2D arrays 2¶
Agenda¶
- Revision
- Transpose
- Reverse every row in the given matrix
- Rotate by 90
- Intro to 2D ArrayList
- Syntax
- Functions
- Return even elements from everyrow.
Question¶
How do you declare an int 2D array in Java?
Choices¶
- int[][] mat = new int[rows][cols]
- int[][] mat = new int[cols][rows]
- int[][] mat = new int[rows][rows]
- int[][] mat = new int[cols][cols]
Question¶
How do you get the no. of rows in a 2D matrix mat?
Choices¶
- mat.length
- mat.length()
- mat.size
- mat.size()
Question¶
How do you get the number of columns in a 2D matrix for row index x?
Choices¶
- mat[x].length()
- mat[x].length
- mat[x].size
- mat[x].size()
Question¶
int[][] nums = {{1, 2, 3}, {4, 5, 6}, {7, 8, 9}};
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9
System.out.println(nums[1][2]);
Choices¶
- 4
- 5
- 6
- ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException
Transpose¶
Given an rectangular matrix return the transpose of the matrix¶
Rectangular matrix is matrix having number of rows not equal to number of columns
Transpose of the matrix is new matrix in which the row of certain number in old matrix is converted to column of that particular number in new matrix like -
Row 1 of old matrix ---> column 1 of new matrix
Row 2 of old matrix ---> column 2 of new matrix
and so on...
Example 1¶
mat[3][5]
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
Explaination and solution¶
Intial matrix :-
mat[3][5]
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
Step 1 :- convert row 1 of intial to column 1
| 1 |
|---|
| 2 |
| 3 |
| 4 |
| 5 |
Step 2:- convert row 2 of intial to column 2
| 1 | 6 |
|---|---|
| 2 | 7 |
| 3 | 8 |
| 4 | 9 |
| 5 | 10 |
Step 3 :- convert row 3 of intial to column 3
| 1 | 6 | 11 |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 7 | 12 |
| 3 | 8 | 13 |
| 4 | 9 | 14 |
| 5 | 10 | 15 |
Transpose of matrix is :-
| 1 | 6 | 11 |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 7 | 12 |
| 3 | 8 | 13 |
| 4 | 9 | 14 |
| 5 | 10 | 15 |
Example 2¶
mat[3][4]
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
Explanation and solution¶
Transpose of matrix is :-
| 1 | 6 | 11 |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 7 | 12 |
| 3 | 8 | 13 |
| 4 | 9 | 14 |
Question¶
For a rectangular matrix, can we have the transpose in the same matrix?
Choices¶
- Yes
- No we need new matrix
- Maybe
Question¶
If dimensions of a matrix A is ( N x M ), and it is declared as int mat[][] = new int[N][M]; How will the transpose be declared?
Choices¶
- int transpose[] = new int[N][M];
- int transpose[][] = new int[N][M];
- int transpose[][] = new int[M][N];
Question¶
What will be the transpose of this matrix?
10, 20, 30
14, 15, 18
Choices¶
- 10,14
20,15
30,18 - 10,20
30,14
15,18 - I am confused about what is transpose :(
Observations :-¶
- if we observe example 1
- Element at row 0 and column 1 in matrix mat becomes Element at column 0 and row 1 in transpose.
- similarly mat[2][3] ---> newMat[3][2]
- mat[1][4] ---> newMat[4][1]
- Is there any pattern between the position of element in intial matrix and tranpose matrix ?
