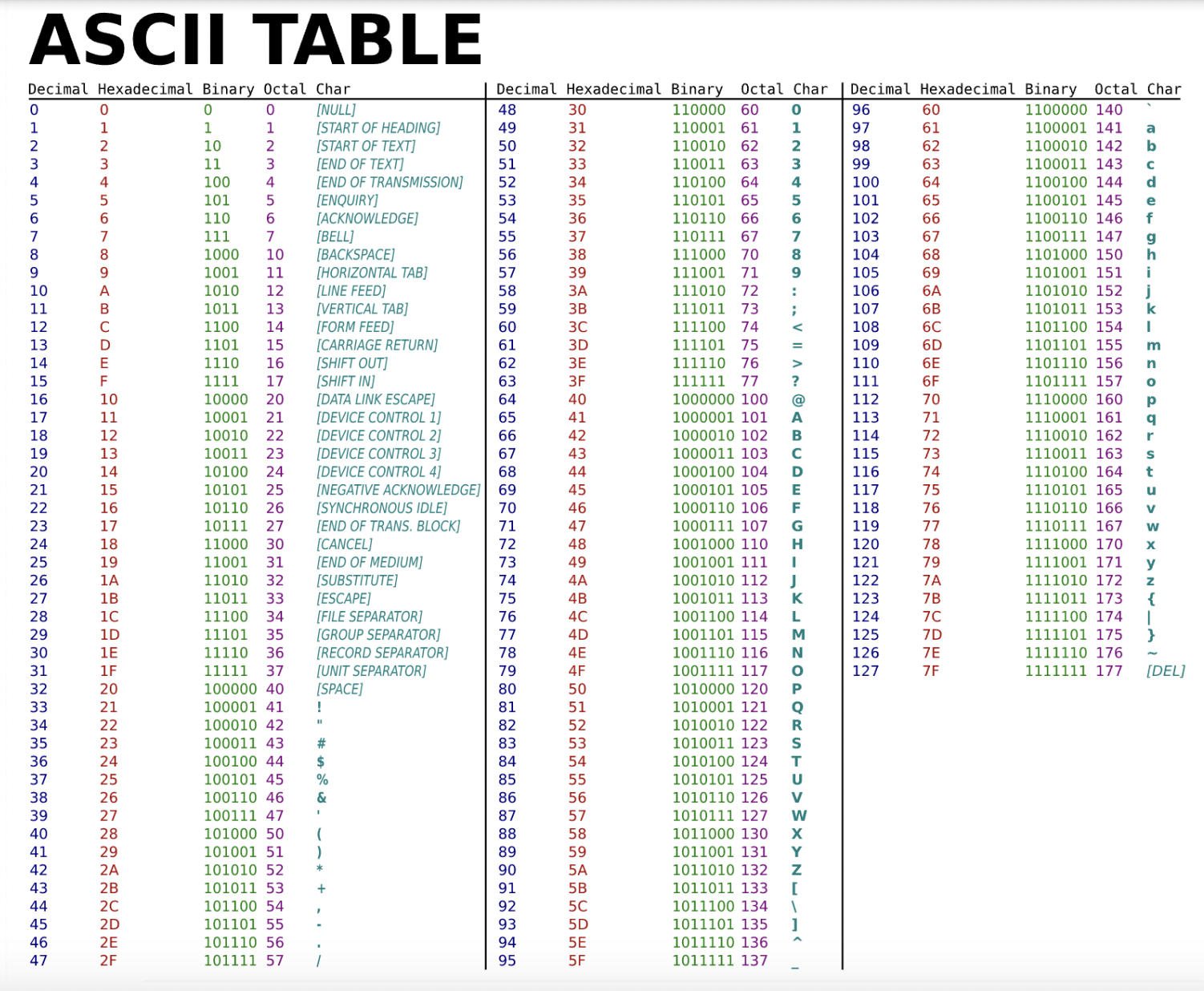
There are a total of 128 characters.
Syntax¶
Example 1:
char ch = 'a';
System.out.println(ch);
Output:
a
Example 2:
char ch = 'ab';
System.out.println(ch);
Error: Only a single symbol is a character.
