Refresher: Iteration 2¶
Introduction¶
Recap¶
- introduction to loop
- while, while else
- break and continue
- print 1 to n, n to 1
- print even numbers, sum
- prime numbers
- scrapers and scissors
Question¶
What is the output of the following?
count = 0
while(count < 10):
print(10, end = ' ')
count += 1
Choices
- 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
- 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10
- Infinite Loop
Question¶
Which is true for an Odd number n?
Choices
- n % 2 == 0
- n % 2 = = 1
Question¶
What operation can be used to get the last digit of a number?
Choices
- n - 10
- n // 10
- int(n / 10)
- n % 10
Question¶
What will be the output of the following?
count = 1
while(count <= 5):
if(count == 2):
break
print(count, end = ' ')
count += 1
Choices
- 1 3 4 5
- 1
- 1 2
- 0 1
Range Function¶
range(n)returns number from 0 to n-1.- start = 0
- jump = 1
- number line example
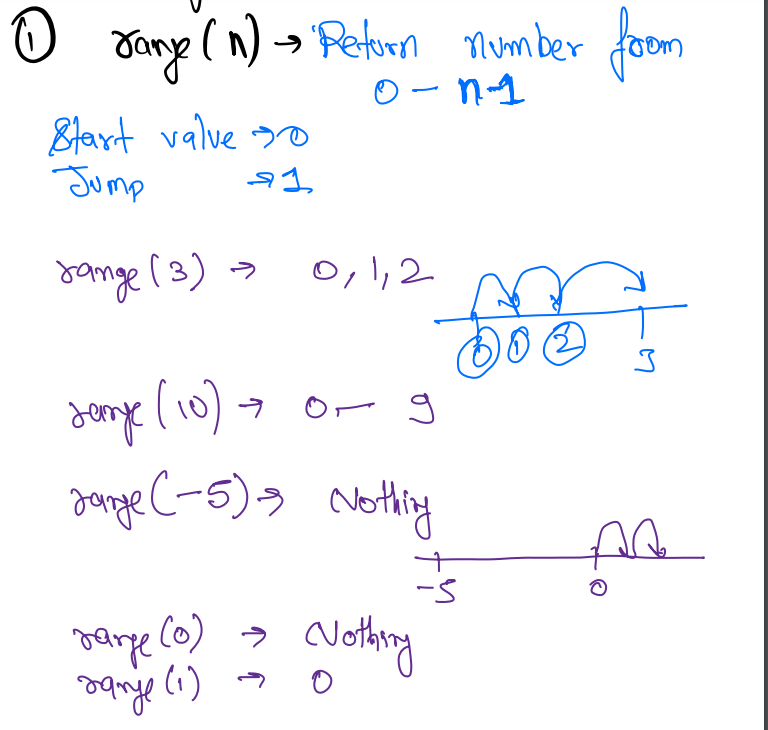
* range(-5) -> nothing as decrementing -5 we will never reach anywhere.