- On observing we can say that :-
Warning
Transpose[i][j] = Mat[j][i]
Warning
If dimensions of Mat are MxN then dimensions of transpose would be NxM
Code¶
static int[][] transposeMatrix(int[][] Mat) {
int m = Mat.length;
int n = Mat[0].length;
int[][] ans = new int[n][m];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
ans[j][i] = Mat[i][j];
}
}
return ans;
}
Reverse every row¶
Given a matrix reverse every row of matrix and return the same matrix
Example 1¶
mat[3][5]
| 3 | 2 | 6 | 1 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14 | 18 | 2 | 4 | 10 |
| 5 | 6 | 3 | 9 | 8 |
Explanation and solution¶
Initial matrix :-
mat[3][5]
| 3 | 2 | 6 | 1 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14 | 18 | 2 | 4 | 10 |
| 5 | 6 | 3 | 9 | 8 |
Step 1 :- Reverse row 1 of matrix
| 9 | 1 | 6 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 14 | 18 | 2 | 4 | 10 |
| 5 | 6 | 3 | 9 | 8 |
Step 2 :- Reverse row 2 of matrix
| 9 | 1 | 6 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 4 | 2 | 18 | 14 |
| 5 | 6 | 3 | 9 | 8 |
Step 4 :- Reverse row 3 of matrix
| 9 | 1 | 6 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 4 | 2 | 18 | 14 |
| 8 | 9 | 3 | 6 | 5 |
Example 2¶
mat[3][4]
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
Explanation and solution¶
| 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 |
| 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 |
Question¶
What will be result if we reverse each row of this matrix?
10, 20, 30
14, 15, 18
Choices¶
-
10, 20, 30
14, 15, 18 -
20, 10, 30
14, 15, 18 -
10, 20, 30
18, 15, 14 -
30, 20, 10
18, 15, 14
Approach¶
- Our approach should be to traverse each row reverse it.
- But how to reverse a row ? Reversing a single row:-
- First element of the row is swapped with the last element of the row. Similarly, the second element of the array is swapped with the second last element of the array and so on.
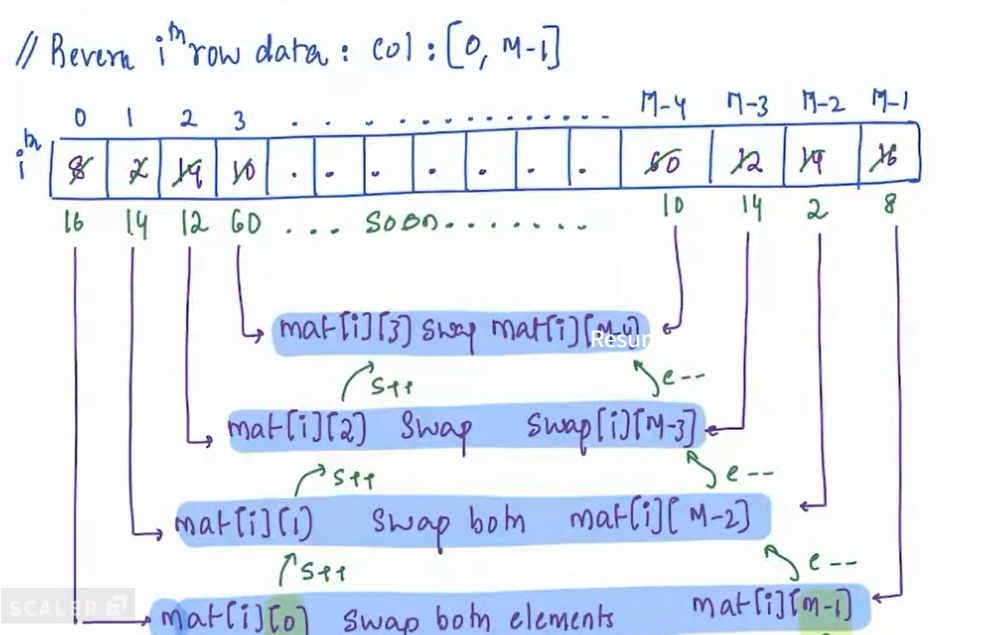
- But if keep on swapping we would end up with intial configuartion again
- So we swap till e>s This way at the end of traversal, we will have the entire row reversed.
Code¶
static int[][] reverseEachRow(int[][] Mat) {
int m = Mat[0].length;
int n = Mat.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int s = 0;
int e = m - 1;
while (e > s) {
// Swap elements in the current row
int temp = Mat[i][s];
Mat[i][s] = Mat[i][e];
Mat[i][e] = temp;
e--;
s++;
}
}
return Mat;
}
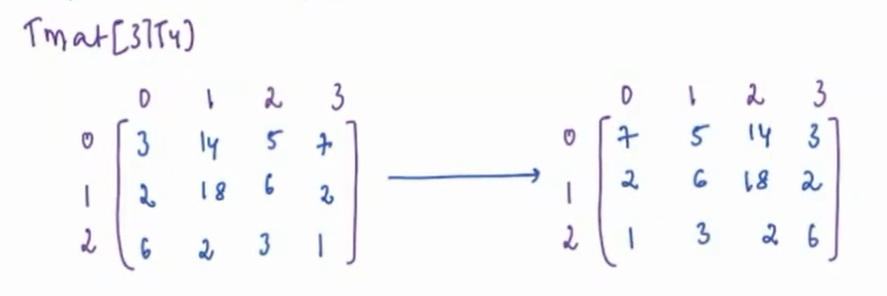
Rotate by 90¶
Given a matrix rotate it by 90o in clockwise direction ?