Why do we need ASCII Codes?¶
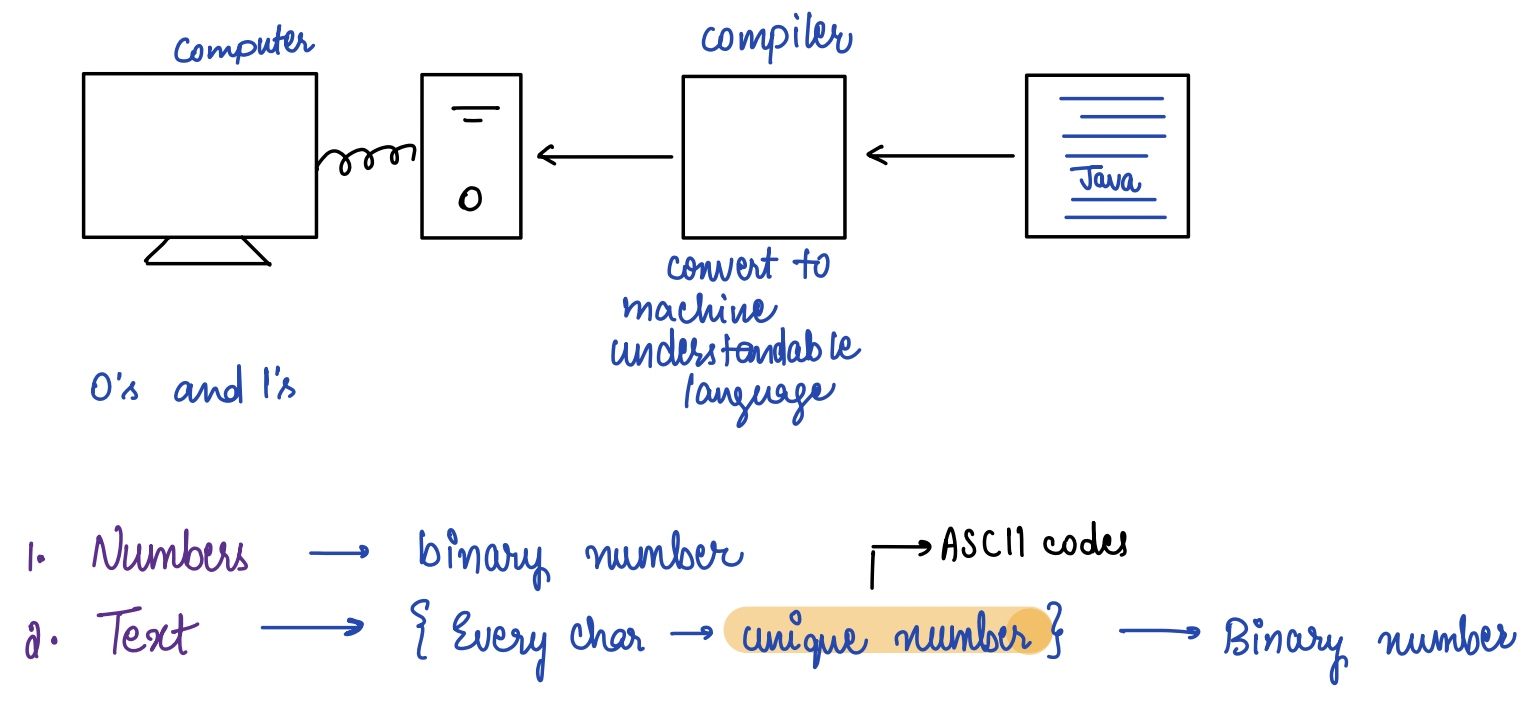
ASCII Codes¶
ASCII stands for American Standard Code for Information Interchange.
These codes are a standardized system of assigning a unique numeric value to each character in the English language and other common characters, such as punctuation marks and symbols.