* range(1) -> 0
- range(start, end) -> general numbers from [start, end-1]
- jump -> +1
- range(1,3) -> 1,2
- range(-5, -1) -> -5, -4, -3, -2
- range(-4, -10) -> nothing
- range(5, 1) -> nothing
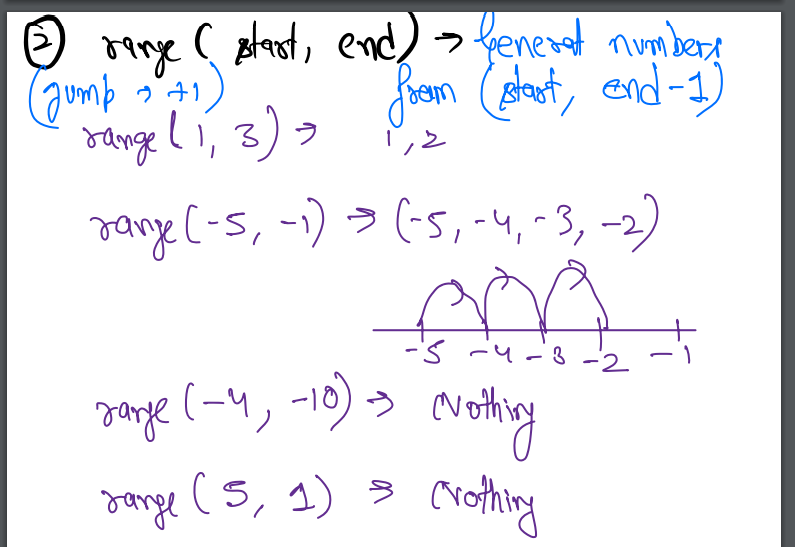
- range(start, end, jump)
- start, end - 1
- range(1,6,2) -> 1, 3, 5
- range(0, -5, -1) -> 0, -1, -2, -3, -4
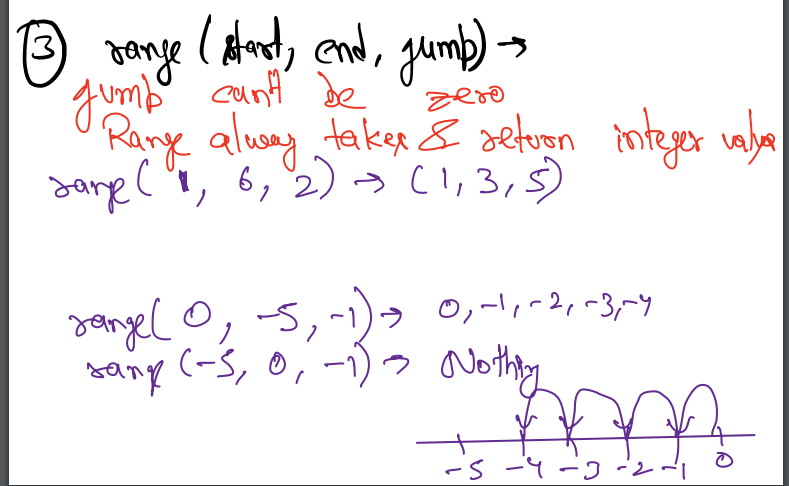
Precautions¶
- jump can not be zero
- range always takes and returns an integer value
Iterables an Iterators¶
- Assume that we have a bag of candies. I put my hand in the bag and take the candies out of the back one by one.
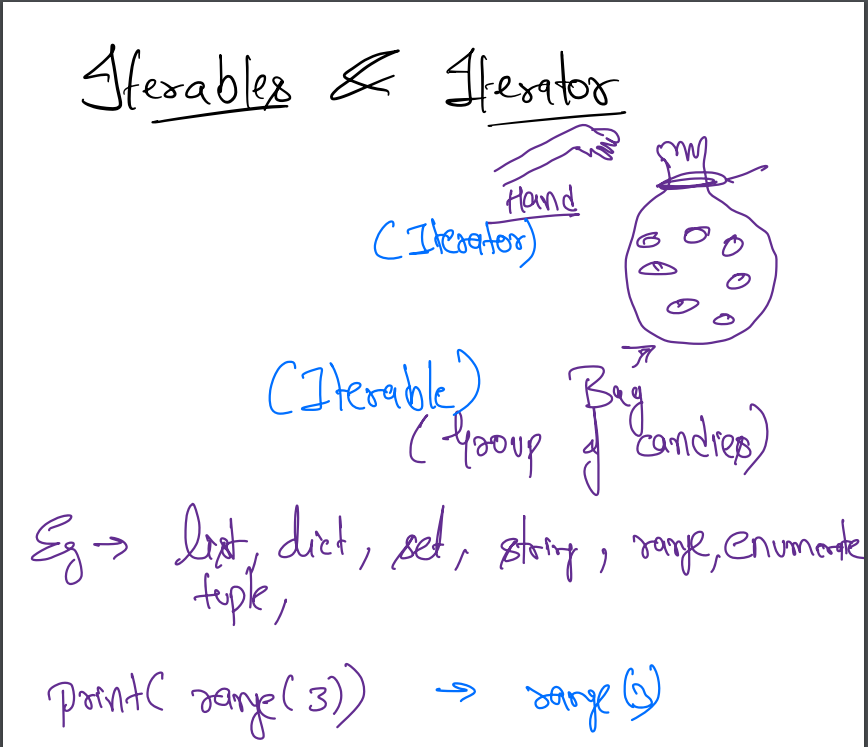
- Examples - list, dict, set, string, range, enumerate, tuple
- Iterables are groups of objects
- Iterator can be related to the hand that we are using to take candies out of the iterables(bag of candies).