Testcase¶

Solution¶
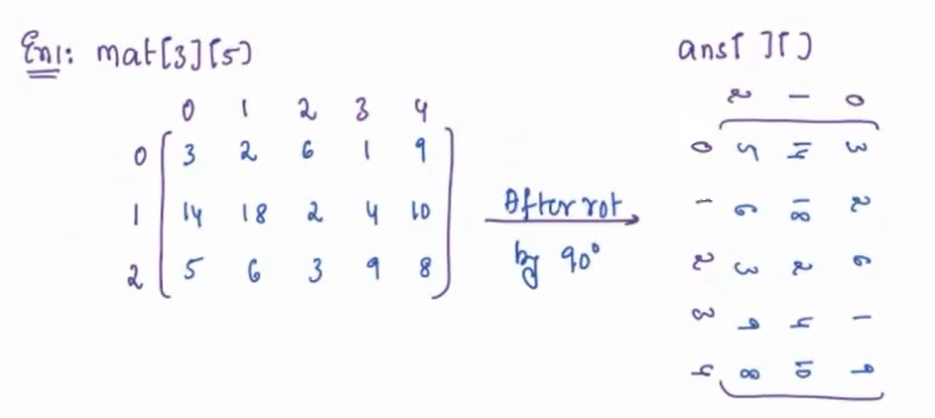
Example¶
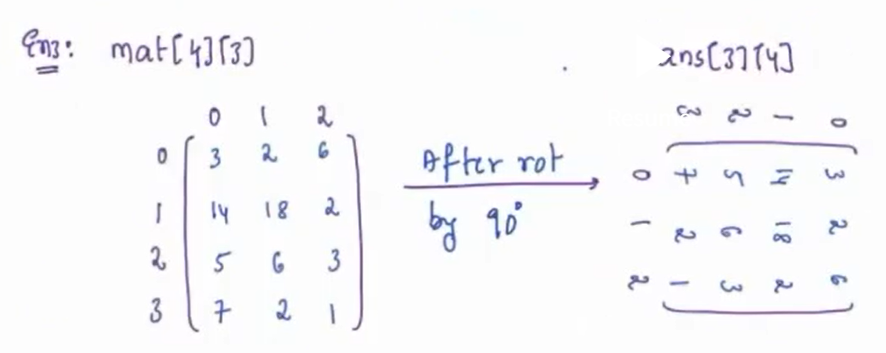
Approach¶
-
First we take transpose of matrix. On taking transpose:-
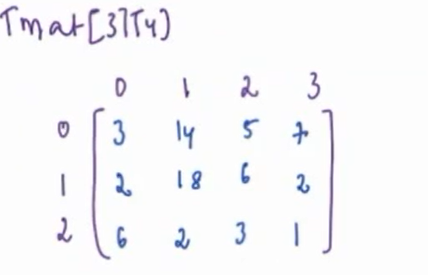
-
Reverse each row of transpose to get the solution.
Code
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static int[][] transposeMatrix(int Mat[][]) {
int m = Mat.length;
int n = Mat[0].length;
int transposeMat[][] = new int[n][m];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
transposeMat[j][i] = Mat[i][j];
}
}
return transposeMat;
}
static int[][] reverseEachRow(int Mat[][]) {
int m = Mat[0].length;
int n = Mat.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int s = 0;
int e = m - 1;
while (e > s) {
int temp = Mat[i][s];
Mat[i][s] = Mat[i][e];
Mat[i][e] = temp;
e--;
s++;
}
}
return Mat;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int Mat[][] = new int[3][4];
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
Mat[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
int transpose[][] = transposeMatrix(Mat);
int matRotatedClockwise90Degree[][] = reverseEachRow(transpose);
}
}
Syntax¶
ArrayList<Integer> l = new ArrayList<>();
Properties¶
1. add(element)¶
It is used to insert elements in ArrayList.