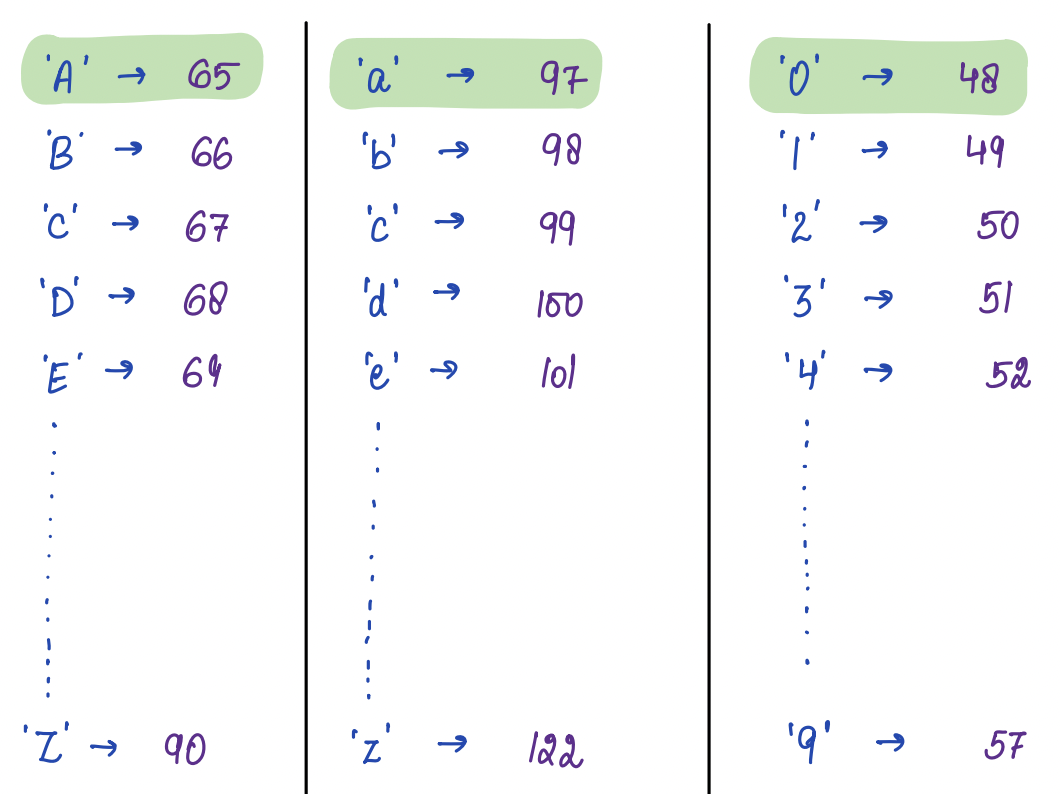
Show the ASCII table in the class¶
Definition¶
In programming, a string is a data type used to represent a sequence of characters.
Syntax¶
The syntax for declaring and initializing a string variable in Java is:
String str = "Hello World!"; // Double quotes are used to define a string
Example -¶
String str = "How are you?"
print(str) // How are you? will be printed
Indexing¶
String indexing starts from 0, where the first character is at index 0, the second character is at index 1, and so on.
Example -
String str = "Hello, World!";
System.out.println(str.charAt(0)); // Output: 'H'
System.out.println(str.charAt(7)); // Output: 'W'
Properties of a String¶
Some of the most commonly used properties of a string include:
-
Length: The length() method of the String class returns the number of characters in a string. For example,
String str = "Priyanshi"; int n = str1.length(); // assigns 9 to variable n as str has 9 characters. System.out.println(str.length()); // 9 -
Access a character: The charAt(index) method of the String class returns the character at that index in a string. Indexing in string is same as that in array and starts from 0. For example,
String str = "Priyanshi";
System.out.println(str.charAt(5)); // output will be 'n'.
-
Iterate a string: We can iterate over the characters of a string using a loop. One way to do this is to use a for loop that iterates over the index positions of the string, and then use the charAt() method to retrieve the character at each position. For example,
String str = "Priyanshi"; for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) { System.out.println(i + " -> " + str.charAt(i)); } -
Update a string: In Java, strings are immutable, meaning that their contents cannot be changed after they are created.
- Concatenating characters to String: In Java, a character can be concatenated after a string by using the + or += operator, or through the concat() method, defined in the java. lang. String class.