Range as an Iterable¶
-
Range is iterable, it is a collection of integers. If the range returns nothing we can say the bag is empty it doesn't return anything.
print(range(3))What will this return? -
Print is not an iterator it will simply return
range(3). - for loop is one of the best iterators.
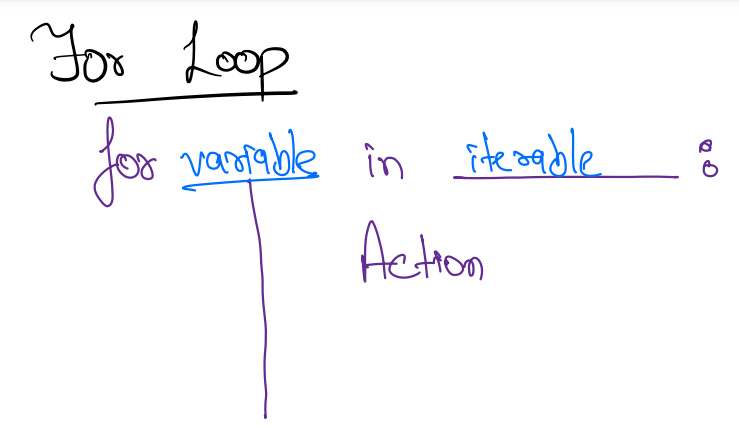
For Loop¶
Syntax:
for variable in iterable:
action
- With for loop we can skip initialization, condition, and updation.
- It is an alternative to the
foreachloop. - The for loop can be used with iterables such as lists, dictionaries, etc. This will be covered when we will discuss lists and other iterables.
Question - Print 1 to 100?¶
for i in range(1, 101):
print(i)
Question¶
What will the sequence be generated by the following?
range(5)
Choices
- 1 2 3 4 5
- 0 1 2 3 4 5
- 1 2 3 4
- 0 1 2 3 4
Question¶
What will the sequence be generated by the following?
range(5,15, 2)
- 5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15
- 5,7,9,11,13,15
- 5,7,9,11,13
- 5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14
Question¶
What will the sequence be generated by the following?
range(-5,0,1)
Choices
- -5,-4,-3,-2,-1,0
- Nothing
- 0,-1,-2,-3,-4,-5
- -5,-4,-3,-2,-1
Question¶
What will the sequence be generated by the following?
range(-10,-5,-1)
Choices
- -10,-9,-8,-7,-6,-5
- -10,-9,-8,-7,-6
- Nothing
- -6,-7,-8,-9,-10
Question¶
What is the output of the following?
for i in range(0,1):
print('Hello')
Choices
- Hello
Hello - Hello
- Nothing
- 0
1
How many values will be returned by this:
range(n) -> n
If you want the loop to run n times just say range(n). The loop will run n times but start with zero till n-1 therefore n values.
range(5) -> 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 => 5 values
Break and Continue in For Loop¶
- Break and Continue is same as we saw in while loop.
- If you want to break out of the loop if a certain condition is met then you use break. It will break the entire loop and execute the next statement.
- It skips the inside loop and continues the loop’s execution.
[ASK THE LEARNERS]
is _(underscore) a valid variable name?
- Variable should start with an alphabet or an
_ - can only have underscore, alphabets, and numbers.
- It should not start with a number.