l.add(20);
l.add(30);
l.add(40);
l.add(35);
| 20 | 30 | 40 | 35 |
|---|---|---|---|
2. set(element)¶
It is used to update values at particular index in ArrayList.
l.set(1, 80);
l.set(0, 90);
| 90 | 80 | 40 | 35 |
|---|---|---|---|
3. get(index)¶
It is used to get values at particular index in ArrayList.
print(l.get(2));
print(l.get(3));
Output :
40
50
4. remove(index)¶
It is used to remove value at particular index in ArrayList.
l.remove(2);
ArrayList :-
| 90 | 80 | 35 |
|---|---|---|
Note:
ArrayList<Integer> l = new ArrayList<>();
2D ArrayList¶
ArrayList of ArrayLists
Syntax for 2D ArrayList¶
ArrayList<ArrayList< Datatype>> a = new ArrayList<>();
How to add elememts in 2D ArrayList¶
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> arr = new ArrayList<>();
Here each Arraylist in arr is of type ArrayList
Pseudocode¶
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> arr = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Integer> d1 = new ArrayList<>();
d1.add(10);
d1.add(20);
d1.add(30);
d1.add(40);
ArrayList<Integer> d2 = new ArrayList<>();
d2.add(-1);
d2.add(4);
d2.add(8);
ArrayList<Integer> d3 = new ArrayList<>();
d1.add(50);
d1.add(60);
d1.add(70);
d1.add(80);
Output:
{
{10,20,30,40},
arr : {-1,4,8},
{50,60,70,80}
}
How to get elememts in 2D ArrayList¶
Note: arr.get(i) = element at ith index.
Pseudocode¶
System.out.println(arr.get(1));
System.out.println(arr.get(2));
Output:
{-1,4,8}
{50,60,70,80}
How to access element from ith ArrayList at jth index¶
Note: arr.get(i).get(j) = element at ith ArrayList and jth index.
Pseudocode¶
System.out.println(arr.get(0).get(0));
System.out.println(arr.get(1).get(2));
System.out.println(arr.get(2).get(1));
10
8
60
How to return no. of elements in ArrayList¶
Pseudocode¶
System.out.println(arr.size());
System.out.println(arr.get(0).size());
System.out.println(arr.get(1).size());
3
4
3
How to modify elements in ArrayList¶
Pseudocode¶
System.out.println(arr.get(0).set(0,14));
System.out.println(arr.get(1).set(2,-9));
System.out.println(arr.get(2).set(0,20));
{
{14,20,30,40},
arr : {-1,4,-9},
{20,60,70,80}
}
Problem 1¶
Print 2D ArrayList.
Pseudocode¶
void print(ArrayList< ArrayList< Integer>> arr) {
int n = arr.size(); // Get the number of rows in the ArrayList
// Iterate through each row
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// Get the number of columns in the current row
int m = arr.get(i).size();
// Iterate through each element in the current row
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
System.out.print(arr.get(i).get(j) + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
Dry run¶

Even numbers¶
Given a 2D ArrayList, return a 2D ArrayList which contains even number from every row.
Example 1¶
arr = {
{3,10,2},
{2,7,6,9,4},
{18,20,11,6}
}
Ans = {
{10, 2}
{2,6,4}
{18,20,6}
}
Example 2¶
arr = {
{3,6,2,9},
{2,4,8,10},
{3,9,7,15},
8,3,2,14,19},
}
Ans = {
{6,2}
{2,4,8,10}
{}
{8,2,14}
}
Observation¶
We will traverse every element in ArrayList and insert even numbers in output.
Pseudocode¶
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> even(ArrayList<>> arr){
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
int n = arr.size();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
ArrayList<Integer> l = new ArrayList<>();
int m = arr[i].get(i).size();
for(int j = 0; j < m; j++){
if( arr.get(i).get(j) % 2 == 0){
l.add(arr.get(i).get(j));
}
}
ans.add(l);
}
return ans;
}