// Concatentaion example
String s1 = "Hello";
String s2 = s1 + "Everyone";
System.out.println(s2); // Output will be "Hello Everyone"
String s3 = "Hi";
s3 = s3 + 'i';
System.out.println(s3); // Output will be "Hii"
s3 = 'e' + s3;
System.out.println(s3); // Output will be "eHii"
s3 = "Bye " + s3;
System.out.println(s3); // Output will be "Bye eHii"
Problem statement:¶
Given a string s, you have to find the length of the longest word in the input string.
Exanple 1:¶
Input:
hi hello bye
Output:
5
Explanation:
In the sentence "hi hello bye", hello is the longest word, whose length is 5.
# Question Given string A, "coding is awesome"
find the length of the longest word in the given string.
Choices¶
- 7
- 6
- 5
- I dont know
Explanation¶
In the sentence "coding is awesome", awesome is the longest word, whose length is 7.
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String line = scanner.nextLine();
int maxLength = 0;
int currentLength = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < line.length(); i++) {
char currentChar = line.charAt(i);
if (currentChar != ' ') {
currentLength++;
} else {
if (currentLength > maxLength) {
maxLength = currentLength;
}
currentLength = 0;
}
}
if (currentLength > maxLength) {
maxLength = currentLength;
}
System.out.println(maxLength);
scanner.close();
}
¶
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String line = scanner.nextLine();
int maxLength = 0;
int currentLength = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < line.length(); i++) {
char currentChar = line.charAt(i);
if (currentChar != ' ') {
currentLength++;
} else {
if (currentLength > maxLength) {
maxLength = currentLength;
}
currentLength = 0;
}
}
if (currentLength > maxLength) {
maxLength = currentLength;
}
System.out.println(maxLength);
scanner.close();
}
Problem¶
Given a string A of length N and a character B, replace all occurrences of B in string A with character '@'.
Input Format
First line is String A Second line is Character B
Example:
abcad
a
Output: @bc@d
Question¶
Given string A,"interviewbit"
String B= "i"
replace all occurrences of B in string A with character '@'.
Choices¶
- @nterv@ewb@t
- i@terv@ewb@t
- @ntervewb@t
- I dont know
Explanation¶
Modified string after Replacement of i at 1st, 7th, and 11th position is @nterv@ewb@t
Idea:¶
- Initialization: Create an empty string result.
- Iterate: Loop through each character in the input string.
- Check and Replace: If the current character matches the target character, append '@' to the result; otherwise, append the current character.
- Final Result: Return the modified string (result).
Psuedo code¶
static String replaceCharacter(String str, char targetChar) {
String result = "";
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
char currentChar = str.charAt(i);
if (currentChar == targetChar) {
result += '@';
} else {
result += currentChar;
}
}
return result;
}
¶
static String replaceCharacter(String str, char targetChar) {
String result = "";
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
char currentChar = str.charAt(i);
if (currentChar == targetChar) {
result += '@';
} else {
result += currentChar;
}
}
return result;
}
Problem:¶
Given a string, Count uppercase and lower case characters and print the values.
Example:¶
String str="Hello World"
Output: Uppercase: 2 Lowercase: 8
Question¶
Given string ElePHant
Count number of Uppercase character first, then lowercase characters.
Choices¶
- 3 lowercase
5 uppercase - 3 uppercase
5 lowercase - 5 uppercase
9 lowercase - I dont know
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner scn = new Scanner(System.in);
String str = scn.next();
int c1 = 0;
int c2 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
char ch = str.charAt(i);
if (ch >= 'A' && ch <= 'Z') {
c1++;
} else if (ch >= 'a' && ch <= 'z') {
c2++;
}
}
System.out.println(c1);
System.out.println(c2);
}
Problem:¶
Count number of characters of first string present in the second string.
Example:¶
String A=abbd
String B=aabb
Output:
Number of common characters: 3(a,b,b)
Pseudo Code¶
static int countCommonCharacters(String str1, String str2) {
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < str1.length(); i++) {
char currentChar = str1.charAt(i);
for (int j = 0; j < str2.length(); j++) {
if (currentChar == str2.charAt(j)) {
count++;
break; // Break the inner loop once a common character is found
}
}
}
return count;
}