- Many programmers use underscore when they don't need a name for a variable in the for loop.
for _ in range(10):
print("hello")
- If we use
_it won't give a warning in case we are not using it. With any other variable name, it will give a warning in Python. - What will be the output of the following:
for i in range(10):
if(i == 4):
break
print(i)
Output:
0
1
2
3
- What will be the output of the following:
for i in range(6):
if(i % 2 == 0):
continue
print(i)
Output:
1
3
5
Pass Statement¶
- It is not to be used in competitive programming or interviews. It is usually used in testing.
- The
passdoes nothing. It signifies that the programmer will later add some code to it. Right now ignore this block.
for i in range(6):
if(i % 2 == 0):
pass
print(i)
- Pass will still print the
i. In case of continuing it will directly begin with a new iteration.
For Else Loop¶
- Else statement will execute if the loop terminates successfully i.e. without a break
- Write a code for the prime number in the for loop.
n = int(input())
for i in range(2,n):
if(n % i == 0):
print("Not Prime")
break
else:
print("Prime")
Question¶
What is the output of the following?
for i in range(0,10):
if(i % 3 == 0):
continue
print(i, end = ' ')
Choices
- 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
- 0 1 2
- 0 1 2 4 5 7 8 9
- 0 1 2 4 5 7 8
Question¶
What is the output of the following?
for i in range(1,10):
if(i % 3 == 0):
break
print(i, end = ' ')
Choices
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
- 1 2
- 1 2 4 5 7 8 9
- 1 2 4 5 6 7 8
Nested Loops¶
- If we write a loop inside a loop it is a nested loop.
- Look at the pattern below and write a code to generate this pattern.
1 2 3 4 5
1 2 3 4 5
1 2 3 4 5
1 2 3 4 5
If I want to print 1 to 5, how will I write the code?
for i in range(1,6):
print(1, end = " ")
Now if I want to do this 5 times will I do this?
for i in range(1,6):
print(1, end = " ")
print()
for i in range(1,6):
print(1, end = " ")
print()
for i in range(1,6):
print(1, end = " ")
print()
for i in range(1,6):
print(1, end = " ")
print()
for i in range(1,6):
print(1, end = " ")
print()
- No right? What principle it is not following?
- DRY (Do not repeat yourself).
- I will use a nested loop.
for _ in range(5):
for i in range(1,6):
print(1, end = " ")
print()
- Single for loop gives 1D data, 2 loops nested will give 2D, and so on.
- Similarly we can write nested while loop
Difference b/w For and While Loop¶
| For | While |
|---|---|
| It is simple to use. Initialization, condition, and updation in a single line. | Complex to use |
| Only for simple iteration | Complex tasks such as scrapper and Scissors can be performed |
Note: Never update the iteration variable in the for loop.
Pattern Printing Problems¶
* * * * *
* * * * *
* * * * *
* * * * *
* * * * *
Warning
Please take some time to think about the solution on your own before reading further.....
Solution 1
for i in range(5):
for j in range(5):
print("*", end = " ")
print()
We are using string to integer multiplication. The statement print("* "*5) will generate a line with 5 stars and a space in between.
for _ in range(5):
print("* " * 5)
Staircase Binding¶
*
* *
* * *
* * * *
* * * * *
Warning
Please take some time to think about the solution on your own before reading further.....
Solution 1
When i is 1 we print 1 star, when i is 2 we print 2 star, and so on.
n = int(input())
for i in range(1, n + 1):
print("* " * i)
Solution 2
We can do it with the nested loop as well
for i in range(1, n + 1):
for j in range(i):
print("*", end = " ")
print()
Reverse Staircase¶
*
* *
* * *
* * * *
* * * * *
- Can you guys do it or should I give you a hint?
No spaces between stars
- Assuming that there is no space between starts. What we are doing is
4 spaces 1 star,3 spaces 2 stars,2 spaces 3 starsand so on.
for i in range(1,6):
spaces = " " * (n - i)
stars = "*" * (i)
print(spaces + stars)
Homework Problem¶